Abstract
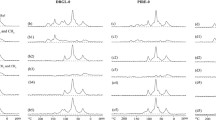
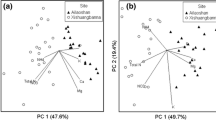
Decomposition is influenced by a wide array of factors including macroclimate, microclimate, soil biota, soil nutrients, substrate piece size and substrate quality. To separate the influence of some of these factors a 10-year study, the Canadian Intersite Decomposition Experiment, was established in 1992 to measure the decay of 11 standard litter types on a range of forest types at 21 sites across Canada. As part of the study we analysed the initial elemental contents (N, P, S, K, Ca, Mg) and carbon (C) fractions (extractables, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin) by13C NMR and wet chemical proximate analysis in a total of 37 primarily foliar litter types representative of the range of species found at the different CIDET sites. Litter types especially non-conifer species varied greatly in their qualities. Principal component analyses showed that the litter types could be distinguished by the elemental macronutrient contents through the ratio of N+P+K:S, by proximate chemical analyses through the ratio of water soluble:acid fractions, and by NMR through the ratio of O-alkyl:alkyl C. Litter quality data was used in three simple models of litter decay to predict how the mass loss of the different litter types could vary. Two models using a linear or single exponential decay equation and litter lignin and N content predicted a 2–5 fold difference in total mass loss for the different litter types. A third model using a summed exponential decay equation for three chemical fractions and a ligno-cellulose index predicted that for all but one litter type, variation in mass loss between types would be less than a 20%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber, J. D., Melillo, J. M. and McClaugherty, C. A.: 1990,Can. J. Bot. 68, 2201–2208.
Albano, C. and Norden, B.: 1988,Fuel 68, 771–775.
Axelson, D. E., Dinel, H., Dudley, R. L., Levesque, M., Mathur, S. P. and Preston, C. M.: 1989,Org. Geochem. 14, 393–403.
Baldock, J. A. and Preston, C. M.:In: Proceedings of 8th N. American Forest Soils Conference. August, 1993. Gainesville, USA, (In press).
Berg, B.: 1984,Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 609–617.
Berg, B. and Staaf, H.: 1980,Structure and Function of Northern Coniferous Forests-An Ecosystem Study 32, 373–390.
Berg, B., Berg, M. P., Bottner, P., Box, E., Breymeyer, A., Calvan De Anta, R., Couteaux, M., Esudero, A., Gallardo, A., Kratz, W., Madeira, M., Malkonen, E., McClaugherty, C., Meentemeyer, V., Munoz, F., Piussi, P., Remacle, J. and Virzo De Santo, A.: 1993,Biogeochemistry 20, 127–159.
Bohlin, E., Hamalainen, M. and Suden, T.: 1989,Soil Sci. 147, 252–263.
Bunnell, F. L., Flanagan, P. W. and Tait, D. E. N.: 1977a,Soil Biol Biochem. 9, 41–47.
Bunnell, F. L., Tait, D. E., Flanagan, P. W. and Van Cleve, K.: 1977b,Soil Biol. Biochem. 9, 33–40.
Bryant, J. P., Clausen, T. P., Reichardt, P. B., McCarthy, M. C. and Werner, R. A.: 1987,Oecologia 73, 513–517.
Ecoregions Working Group: 1989,Ecol. Land Classif. Ser. No. 23, Sustainable Development Branch, Canadian Wildlife Service, Conservation and Protection, Environment Canada, Ottawa, Canada, 119 pp.
Fyles, J. W. and McGill, W. B.: 1987,Can. J. For. Res. 17, 109–114.
Harmon, M. E., Baker, G. A., Greene, S. and Spycher, G.: 1990,For. Ecol. Man. 31, 55–66.
Harmon, M. E. and Melillo, J. M.: 1990,Protocol for Intersite Decomposition Experiments: I. Fine Root, Leaf Litter and Wooden Dowels. Oregon State University. Unpublished Report.
