Conclusions
-
1.
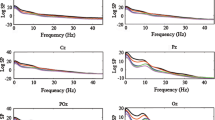
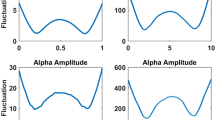
Power spectra of the occipital, parietal, central, and frontal regions of the right and left hemispheres of the healthy human brain are characterized by a high degree of symmetry and stability over a wide range of frequencies and also in the alpha and delta bands separately.
-
2.
The mean levels of coherence of the EEG at symmetrical points of the hemispheres are virtually identical in all subjects studied and exhibit a high degree of stability.
-
3.
The pattern of the coherence spectrum, unlike the mean level of coherence, is characterized by great variability and instability.
-
4.
The degree of symmetry and stability of the individual frequency bands of the EEG of posterior and anterior regions of the hemispheres is determined by the character of the EEG and, in particular, by the special features of the alpha rhythm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
G. V. Vasil'ev and Z. A. Malina, Trudy Akust. Inst. (Moscow), No. 4, 158 (1968).
S. G. Gershman, O. M. Grindel', E. M. Vakar, Z. A. Malina, and T. P. Shol'ts, in: Problems in Ship Building, Acoustics Series [in Russian], No. 2 (1974), p. 57.
O. M. Grindel', Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat.,16, No. 3, 445 (1966).
O. M. Grindel', S. G. Gershman, G. N. Boldyreva, E. M. Vakar, Z. A. Malina, I. S. Dobronravova, and N. S. Galkina, Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat.,23, No. 4, 771 (1973).
O. M. Grindel', N. N. Bragina, I. S. Dobronravova, and V. I. Salalykin, Vorp. Neirokhir., No. 4, 9 (1975).
G. Jenkins and D. Watts, Spectral Analysis and Its Applications [Russian translation], Vols. 1 and 2, Mir, Moscow (1972).
J. de Lange, W. Storm van Leeuwen, and P. Werre, in: Electroencephalographic Investigations of Higher Nervous Activity [Russian translation], Izd. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow (1962), p. 339.
M. N. Livanov, Spatial Organization of Brain Processes [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1972).
V. D. Nebylitsyn, in: Typological Features of Human Higher Nervous Activity [in Russian], Izd. Akad. Pedagog. Nauk SSSR, Moscow (1963), p. 47.
V. D. Nebylitsyn, Basic Properties of the Human Nervous System [in Russian], Prosveshchenie, Moscow (1966).
V. S. Rusinov, The Dominant Focus, New York (1973).
V. S. Rusinov, O. M. Grindel', and G. N. Boldyreva, Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat.,20, No. 2, 280 (1970).
V. S. Rusinov and O. M. Grindel', Vorp. Neirokhir., No. 4, 3 (1973).
V. S. Rusinov and O. M. Grindel', Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat.,25, No. 3, 552 (1975).
W. Grey Walter, in: Reflexes of the Brain [Russian translation], Nauka, Moscow (1965), p. 365.
E. Berger and R. Bockford, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,36, No. 2, 209 (1974).
G. Boldyreva and N. Bragina, Electroenceph. Clin, Neurophysiol.,34, No. 7, 764 (1973).
M. Brazier, J. Finesinger, and S. Cobb, Am. J. Psychiat.,101, 443 (1945).
H. Corbin and G. Bickford, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,7, No. 1, 9 (1955).
C. Darrow, R. Vieth, J. Mailer, and J. Wilson, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,12, No. 1, 238 (1960).
Z. Drohocki, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,24, No. 5, 488 (1968).
G. Frank, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,19, No. 4, 516 (1965).
D. Giannitrapani, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,34, No. 7, 733 (1973).
D. Giannitrapani, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,38, No. 1, 102 (1975).
A. Glass and S. Butler, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,34, No. 7, 729 (1973).
L. Goldstein, A. Sugerman, H. Stolberg, H. Murphree, and C. Pfeiffer, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,19, No. 4, 350 (1965).
G. Guttmann, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,24, No. 4, 390 (1968).
L. Johson and E. Ulett, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,11, No. 2, 233 (1959).
A. Lubin, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,34, No. 7, 689 (1973).
A. Mundy-Castle, in: Conditionnement et Réactivité en Electroencéphalographie, Paris (1957), p. 221.
H. Scheich, Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,26, No. 4, 442 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel'nosti, Vol. 26, No. 3, pp. 576–587, May–June, 1976.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rusinov, V.S., Grindel', O.M., Boldyreva, G.N. et al. Symmetry and stability of EEG spectra in healthy subjects. Neurosci Behav Physiol 7, 348–357 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181845
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181845