Conclusions
-
1.
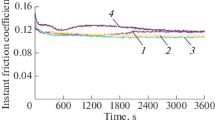
In assessing the properties of antifriction parts of iron-graphite porous ceramic alloys, the form in which the structurally free cementite is distributed throughout the structure is important. Cementite within the ferrite improves the antifriction properties and permits high specific pressures and angular velocity.
-
2.
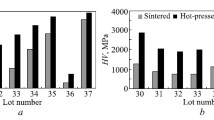
In the presence of 20–25% of structurally free cementite, the friction load of iron-graphite bearings can be increased to 200–300 kgm/sq.cm·sec.
-
3.
The data presented show that the existing views on the detrimental effect of cementite, no matter what its form and distribution in the microstructure, are erroneous.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pozdnyak, N.Z., Ponomarenko, E.K. Study of cementite in iron-graphite [powder] alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 2, 675–676 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01166750
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01166750