Heal, O. W. and French, D. D.: 1974,In: Holding, A. J., Heal, O. W., MacLean, S. F. Jr. and Flanagan, P. W. (eds.)Soil Organisms and Decomposition in Tundra. IBP Tundra Biome Steering Committee, Stockholm, Sweden, pp. 227–248.
Hunt, H. W., Ingham, E. R., Coleman, D. C., Elliott, E. T. and Reid, C. P. P.: 1988,Ecology 69, 1009–1016.
Lason, G. R. and Hester, A. J.: 1993,J. Ecol. 81, 75–80.
Kiilsgaard, C. W., Greene, S. E. and Stafford, S. G.: 1987,Plant and Soil 102, 223–227.
Kurz, W. A., Apps, M. J., Webb, T. M. and McNamee, P. J.: 1992,The Carbon Budget of the Canadian Forest Sector: Phase I. For Can. Inf. Rep. NOR-X-326, Forestry Canada, Northwest Region, Edmonton, Canada, 93pp.
Long-Term Intersite Decomposition Experiment Team (LIDET):Bioscience (In press)
Lousier, J. D. and Parkinson, D.: 1976,Can. J. Bot. 54, 419–436.
MacLean, D. A. and Wein R. W.: 1978,Can. J. Bot. 56, 2730–2749.
McClaugherty, C. A., Pastor, J., Aber, J. D. and Melillo, J. M.: 1985,Ecology 66, 266–275.
Meentemeyer, V.: 1978,Ecology 59, 465–472.
Melin, E.: 1930,Ecology 11, 72–101.
Melillo, J. M., Aber, J. D. and Muratore, J. F.: 1982,Ecology 63, 621–626.
Minderman, G.: 1968,Ecology 56, 355–362.
Moore, T. R.: 1984,Ecology 65, 299–308.
Norden, B. and Berg, B.: 1990,Soil Biol. Biochem. 22, 271–275.
Parkinson, J. A. and Allen, S. E.: 1975,Comm. in Soil Sci. Plant Analysis 6 (1), 1–11.
Parton, W. J., Schimel, D. S., Cole, C. V. and Ojima, D. S.: 1987,Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51, 1173–1179.
Paul, E. A. and Voroney, P.: 1980. In: Ellwood, D. C., Hedges, J. N., Latham, M. H. and Slater, J. H. (eds.)Contemporary microbial Ecology. Academic Press, London, UK, pp. 215–237.
Preston, C. M., Hempfling, R., Schulten, H. R., Schnitzer, M., Trofymow, J. A. and Axelson, D. E.: 1994,Plant and Soil 158, 69–82.
Ryan, M. G., Melillo, J. M. and Ricca, A.: 1990,Can. J. For. Res. 20, 166–171.
SAS Institute Inc.: 1985,SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5 Edition. SAS Institute Inc. Cary, USA 956 pp.
Stump, L. M. and Binkley, D.: 1993,Can. J. For. Res. 23, 492–502.
Swift, M. J., Heal, O. W. and Anderson, J. M.: 1979,Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems. University of California Press, Berkley, USA, 362 p.
Taylor, B. R., Prescott, C. E., Parsons, W. F. J. and Parkinson, D.: 1991,Can. J. Bot. 69, 2242–2250.
Trofymow, J. A., Barclay, H. J. and McCullough, K.: 1991,Can. J. For. Res. 21, 1601–1615.
Waring, R. H., McDonald, A. J. S., Larsson, S., Ericsson, T., Wiren, A., Arwidsson, E., Ericsson, A. and Lohammar, T.: 1985,Oecologia 66, 157–160.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trofymow, J.A., Preston, C.M. & Prescott, C.E. Litter quality and its potential effect on decay rates of materials from Canadian forests. Water Air Soil Pollut 82, 215–226 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01182835
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01182835