Summary
-
1.
The form of liquidus curves in binary systems of the eutectic type having nondissociating components was investigated by methods of mathematical analysis.
-
2.
It was shown that in ideal systems for which ΔCP = 0 the form of the liquidus curves is determined completely by the entropy change in the passage of the component from the crystalline state to the solution.
-
3.
For ΔCP ≠ 0, the form of the liquidus curves of ideal systems depends substantially on the value and sign of the ratio\(\frac{{\Delta C_p }}{{\Delta S_i }}\).
-
4.
It was shown that linearity of the liquidus curve is not a criterion of nonideality of the system.
-
5.
In real systems the form of the liquidus curve depends greatly on the type of departure from ideality and the character of the relation of activity coefficient to temperature and concentration.
-
6.
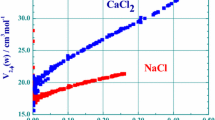
When the departures of mixtures from Raoult's law are not too small, the form of liquidus curves at Ni = 1.0-0.8 is associated unequivocally with the type of departure from Raoult's law, so that for γi > 1 the liquidus curves are convex toward the composition axis and for γi < 1 they are convex in the direction away from the composition axis. The proportion of exceptions to this rule should not be more than about 5%
-
7.
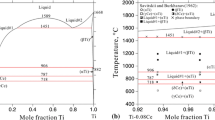
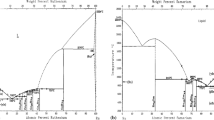
The conclusions concerning the form of liquidus curves of eutectic systems were extended to binary systems with layer separation in the liquid phase ( γi > 1) and with compound formation γi < 1).
-
8.
All the theoretical conclusions were checked against experimental data and were found to be in good agreement with them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
H. W. Bakhius, Roozeboom, Die heterogenen Gleichgewichte vom Standpunkte der Phasenlehre, 2 Heft, 1 Teil, S. 276. Braunschweig, 1904.
N. V. Lipin, Bull. Inst. Phys.-chem. Anal., 4, No. 1, 48 (1928).
W. Argersinger, Trans. Kansas Acad. Sci. 50, 216 (1947); Cited in C. A. 42, 442f (1948).
V. Mathot, Bul. Soc. chim. Belges 59, 137 (1950).
V. Ya. Anosov, Bull. Sector Phys.-chem. Anal 22, 67 (1963).
F. D. Rossini, D. D. Wagman, W. H. Evans, S. Levine and I. Jaffe, Selected Values of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties, Washington, 1952.
A. Eucken and E. Schröder, Z. phys. Chem. B 41, 307 (1938).
E. V. Britske, A. F. Kapustinsky, B. K. Veselovsky, L. M. Shamovsky, L. G. Chentsova and V. I. Anvaer, Thermal Constants of Inorganic Substances, Izd. AN SSSR, Moscow, 1949.
J. J. Van Laar, Z. phys. Chem. 72, 723 (1910); 83, 599 (1913).
J. H. Hildebrand, Solubility of Nonelectrolytes, GONTI, Moscow, 1938.
J. Dauphin, Bull. 1954, 53.
A. V. Nikolskaya and Ya. I. Gerasimov, J. Phys. Chem. 28, 713 (1954).
V. M. Kravchenko, J. Phys. Chem. 13, 139 (1939).
Landolt-Börnstein, Phys. Chem. Tabellen, 5 Aufl., I (1923).
V. Ya. Anosov and S. A. Pogodin, Fundamental Principles of Physicochemical Analysis, Izd. AN SSSR, Moscow, 1947.
J. Chipman, Disc. Faraday Soc. 4, 23 (1948).
V. N. Eremenko, O. M. Eremenko and T. P. Bruevich, Ukrain. Chem. J., 17, 658 (1951).
M. Hansen, Structures of Binary Alloys, Metallurgy Press, Moscow, 1941.
W. E. Barlow, Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 70, 183 (1911).
A. F. Kapustinsky and S. I, Drakin, Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1947, 435.
C. T. Heycock, and F. H. Neville, J. Chem. Soc. 61, 895 (1892).
O. J. Kleppa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 6047, 6051 (1952).
N. W. Taylor, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 45, 2865 (1923).
A. Stoffel, Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 53, 137 (1907).
W. J. Svirbely and S. M. Selis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75, 1532 (1953).
A. F. Kapustinsky and Yu. M. Kess.er, Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci, 1956, 899.
J. Fischer and R. C. Vogel, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 76, 4829 (1954).
V. P. Shishokin and M. I. Muskina, Bull. Acad. Sci., Chem. Series No, 4, 793 (1938).
V. P. Shishokin, Bull. Inst. Phys.-chem. Anal., 4, No. 1, 195 (1928).
R. F. Adamsky and C. M. Wheeler, J. Phys. Chem. 58, 225 (1954).
J. Fischer and R. C. Vogel, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 76, 4862 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kessler, Y.M. Form of liquidus curves of binary systems. Russ Chem Bull 6, 923–932 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01173586
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01173586