Abstract
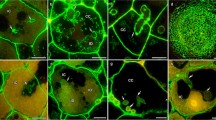
Root nodules induced inPhaseolus vulgaris L. by the wild-type (WT) and a C4-dicarboxylic-acid mutant strain ofRhizobium leguminosarum biovar.phaseoli were compared on the basis of ultrastructure and cytochemistry of cellulose subunits. The mutant bacteroids failed to colonize infected host cells in a normal manner, and presented a premature degenerative appearance. Starch granules, rough endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria were found to accumulate in the ineffective nodules. The most striking difference between effective and ineffective nodules was the presence of unusual spherical, laminated structures in plastids of mutant-infected host cells only. Cytochemical observations showed that these structures containβ-1,4-glucans. The presence ofβ-1,4-glucans within such structures may be caused by the activity of a cellulase which is produced by either the bacteroids or the host cell and is locally hydrolyzing the host cell-wall, thus releasing cellulose subunits into the cytoplasm. Another possibility is denovo synthesis ofβ-1,4-glucans in the host cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PEG:
-
polyethylene glycol
- PHB:
-
poly-β-hydroxybutyrate
- RER:
-
rough endoplasmic reticulum
- TTC:
-
2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride
- WT:
-
wild-type
- B :
-
bacteroid
- C :
-
cortex
- Cy :
-
cytoplasm
- CC :
-
central core
- HCW :
-
host cell-wall
- IC :
-
infected cell
- IS :
-
inter-cellular space
- LS :
-
laminated structure
- N :
-
nucleus
- P :
-
peroxisome
- PHB :
-
poly-β-hydroxybutyrate
- Pl :
-
plastid
- PlM :
-
plastid matrix
- PM :
-
peribacteroid membrane
- RER :
-
rough endoplasmic reticulum
- S :
-
starch grain
- UC :
-
uninfected cell
- Va :
-
vacuole
- VB :
-
vascular bundle
References
Arwas, R., McKay, I.A., Rowney, F.R.P., Dilworth, M.J., Glenn, A.R. (1985) Properties of organic acid utilization mutants ofRhizobium leguminosarum strain 300. J. Gen. Microbiol.131, 2059–2066
Baird, L.M., Webster, B.D. (1982) Morphogenesis of effective and ineffective root nodules inPhaseolus vulgaris. L. Bot. Gaz.143, 41–51
Benhamou, N. (1989) Cytochemical localization of β-(1→ 4)-d-glucans in plant and fungal cells using an exoglucanase-gold complex. Electron Microsc. Rev.2, 123–138
Benhamou, N., Chamberland, H., Ouellette, G.B., Pauzé, F.J. (1987) Ultrastructural localization of β-(1→4)-d-glucans in two pathogenic fungi and in their host tissues by means of an exoglucanase-gold complex. Can. J. Microbiol.33, 405–417
Bergersen, F.J. (1957) The structure of ineffective nodules of legumes: an unusual type of ineffectiveness and an appraisal of present knowledge. Aust. J. Biol. Sci.10, 233–242
Berghem, L.E.R., Pettersson, L.G. (1973) The mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation. Purification of a cellulocytic enzyme fromTrichoderma viride active on highly ordered cellulose. Eur. J. Biochem.37, 21–30
Berghem, L.E.R., Pettersson, L.G., Axiö-Fredricksson, U.-B. (1975) The mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation. Characterization and enzymatic properties of a β-1,4-glucan cellobiohydrolase fromTrichoderma viride. Eur. J. Biochem.53, 55–62
Chalifour, F.-P., Benhamou, N. (1989) Indirect evidence for cellulase production byRhizobium in pea root nodules during bacteroid differentiation: cytochemical aspects of cellulose breakdown in rhizobial droplets. Can. J. Microbiol.35, 821–829
Dazzo, F.B., Truchet, G.L. (1983) Interactions of lectins and their saccharide receptors in theRhizobium-legume symbiosis. J. Membr. Biol.73, 1–16
Doherty, D., Leigh, J.A., Glazebrook, J., Walker, G.C. (1988)Rhizobium meliloti mutants that overproduce theR. meliloti acidic calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol.170, 4249–4256
Finan, T.M., Wood, J.M., Jordan, D.C.. (1983) Symbiotic properties of C4-dicarboxylic acid transport mutants ofRhizobium leguminosarum. J. Bacteriol.154, 1403–1413
Frens, G. (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold solutions. Nature (London), Phys. Sci.241, 20–22
Huber, J.D., Parker, F., Odland, G.F. (1968) A basic fuchsin and alkalinized methylene blue rapid stain for epoxy-embedded tissue. Stain Technol.43, 83–87
Lafontaine, P.J., Lafrenière, C., Antoun, H. (1989a) Some properties of carbohydrate and C4-dicarboxylic acid utilization negative mutants ofRhizobium leguminosarum biovarphaseoli strain P121. Plant Soil120, 195–201
Lafontaine, P.J., Lafrenière, C., Chalifour, F.-P., Dion, P., Antoun, H. (1989b) Carbohydrate and organic acid composition of effective and ineffective root nodules ofPhaseolus vulgaris Physiol. Plant.76, 507–513
Lafrenière, C., Lafontaine, P.J., Marion, C., Antoun, H. (1987) Oxidation of substrate in organic acids utilization negative mutants and the wild typeRhizobium meliloti strain S14. Plant Soil101, 73–78
Lalande, R., Antoun, H., Paré, T., Joyal, P. (1986) Effets de l'inoculation avec des sourches duRhizobium leguminosarum biovarphaseoli sur le rendement et la teneur en azote du haricot (Phaseolus vulgaris). Naturaliste Can. (Rev. Ecol. Syst.)113, 337–346
Leigh, J.A. Lee, C.C. (1988) Characterization of polysaccharidesof Rhizobium meliloti exo mutants that form ineffective nodules. J. Bacteriol.170, 3327–3332
Leigh, J.A., Reed, J.W., Hanks, J.F., Hirsh, A.M., Walker, G.C. (1987)Rhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to succinylate their calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide are defective in nodule invasion. Cell51, 579–587
Long, S.R. Cooper, J. (1988) Overview of symbiosis. In: Proc. 4th Int. Symp. Mol. Gen. Plant Microbe Interact., Acapulo, Mexico, pp. 163–177, Palacios, R., Verma, D.P.S., eds. American Phytopathological Society, Press, St. Paul, Minn., USA
Long, S., Reed, J.W., Himawan, J., Walker, G.C. (1988) Genetic analysis of a cluster of genes required for synthesis of the calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide ofRhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol.170, 4239–4248
Martinez-Molina, E., Morales, V.M., Hubbell, D.H. (1979) Hydrolytic enzyme production byRhizobium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.38, 1186–1188
MacKenzie, C.R., Jordan, D.C. (1974) Ultrastructure of root nodules formed by ineffective strains ofRhizobium meliloti. Can. J. Microbiol.20, 755–758
Newcomb, W., Syono, K., Torrey, J.G. (1977) Development of an ineffective pea root nodule: morphogenesis, fine structure, and cytokinin biosynthesis. Can. J. Bot.55, 1891–1907
Newcomb, E.H., Tandon, Sh.R., Kowal, R.R. (1985) Ultrastructural specialization for ureide production in uninfected cells of soybean root nodules. Protoplasma125, 1–12
Nogueira, N.D.L., Da Silva, D.M., Saito, S.M.T. (1979) