Summary
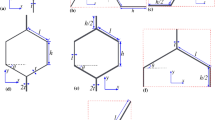
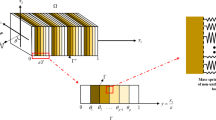
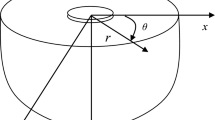
This paper is concerned with flexural vibrations of composite plates, where piezoelastic layers are used to generate distributed actuation or to perform distributed sensing of strains in the plate. Special emphasis is given to the coupling between mechanical, electrical and thermal fields due to the direct piezoelectric effect and the pyroelectric effect. Moderately thick plates are considered, where the influence of shear and rotatory inertia is taken into account according to the kinematic approximations introduced by Mindlin. An equivalent single-layer theory is thus derived for the composite plates. It is shown that coupling can be taken into account by means of effective stiffness parameters and an effective thermal loading. Polygonal plates with simply supported edges are treated in some detail, where quasi-static thermal bending as well as free, forced and actuated vibrations are studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, T., Hubbard Jr., J. E.: Distributed piezoelectric-polymer active vibration control of a cantilever beam. J. Guidance Control and Dynamics8, 605–611 (1985).
Lee, C. K.: Piezoelectric laminates: Theory and experiments for distributed sensors and actuators. In: Intelligent Structural Systems (Tzou, H. S., Anderson, G. L., eds.), pp. 75–167, Dordrecht: Kluwer 1992.
Crawley, E. F.: Intelligent structures for aerospace: A technology overview and assessment. AIAA Journal32, 1689–1699 (1994).
Rao, S. S., Sunar, M.: Piezoelectricity and its use in disturbance sensing and control of flexible structures: A survey. Appl. Mech. Rev.47, 113–123 (1994).
Miu, D. K.: Mechatronics: Electromechanics and contromechanics. New York: Springer 1993.
Mindlin, R. D.: Influence of rotatory inertia and shear on flexural motions of isotropic, elastic plates. J. Appl. Mech.18, 31–38 (1951).
Saravanos, D. A., Heyliger, P. R., Hopkins, D. A.: Layerwise mechanics and finite element for the dynamic analysis of piezoelectric composite plates. Int. J. Solids Struct.34, 359–378 (1997).
Krommer, M., Irschik, H.: On the influence of the electric field on free transverse, vibrations of smart beams. J. Smart Mater. Struct.8, 401–410 (1999).
Mura, T.: Micromechanics of defects in solids. Dordrecht: Kluwer 1991.
Tauchert, T. R.: Piezothermoelastic behavior of a laminate plate. Thermal Stresses15, 25–37 (1992).
Vinson, J. R.: The behavior of shells composed of isotropic and composite materials. Dordrecht: Kluwer 1993.
Irschik, H.: On vibrations of layered beams and plates. ZAMM73, T34–45 (1993).
Yu, Y. Y.: Vibrations of elastic plates. New York: Springer 1996.
Tzou, H. S., Bao, Y.: Modelling of thick anisotropic composite triclinic shell transducer laminates. Smart Mater. Struct.3, 285–292 (1994).
Tzou, H. S., Bao, Y.: A theory on anisotropic piezothermoelastic shell laminates with sensor/actuator applications. Journal of Vibration and Sound184, 453–473 (1995).
Mitchell, J. A., Reddy, J. N.: A refined hybrid plate theory for composite laminates with piezoelectric laminae. Int. J. Solids Struct.32, 2345–2367 (1995).
Tiersten, H. F.: Linear piezoelectric plate vibrations. New York: Plenum 1969.
Parkus, H.: Variational principles in thermo- and magneto-elasticity. New York: Springer 1970.
Crawley, E. F., de Luis, J.: Use of piezoelectric actuators as elements of intelligent structures, AIAA-Journal25, 1373–1385 (1987).
Zhou, Y. S., Tiersten, H. F.: An elastic analysis of laminated composite plates in cylindrical bending due to piezoelectric actuators. J. Smart Mater. Struct.3, 255–265 (1994).
Irschik, H.: Membrane-type eigenmotions of Mindlin plates. Acta Mech.55, 1–20 (1985).
Irschik, H., Heuer, R., Ziegler, F.: Dynamic analysis of polygonal Mindlin plates on two-parameter foundations using classical plate theory and an advanced BEM. Comp. Mech.4, 293–300 (1989).
Irschik, H., Pachinger, F.: On thermal bending of moderately thick polygonal plates with simply supported edges. J. Thermal Stresses18, 59–68 (1995).
Saravanos, D. A., Heyliger, P. R.: Coupled layerwise analysis of composite beams with embedded piezoelectric sensors and actuators. J. Intelligent Material Systems and Structures6, 350–363 (1995).
Lee, H.-J., Saravanos, D. A.: Coupled layerwise analysis of thermopiezoelectric composite beam. AIAA-Journal34, 1231–1237 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krommer, M., Irschik, H. A Reissner-Mindlin-type plate theory including the direct piezoelectric and the pyroelectric effect. Acta Mechanica 141, 51–69 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01176807
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01176807