Summary
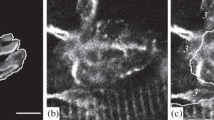
Voltage-dependent sodium channels (Na+ channels) were localized by autoradiography on mouse skeletal muscle using both light and electron microscopy.125I-scorpion toxins (ScTx) of both the a and β type were used as probes. The specificity of labelling was verified by competitive inhibition with unlabelled toxin and by inhibition of αScTx labelling in depolarizing conditions. Under light microscopy, the labelling of the myocyte surface appeared randomly distributed with both the a and β toxins. No difference in the labelling density obtained with βScTx was observed between a 2 mm central segment of the fibre containing the endplate and an adjacent segment not containing the endplate. At the endplate, however, the βScTx binding site density was about seven fold higher at the edge of the synaptic primary clefts. This density decreased with distance from the synaptic cleft reaching the extrasynaptic value at 30–40 μm. An analysis of myocyte labelling using electron microscopy provided evidence for a specific, but very low labelling of the myocyte interior which can be attributed to the T-tubules. These results confirm a relatively high density of Na+ channels in a perijunctional zone about 50 μm in width, which could ensure the initial spread of the surface depolarization with a high safety factor, and a homogeneous distribution over the remaining surface with a low density evaluated at 5–10 per μm2. However, the very low labelling of T-tubules could be attributed mainly to a low density of tubular Na+ channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R. H. &Peachey, L. D. (1973) Reconstruction of the action potential of frog sartorius muscle.Journal of Physiology 235, 103–31.
Almers, W., Stanfield, P. R. &Stuhmer, W. (1983) Lateral distribution of sodium and potassium channels in frog skeletal muscle: Measurements with a patch-clamp technique.Journal of Physiology 336, 261–84.
Angelides, K. J. (1986) Fluorescently-labelled Na+ channels are localized and immobilized to synapses of innervated muscle fibres.Nature 321, 63–6.
Ariyasu, R. G., Deerinck, T. J., Levinson, S. R. &Ellisman, M. H. (1987) Distribution of (Na++K+)ATPase and sodium channels in skeletal muscle and electroplax.Journal of Neurocytology 16, 511–22.
Barhanin, J., Giglio, J. R., Leopold, P., Schmid, A., Sampaio, S. V. &Lazdunski, M. (1982)Tityus serrulatus venum contains two classes of toxins:Tityus γ toxin is a new tool with a very high affinity for studying the Na+ channel.Journal of Biological Chemistry 257, 12553–8.
Barhanin, J., Ildefonse, M., Rougier, O., Sampaio, S. V., Giglio, J. R. &Lazdunski, M. (1984)Tityus gamma toxin, a high affinity effector of the Na+ channel in muscle, with a selectivity for channels in the surface membrane.Pflügers Archiv 400, 22–7.
Beam, K. G., Caldwell, J. H. &Campbell, D. T. (1985) Na channels in skeletal muscle concentrated near the neuromuscular junction.Nature 313, 588–90.
Betz, W. J., Caldwell, J. H. &Kinnamon, S. C. (1984) Increased sodium conductance in the synaptic region of rat skeletal muscle fibres.Journal of Physiology 352, 189–202.
Boudier, J. A., Berwald-Netter, Y., Dellmann, H. D., Boudier, J. L., Couraud, F., Koulakoff, A. &Cau, P. (1985) Ultrastructural visualization of Na+-channel associated (125I) alpha-Scorpion toxin binding sites on fetal mouse nerve cells in culture.Developmental Brain Research 20, 137–42.
Boudier, J. L., Jover, E. &Cau, P. (1988) Autoradiographic localization of voltage-dependent sodium channels on the mouse neuromuscular junction using125I-alpha Scorpion toxin: Preferential labelling of glial cells.Journal of Neurostience 8, 1469–78.
Caille, J., Ildefonse, M. &Rougier, O. (1975) Relations between membrane potential sodium currents and contraction in frog twitch muscle fibres.Journal of Physiology 249, 26–8.
