Abstract
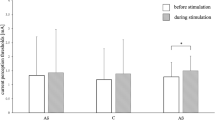
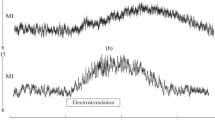
Quantitative characteristics of afferent flows coding information from a number of receptors were obtained by the gliding impulses method. The frequency spectrum of activity in a cutaneous nerve, the relative numbers of active Aβ, AΔ, and C fibers and their distribution by impulse transition frequency during stimulation of the cat's skin with pins and needles were determined. The afferent flow recorded in the nerve during pricking of the skin is characterized by high density, due to the number of excited fibers and the frequency of activity in them. The higher density of the afferent flow during the application of a painful than of a painless stimulus is mainly due to activity in C fibers. Unmyelinated fibers subjected to the action of the same stimulus and of chemically active substances liberated from the cells during tissue injury are excited directly and generate high-frequency spikes which increase the flow density in the nerve. The number of active myelinated fibers and the spike frequency during the action of a painful stimulus are only a little greater than the corresponding characteristics of the afferent discharge during painless stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
B. I. Balanter, A. V. Zeveke, and V. M. Khayutin, “Determination of the frequency spectrum of afferent impulses and the law of distribution of receptors by impulse frequency during recording of potentials from a whole nerve,” in: Current Problems in the Physiology and Pathology of the Nervous System [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1965), pp. 199–210.
L. A. Baraz and V. M. Khayutin, “Differentiation of the action of chemical stimuli on receptors and sensory fibers of the small intestine,” Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,47, 1289 (1961).
A. A. Velumyan, I. M. Rodionov, and L. I. Chudakov, “Investigation of the frequency distribution of natura activity in a mixed nerve trunk by the colliding impulse method,” Neirofiziologiya,6, 318 (1974).
A. V. Zeveke and O. S. Gladysheva, “Changes in the frequency spectrum in myelinated AΔ afferent fibers during stimulation of skin mechanoreceptors,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,189, 1150 (1969).
A. V. Zeveke, E. D. Efes, G. I. Malysheva, and V. L. Shaposhnikov, “Analysis of Activity in A and C fibers during mechanical and temperature stimulation of a receptive field of the skin,” Abstracts of Proceedings of a Symposium on Tissue Reception [in Russian], Leningrad (1974), pp. 62–72.
A. V. Zeveke and G. I. Malysheva, “Types of fibers conducting impulses during nociceptive stimulation of the skin,” Byull. Éksp. Biol. Med.,72, No. 9, 3 (1971).
A. V. Zeveke and V. M. Khayutin, “Changes in the frequency spectrum of afferent impulses in the whole nerve trunk,” Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,52, 258 (1966).
G. I. Malysheva, A. V. Zeveke, V. L. Shaposhnikov, and V. K. Chigin, “Nociceptive pressor reflexes and impulsation in a nerve following injection of potassium chloride into the cat's skin,” Byull. Éksp. Biol. Med.,72, No. 8, 6 (1971).
G. I. Malysheva and A. V. Zeveke, “Nociceptive responses to mechanical stimuli,” Byull. Éksp. Biol, Med.,77, No. 1, 11 (1974).
G. I. Malysheva and A. V. Zeveke, “Some characteristics of the afferent flow during noxious stimulation of the skin,” Neirofiziologiya,8, 168 (1976).
V. M. Khayutin, Vasomotor Reflexes [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1964), p. 376.
V. M. Khayutin et al., “Construction of a theory of pain: the afferent code and operations of neuronal systems responsible for nociceptive responses,” in: Neuronal Mechanisms of Pain. Proceedings of an All-Union Symposium [in Russian], Leningrad (1973), pp. 26–29.
E. D. Adrian, Basis of Sensation. The Action of Sense Organs, London (1928), p. 122.
P. Bessou and E. R. Perl, “Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibers to noxious stimuli,” J. Neurophysiol.,32, 1025 (1969).
