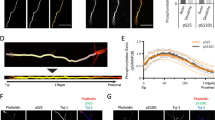
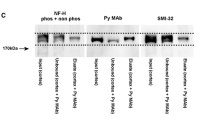
Summary
The distribution and expression of developmentally regulated phosphorylation epitopes on the microtubule-associated protein 1B and on neurofilament proteins recognized by monoclonal antibody (mAb) 150 and mAb SMI-31 was investigated in the developing rat spinal cord. In the embryonic day 11 spinal cord, mAb 150 stained the first axons to appear, whereas mAb SMI-31 staining did not appear until embryonic day 12. At the start of axonogenesis, mAb 150 stained neuronal cell bodies and axons whereas at later times only the distal axon was stained, this is the first demonstrationin vivo of a mAb 150 axonal gradient similar to that seen previouslyin vitro (Mansfield et al., 1991). During the postnatal period, axonal staining by mAb 150 dramatically declined so that by the third postnatal week, only the corticospinal tract, which contains axons that are still growing, was labelled. There was no evidence of dendritic staining except of adult primary motoneurons. In contrast, mAb SMI-31 staining of axons was not present as a gradient. Instead, mAb SMI-31 staining increased progressively throughout this period, persisted into adulthood and was shown by immunoblotting to be related to the increased phosphorylation of the medium and heavy neurofilament proteins. Axonal staining by mAb 150 re-appears in a sub-population of the SMI-31-labelled myelinated axons in the adult spinal cord and PNS and in the perikarya and dendrites of primary motoneurons, where it probably recognizes a phosphorylation epitope on heavy neurofilament proteins. This late appearing epitope has some similarities to that recognized by mAb SMI-31 on neurofilaments, but it is not identical. These cross-reactivities of mAbs that recognize phosphorylation epitopes on otherwise unrelated proteins dictate caution in interpreting immunohistochemical data. It may now be necessary in some cases to re-appraise published studies using these two antibodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aletta, J. M., Lewis, S. A., Cowan, N. J. &Greene, L. A. (1988) Nerve growth factor regulates both the phosphorylation and steady-state levels of microtubule associated protein 1.2 (MAP 1.2).Journal of Cell Biology 106, 1573–81.
Altman, J. &Bayer, S. A. (1984) The development of the rat spinal cord.Advances in Anatomy and Cell Biology 85, 1–166.
Asai, D. J., Thompson, W. C., Wilson, L., Dresden, C. P., Schulman, H. &Purich, D. L. (1985) Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs): a monoclonal antibody to MAP 1 decorates microtubulesin vitro but stains stress fibers and not microtubulesin vivo.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 82, 1434–8.
Hamburg, J. R., Bray, D. &Chapman, K. (1986) Assembly of microtubules at the tip of growing axons.Nature 321, 788–90.
Bastiani, M. J. &Goodman, C. S. (1984) Neuronal growth cones: specific interactions mediated by filopodial insertion and induction of coated vesicles.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 81, 1849–53.
Bershadsky, A. D. &Vasiliev, J. M. (1988)Cytoskeleton. New York: Plenum Press.
Black, M. M., Slaughter, T. &Fischer, I. (1994) Microtubule-associated protein 1b (MAP 1b) is concentrated in the distal region of growing axons.Journal of Neuroscience 14, 857–70.
Bloom, G. S., Schoenfeld, T. A. &Vallee, R. B. (1984) Widespread distribution of the major polypeptide component of MAP 1 (microtubule-associated protein 1) in the nervous system.Journal of Cell Biology 98, 320–30.
Bloom, G. S., Luca, F. C. &Vallee, R. B. (1985a) Identification of high molecular weight microtubule associated proteins in anterior pituitary tissue and cells using taxol dependent purification combined with microtubule associated protein specific antibodies.Biochemistry 24, 4185–91.