Caille, J., Ildefonse, M. &Rougier, O. (1978) Existence of a sodium current in the tubular membrane of frog twitch muscle fibre; its possible role in the activation of contraction.Pfügers Archiv 374, 167–77.
Caldwell, J. H., Campbell, D. T. &Beam, K. G. (1986) Na channel distribution in vertebrate skeletal muscle.Journal of General Physiology 87, 907–32.
Caldwell, J. H. &Milton, R. L. (1988) Sodium channel distribution in normal and denervated rodent and snake skeletal muscle.Journal of Physiology 401, 145–61.
Campbell, D. T. &Rille, B. (1976) Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle.Journal of General Physiology 67, 309–23.
Catterall, W. A. (1984) The molecular basis of neuronal exitability.Science 223, 653–61.
Cau, P., Massacrier, A., Boudier, J. L. &Couraud, F. (1985) Ultrastructural localization of voltage-sensitive sodium channels using [125I]alpha Scorpion toxin.Brain Research 334, 9–17.
Chiu, S. Y., Schrager, P. &Ritchie, J. M. (1984) Neuronaltype Na+ and K+ channels in rabbit cultured Schwann cells.Nature 311, 156–7.
Costantin, L. L. (1970) The role of sodium current in the radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres.Journal of General Physiology 55, 703–15.
Couraud, F., Jover, E., Dubois, J. M. &Rochat, H. (1982) Two types of Scorpion toxin receptor sites, one related to the activation, the other to the inactivation of the action potential channel.Toxicon 20, 9–16.
Dreyfus, P. Rieger, F., Murawsky, M., Garcia, L., Lombet, A., Fosset, M., Pauron, D., Barhanin, J. &Lazdunski, M. (1986) The voltage-dependent sodium channel is co-localized with the acetylcholine receptor at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction.Biochemical Biophysical Research Communication 139, 196–201.
Eisenberg, B. R. &Kuda, A. M. (1976) Discrimination between fibre populations in mammalian skeletal muscle by using ultrastructural parameters.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 54, 76–88.
Eisenberg, B. R., Kuda, A. M. &Peter, J. B. (1974) Stereological analysis of mammalian skeletal muscle. I. Soleus muscle of the adult guinea pig.Journal of Cell Biology 60, 732–54.
Fertuck, H. C. &Salpeter, M. M. (1974) Sensitivity in electron microscope autoradiography for125I.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 22, 80–7.
Fertuck, H. C. &Salpeter, M. M. (1976) Quantitaton of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after125I-alpha bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junction.Journal of Cell Biology 69, 144–58.
Flucher, B. E. &Daniels, M. P. (1989) Distribution of Na+ channels and ankyrin in neuromuscular junctions is complementary to that of acetylcholine receptors and the 43 KD protein.Neuron 3, 163–75.
Haimovich, B., Bonilla, E., Casadei, J. &Barchi, R. (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of the mammalian voltage-dependent sodium channel using polyclonal antibodies against the purified protein.Journal of Neuroscience 4, 2259–68.
Haimovich, B., Scotland, D. L., Fieles, W. E. &Barchi, R. L. (1987) Localization of sodium channel subtypes in adult rat skeletal muscle using channel-specific monoclonal antibodies.Journal of Neurostience 7, 2957–66.
Hansen Bay, C. M. &Strichartz, G. R. (1980) Saxitoxin binding to sodium channels of rat skeletal muscles.Journal of Physiology 300, 89–103.
Hille, B. (1984)Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Association.
Jaimovich, E., Ildefonse, M., Barhanin, J., Rougier, O. &Lazdunski, M. (1982) Centruroides toxin, a selective blocker of surface Na+ channels in skeletal muscle: Voltage-clamp analysis and biochemical characterization of the receptor.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 79, 3896–900.
Jaimovich, E., Venosa, R. A., Shrager, P. &Horowicz, P., (1976) Density and distribution of tetrodoxin receptors in normal and detubulated frog sartorius muscle.Journal of General Physiology 67, 399–416.
Karnovsky, M. J. &Rice, D. F. (1969) Exogenous cytochrome C as an ultrastructural tracer.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 17, 751–3.
