Summary
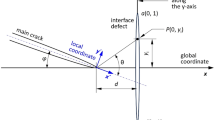
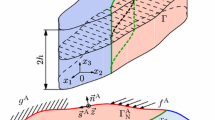
The interfacial debonding is observed as the earliest form of damage in reinforced composite materials. In this paper is considered the crack initiated from the ends of the partially debonded surfaces of a flat inclusion in the framework of the two-dimensional theory of elasticity. The analysis is based on the singular point method. The flat inclusion is simulated by a continuous distribution of concentrated forces since it is of very small thickness. The initiated cracks are replaced by continuous distributions of edge dislocations. Then we obtain a system of singular integral equations with Cauchy kernels. The solution is assumed in the form of the product of an unknown function and the weight function of Jacobi polynomials, and is determined by using a collocation method. Numerical calculations are carried out for the energy release rate and the crack initiation from the ends of the debonded surfaces is discussed. The maximum energy release rate and its direction for Poisson's ratio of matrices are shown in figures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Owen, M. J., Dukes, R.: Failure of glass-reinforced plastics under single and repeated loading. J. Strain Analysis2, 272–279 (1967).
Brussat, T. R., Westmann, R. A.: Interfacial slip around rigid fiber inclusions. J. Composite Materials8, 364–377 (1974).
Schneider, G. J., Conway, H. D.: Effect of fiber geometry and partial debonding on fiber-matrix bond stresses. J. Composite Materials3, 116–135 (1969).
Özbek, T., Erdogan, F.: Some elasticity problems in fiber-reinforced composites with imperfect bonds. Int. J. Engng. Sci.7, 931–946 (1969).
Sekine, H.: Mechanics of debonding along the surfaces of dispersed flat inclusions in composite materials (A model of debonding along the surface of a flat inclusion). Trans. JSME48A, 1415–1420 (1982). (In Japanese).
Wu, C. H.: Fracture under combined loads by maximum-energy-release-rate criterion. Trans. ASME, J. Appl. Mech.45, 553–558 (1978).
Wu, C. H.: Maximum-energy-release-rate criterion applied to a tension-compression specimen with crack. J. Elasticity8, 235–257 (1978).
Gupta, G. D.: Strain energy release rate for mixed mode crack problem. ASME paper No. 76-WA/PVP-7, 1976.
Hayashi, K., Nemat-Nasser, S.: Energy-release rate and crack kinking under combined loading. Trans. ASME, J. Appl. Mech.48, 520–524 (1981).
Muskhelishvili, N. I.: Some basic problems in the mathematical theory of elasticity, 4th ed., p. 104. Groningen: Noordhoff 1963.
Erdogan, F.: Mixed boundary-value problems in mechanics. In: Mechanics today, Vol. 4 (Nemat-Nasser, S., ed.), p. 1–86. New York: Pergamon Press 1978.
Williams, M. L.: Stress singularities resulting from various boundary conditions in angular corners of plates in extension. Trans. ASME, J. Appl. Mech.19, 526–528 (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 4 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamate, O., Sekine, H. & Ozawa, Y. Crack initiation from the ends of partially debonded surfaces of a flat inclusion. Acta Mechanica 50, 59–70 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01170441
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01170441