Bloom, G. S., Luca, F. C. &Vallee, R. B. (1985b) Microtubule-associated protein 1B: identification of a major component of the neuronal cytoskeleton.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 82, 5404–8.
Brugg, B. &Matus, A. (1988) PC12 cells express juvenile microtubule-associated proteins during nerve factorinduced neurite outgrowth.Journal of Cell Biology 107, 643–50.
Brugg, B., Reddy, D. &Matus, A. (1993) Attenuation of MAP 1B (MAP5) expression by antisense oligodeoxy-nucleotides inhibits initiation of neurite outgrowth.Neuroscience 52, 489–96.
Calvert, R. &Anderton, B. H. (1985) A microtubule associated protein MAP 1 which is expressed at elevated levels during development of rat cerebellum.EMBO Journal 4, 1171–6.
Carden, M. J., Trojanowski, J. Q., Schlaepfer, W. W. &Lee, V. M.-Y. (1987) Two-stage expression of neurofilament polypeptides during rat neurogenesis with early establishment of adult phosphorylation patterns.Journal of Neuroscience 7, 3489–504.
Curtis, R., Hardy, R., Reynolds, R., Spruce, B. A. &Wilkin, G. P. (1991) Down-regulation of GAP-43 during oligodendrocyte development and lack of expression by astrocytesin vivo: implications for macroglial differentiation.European Journal of Neuroscience 3, 876–86.
Daniels, M. (1972) Colchicine inhibition of nerve fiber formationin vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 53, 164–76.
Dewaegh, S. M., Lee, V. M.-Y. &Brady, S. T. (1992) Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal caliber, and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells.Cell 68, 451–63.
Díaz-Nido, J., Serrano, L., Mendez, E. &Avila, J. (1988) A casein-kinase II-related activity is involved in phosphorylation of microtubule associated protein MAP 1B during neuroblastoma cell differentiation.Journal of Cell Biology 106, 2057–65.
Díaz-Nido, J., Serrano, L., Hernandez, M. A. &Avila, J. (1990) Phosphorylation of microtubule proteins in rat brain at different developmental stages: comparison with that found in neural cultures.Journal of Neurochemistry 54, 211–22.
Díaz-Nido, J., Armas-Portela, R., Martinez, A., Rocha, M. &Avila, J. (1991) Role of microtubules in neurite outgrowth. InThe Nerve Growth Cone (edited byKater, S. B., Letourneau, P. C. &Macagno, E. R.), pp. 65–77. New York: Raven Press.
Drubin, D. G., Feinstein, S., Shooter, E. &Kirschner, M. (1985) Nerve growth factor induced outgrowth in PC12 cells involves the coordinate induction of microtubule assembly and assembly promoting factors.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 1799–807.
Fischer, I. &Romano-Clarke, G. (1990) Changes in microtubule-associated protein MAP 1B phosphorylation during rat brain development.Journal of Neurochemistry 55, 328–33.
Fitzgerald, M., Reynolds, M. L. &Benowitz, L. I. (1991) GAP-43 expression in the developing rat lumbar spinal cord.Neuroscience 41, 187–99.
Gard, D. L. &Kirschner, M. W. (1985) A polymerdependent increase in phosphorylation ofβ-tubulin accompanies differentiation of a neuroblastoma cell line.Journal of Cell Biology 100, 764–74.
Garner, C. C., Matus, A., Anderton, B. &Calvert, R. (1989) Microtubule-associated proteins MAP5 and MAP 1x: closely related components of the neuronal cytoskeleton with different cytoplasmic distribution in the developing brain.Molecular Brain Research 5, 85–92.
Garner, C. C., Garner, A., Huber, G., Kozak, C. &Matus, A. (1990) Molecular cloning of MAP 1 (MAP 1A) and MAP 5 (MAP IB): identification of distinct genes and their differential expression in developing brain.Journal of Neurochemistry 55, 146–54.