M. B. Bromberg and D. Whitehorn, “Myelinated fiber types in the superficial radial nerve s of the cat and their central projections,” Brain Res.,78, 157 (1974).
A. G. Brown and A. Iggo, “A quantitative study of cutaneous receptors and afferent fibres in the cat and rabbit,” J. Physiol. (London),193, 707 (1967).
P. R. Burgess, “Pattern of discharge evoked in cutaneous nerves and their significance for sensation,” Adv. Neurol.,4, 11 (1974).
P. R. Burgess and E. R. Perl. “Myelinated afferent fibres responding specifically to noxious stimulation of the skin,” J. Physiol. (London),190, 541 (1967).
P. R. Burgess, E. Petit, and R. M. Warren, “Receptor types in cat hairy skin supplied by myelinated fibers,” J. Neurophysiol.,31, 833 (1968).
W. W. Douglas and J. M. Ritchie, “Technique for recording functional activity in specific groups of medullated and nonmedullated fibres in whole nerve trunks,” J. Physiol. (London),138, 19 (1957).
W. W. Douglas and J. M. Ritohie, “Nonmedullated fibres in the saphenous nerve which signal touch,” J. Physiol. (London),139, 385 (1957).
W. W. Douglas and J. M. Ritchie, “On the frequency of firing of mammalian nonmedullated nerve fibres,” J. Physiol. (London),139, 400 (1957).
W. W. Douglas and J. M. Ritchie, “The sensory functions of the nonmyelinated afferent nerve fibres from the skin,” in: Pain and Itch, London (1959), pp. 26–40.
D. N. Franz and A. Iggo, “Conduction failure in myelinated and nonmyelinated axons at low temperature,” J. Physiol. (London),119, 319 (1968).
A. Goldscheider, “Uber den Schmerz in physiologischer und Klinischer Hinsicht,” Hirschwald, Berlin (1894), p. 42.
R. G. Hallin and H. E. Torebjork, “Afferent and efferent C units recorded from human skin nerves in situ, ”Acta Soc. Med. Upsal.,75, 277 (1970).
C. C. Hunt, “Relation of function to diameter in afferent fibres of muscle nerves,” J. Gen. Physiol.,38, 117 (1954).
A. Iggo, “Cutaneous heat and cold receptors with slowly conducting afferent fibres,” Quart. J. Exp. Physiol.,44, 362 (1959).
A. Iggo, “Cutaneous mechanoreceptors with afferent C fibres,” J. Physiol. (London),152, 337 (1960).
A. Iggo, “Cutaneous receptors with a high sensitivity to mechanical displacement,” in: Touch, Heat and Pain, Longman, New York (1966), pp. 237–260.
C. A. Keele and D. Armstrong, “Substances producing pain and itch,” Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore (1964), p. 399.
R. K. S. Lim, “Pain,” Ann. Rev. Physiol.,32, 269 (1970).
E. R. Perl, “Myelinated afferent fibres innervating the primate skin and their response to noxious stimuli,” J. Physiol. (London),197, 593 (1969).
G. Weddell, “The pattern of cutaneous innervation in relation to cutaneous sensibility,” J. Anat.,75, 346 (1941).
G. Weddell and S. Miller, “Cutaneous sensibility,” Ann. Rev. Physiol.,24, 199 (1962).
Y. Zotterman, “Touch, pain, and tickling: an electrophysiological investigation on cutaneous sensory nerves,” J. Physiol. (London),95, 1 (1939).
Y. Zotterman, “The peripheral nervous mechanism of pain: a brief review,” in: Pain and Itch, London (1959), pp. 13–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 8, No. 4, pp. 391–399, July–August, 1976.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malysheva, G.I., Zeveke, A.V. Afferent flow patterns in a cat cutaneous nerve during painful and painless mechanical stimulation of the skin. Neurosci Behav Physiol 8, 144–151 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186945
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186945