Kehle, T. &Herzog, V. (1989) A colloidal gold labelling technique for the direct determination of the surface area of eukaryotic cells.European Journal of Cell Biology 48, 19–26.
Land, B. R., Podleski, T. R., Salpeter, E. E. &Salpeter, M. M. (1977) Acetylcholine receptor distribution on myotubes in culture correlated to acetycholine sensitivity.Journal of Physiology 269, 155–76.
Larra, F. &Droz, B. (1970) Techniques radioautographiques et leur application a l'étude du renouvellement des constituants cellulaires.Journal de Microscopic 9, 845–80.
Martin, M. F., Ferez, L. G., El Ayeb, M., Kopeyan, C., Bechis, G., Jover, E. &Rochat, H. (1987) Purification and chemical and biological characterizations of seven toxins from the mexican scorpion,Centruroides suffusus suffusus.Journal of Biological Chemistry 262, 4452–9.
McArdle, J. J., Angaut-Petit, D., Mallart, A., Bournaud, R., Faille, L. &Brigant, J. L. (1981) Advantages of the Triangularis sterni muscle of the mouse for investigations of synaptic phenomena.Journal of Neurostience Methods 4, 109–15.
McDermott, A. B. &Westbrook, G. L. (1986) Early development of voltage-dependent sodium currents in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons.Developmental Biology 113, 317–26.
Pfeiffer, J. R., Oliver, J. M. &Berlin, R. D. (1980) Topographical distribution of coated pits.Nature 286, 727–9.
Ritchie, J. M. &Rogart, R. B. (1977) The binding of a labelled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in normal and denervated mammalian muscle, and in amphibian muscle.Journal of Physiology 269, 341–54.
Roberts, W. M. (1987) Sodium channels near end-plates and nuclei of snake skeletal muscle.Journal of Physiology 388, 213–32.
Rogers, A. W. (1979)Techniques of Autoradiography. Amsterdam: Elsevier, North Holland.
Salpeter, M. M., Bachmann, L. &Salpeter, E. E. (1969) Resolution in electron microscope radioautography.Journal of Cell Biology 41, 1–20.
Salpeter, M. M., Budd, G. C. &Mattimoe, S. (1974) Resolution in autoradiography using semi-thin sections.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 22, 217–22.
Salpeter, M. M., Fertuck, H. C. &Salpeter, E. E. (1977) Resolution in electron microscope autoradiography. III Iodine-125. The effect of heavy metal staining, and a reassessment of critical parameters.Journal of Cell Biology 72, 161–73.
Salpeter, M. M., Marchaterre, M. &Harris, R. (1988) Distribution of extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors on a vertebrate muscle: Evaluated by using a scanning electron microscope procedure.Journal of Cell Biology 106, 2087–93.
Schrager, P., Chiu, S. Y. &Ritchie, J. M. (1985) Voltage dependant sodium and potassium channels in mammalian cultured Schwann cells.Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 82, 948–52.
Sherman, S. J., Lawrence, J. C., Messner, D. J., Jacoby, K. &Catterall, W. A. (1983) Tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in rat muscle cells developingin vitro.Journal of Biological Chemistry 258, 2488–95.
Waxman, S. G., Black, J. A., Kocsis, J. D. &Ritchie, J. M. (1989) Low density of sodium channels supports action potential conduction in axons of neonatal rat optic nerve.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 86, 1406–10.
Weibel, E. R. (1979)Stereological Methods. Vol.1. Practical Methods for Biological Morphometry. London: Academic Press.
Williams, M. A. (1977) The analysis of electron microscope autoradiographs. InPractical methods in electron microscopy. Vol. 6. Quantitative methods in biology (edited byGlauert, A. M.), pp. 85–169. Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Treut, T., Boudier, J.L., Jover, E. et al. Localization of voltage-sensitive sodium channels on the extrasynaptic membrane surface of mouse skeletal muscle by autoradiography of scorpion toxin binding sites. J Neurocytol 19, 408–420 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01188407
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01188407