Goldstein, M. E., Sternberger, L. A. &Sternberger, N. H. (1983) Microheterogeneity ('neurotypy') of neurofilament proteins.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 80, 3101–5.
Gordon-Weeks, P. R. (1993) Organization of microtubules in neuronal growth cones: role of MAP 1B.Journal of Neurocytology 22, 717–25.
Gordon-Weeks, P. R. &Mansfield, S. G. (1991) The assembly of microtubules in growth cones: the role of microtubule-associated proteins. InThe Nerve Growth Cone (edited byKater, S. B., Letourneau, P. C. &Macagno, E. R. pp. 65–77. New York: Raven Press.
Gordon-Weeks, P. R., Mansfield, S. G., Alberto, C., Johnstone, M. &Moya, F.(1993) Distribution and expression of a phosphorylation epitope on MAP 1B that is transiently expressed in growing axons in the developing rat nervous system.European Journal of Neuroscience 5, 1302–11.
Gorgels, T. G. M. F. (1991) Junctional specializations between growth cones and glia in the developing rat pyramidal tract: synapse-like contacts and invaginations.Journal of Comparative Neurology 306, 117–28.
Greene, L. A., Liem, R. K. H. &Shelanski, M. L. (1983) Regulation of a high molecular weight microtubule associated protein in PC12 cells by nerve growth factor.Journal of Cell Biology 96, 76–83.
Holley, J. A. (1982) Early development of the circumferential axonal pathway in mouse and chick spinal cord.Journal of Comparative Neurology 205, 371–82.
Hoshi, M., Nishida, E., Inagaki, M., Gotoh, Y. &Sakai, H. (1990) Activation of a serine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 1Bin vitro by growth factors and phorbol esters in quiescent rat fibroblastic cells.European Journal of Biochemistry 193, 513–19.
Kirsch, J., Littauer, U. Z., Schmitt, B., Prior, P., Thomas, L. &Betz, H. (1990) Neuraxin corresponds to a C-terminal fragment of microtubule-associated protein 5 (MAP 5).FEBS Letters 262, 259–62.
Kudo, N. &Yamada, T. (1987) Morphological and physiological studies of development of the monosynaptic reflex pathway in the rat lumbar spinal cord.Journal of Physiology 389, 441–59.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature 227, 680–5.
Lee, G. (1993) Non-motor microtubule-associated proteins.Current Opinion in Cell Biology 5, 88–94.
Lee, V. M.-Y., Otvos, L., Garden, M., Hollosi, M., Dietzschold, B. &Lazzarini, R. (1988) Identification of the major multiphosphorylation site in mammalian neurofilaments.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 85, 1998–2002.
Letourneau, P. C. &Ressler, A. H. (1984) Inhibition of neurite initiation and growth by taxol.Journal of Cell Biology 98, 1355–62.
Lichtenberg-Kraag, B., Mandelkow, E.-M., Biernat, J., Steiner, B., Schröter, C., Gustke, N., Meyer, H. E. &Mandelkow, E. (1992) Phosphorylation-dependent epitopes of neurofilament antibodies on tau protein and relationship with Alzheimer tau.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 89, 5384–8.
Lindwall, G. &Cole, R. D. (1984) Phosphorylation affects the ability of tau protein to promote microtubule assembly.Journal of Cell Biological Chemistry 259, 5301–5.
Loeb, D. M., Tsao, H., Cobb, M. H. &Greene, L. A. (1992) NGF and other growth factors induce an association between ERK1 and the NGF receptor, gp 140prototrk Neuron 9, 1053–65.
Luca, F. C., Bloom, G. S. &Vallee, R. B. (1986) A monoclonal antibody that cross-reacts with phosphorylated epitopes on two microtubule-associated proteins and two neurofilament polypeptides.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 83, 1006–10.
Mansfield, S. G. &Gordon-Weeks, P. R. (1991) Dynamic post-translational modification of tubulin in rat cerebral cortical neurons extending neurites in culture: effects of taxol.Journal of Neurocytology 20, 654–66.
Mansfield, S. G., Díaz-Nido, J., Gordon-Weeks, P. R. &Avila, J. (1991) The distribution and phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein MAP 1B in growth cones.Journal of Neurocytology 21, 1007–22.
Matus, A. (1988) Microtubule-associated proteins: their potential role in determining neuronal morphology.Annual Review of Neuroscience 11, 29–44.
Murthy, A. &Flavin, M. (1983) Microtubule assembly using the microtubule-associated protein MAP 2 prepared in defined states of phosphorylation with protein kinase and phosphatase.European Journal of Biochemistry 137, 37–46.
Noble, M., Lewis, S. A. &Cowan, N. J. (1989) The microtubule binding domain of microtubule associated protein MAP 1B contains a repeated sequence motif unrelated to that of MAP 2 and tau.Journal of Cell Biology 109, 3367–76.
Olmsted, J. B. (1986) Microtubule-associated proteins.Annual Review of Neuroscience 11, 29–44.
Price, R. L., Lasek, R. J. &Katz, M. J. (1990) Internal axonal cytoar chitecture is shaped locally by external compressive forces.Brain Research 530, 205–14.
Riederer, B., Cohen, R. &Matus, A. (1986) MAP5: a novel microtubule associated protein under strong developmental regulation.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 763–75.
Riederer, B. M., Guadano-Ferraz, A. &Innocenti, G. M. (1990) Difference in distribution of microtubule-associated proteins 5a and 5b during the development of cerebral cortex and corpus callosum in cats: dependence on phosphorylation.Developmental Brain Research 56, 235–43.
Rienitz, A., Grenningloh, G., Hermans-Borgmeyer, L., Kirsch, J., Littauer, U. Z., Prior, P., Gundelfinger, E. D., Schmitt, B. &Betz, H. (1989) Neuraxin, a novel putative structural protein of the rat central nervous system that is immunologically related to microtubule-associated protein 5.EMBO Journal 8, 2879–88.
Safaei, R. &Fischer, I. (1989) Cloning of a cDNA encoding Map 1B in rat brain: regulation of mRNA levels during development.Journal of Neurochemistry 52, 1871–9.
Sato-Yoshitake, R., Shiomura, Y., Miyasaka, H. &Hirokawa, N. (1989) Microtubule-associated protein 1B: molecular structure, localization and phosphorylationdependent expression in developing neurons.Neuron 3, 229–38.
Schoenfeld, J. A., Mckerracher, L., Obar, R. &Vallee, R. B. (1989) MAP 1A and MAP 1B are structurally related microtubule-associated proteins with distinct developmental patterns in the CNS.Journal of Neurosdence 9, 1712–30.
Scott, C. W., Vulliet, P. R. &Caputo, C. B. (1993) Phosphorylation of tau by proline-directed protein kinase (p34cdc2/p58cyclin A) Decreases tau-induced microtubule assembly and antibody SMI33 reactivity.Brain Research 611, 237–42.
Seeds, N. W., Gilman, A. G., Amano, T. &Nirenberg, M. W. (1970) Regulation of axon formation by clonal lines of a neural tumor.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 66, 160–7.
Sloan, K. E., Stevenson, J. A. &Bigbee, J. W. (1991) Qualitative and quantitative comparison of the distribution of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes within central and peripheral axons of adult hamster (Mesocricetus auratus).Cell and Tissue Research 263, 265–70.
Smith, C. L. (1983) The development and postnatal organization of primary afferent projections to the rat thoracic spinal cord.Journal of Comparative Neurology 220, 29–43.
Sternberger, L. A. &Sternberger, N. H. (1983) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish between phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilamentsin situ.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 80, 6126–30.
Takemura, R., Okabe, S., Umeyama, T., Kanai, Y., Cowan, N. J. &Hirokawa, N. (1992) Increased microtubule stability and alpha tubulin acetylation in cells transfected with microtubule-associated proteins MAP 1B, MAP 2 or tau.Journal of Cell Science 103, 953–64.
Tanaka, Y., Kawahata, K., Nakata, T. &Hirokawa, N. (1992) Chronological expression of microtubule associated proteins (MAPs) in EC cell P19 after neuronal induction by retinoic acid.Brain Research 596, 269–78.
Teichman-Weinberg, A., Littauer, U. Z. &Ginzburg, I. (1988) The inhibition of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by tubulin antisense oligodeoxynucleotides.Gene 72, 297–307.
Tombes, R. M., Peloquin, J. G. &Borisy, G. G. (1991) Specific association of an M-phase kinase with isolated mitotic spindles and identification of two of its substrates as MAP 4 and MAP 1B.Cell Regulation,2, 861–74.
Tsao, H., Aletta, J. M. &Greene, L. A. (1990) Nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor selectively activate a protein kinase that phosphorylates high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins.Journal of Biological Chemistry 265, 15471–80.
Tucker, R. P. (1990) The roles of microtubule-associated proteins in brain morphogenesis: a review.Brain Research Review 15, 101–20.
Tucker, R. P., Binder, L. I. &Matus, A. I. (1988) Neuronal microtubule-associated proteins in the embryonic avian spinal cord.Journal of Comparative Neurology 271, 44–55.
Ulloa, L., Avila, J. &Diaz-Nido, J. (1993a) Heterogeneity in the phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein MAP 1B during rat brain development.Journal of Neurochemistry 61, 961–72.
Ulloa, L., Díaz-Nido, H. &Avila, J. (1993b) Depletion of casein kinase II by antisense oligonucleotide prevents neuritogenesis in neuroblastoma cells.EMBO Journal 12, 1633–40.
Ulloa, L., Dombrádi, V., Díaz-Nido, J., SzÜcs, K., Gergerly, P., Friedrich, P. &Avila, J. (1993c) Dephosphorylation of distinct sites on microtubuleassociated protein MAP 1B by protein phosphatases 1, 2A and 2B.FEBS Letters 330, 85–9.
Viereck, C. &Matus, A. (1990) The expression of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of MAP 5 in the amphibian CNS.Brain Research 508, 257–64.
Viereck, C., Tucker, R. P. &Matus, A. (1989) The adultrat olfactory system expresses microtubule-associated proteins found in the developing brain.Journal of Neuroscience 9, 3547–57.
Wiche, G., Oberkanins, C. &Himmler, A. (1991) Molecular structure and function of microtubule-associated proteins.International Review of Cytology 124, 217–73.
Wilson, S. W. &Easter, S. S. Jr (1991) A pioneering growth cone in the embryonic zebrafish brain.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 88, 2293–6.
Wuerker, R. &Palay, S. L. (1969) Neurofilaments and microtubules in anterior horn cells of the rat.Tissue and Cell 1, 387–402.
Yaginuma, H., Homma, S., Kunzi, R. &Oppenheim, R. W. (1991) Pathfinding by growth cones of commissural interneurones in the chick embryo spinal cord: a light and electron microscopic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 304, 78–102.
Yamada, K. M., Spooner, B. S. &Wessells, N. K. (1970) Axon growth: roles of microfilaments and microtubules.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 66, 1206–12.
Yamada, K. M., Spooner, B. S. &Wessells, N. K. (1971) Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells.Journal of Cell Biology 49, 614–35.
Zauner, W., Kratz, J., Staunton, J., Feick, P. &Wiche, G. (1992) Identification of two distinct microtubule binding domains on recombinant rat MAP 1B.European Journal of Cell Biology 57, 66–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bush, M.S., Gordon-Weeks, P.R. Distribution and expression of developmentally regulated phosphorylation epitopes on MAP 1B and neurofilament proteins in the developing rat spinal cord. J Neurocytol 23, 682–698 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181643
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01181643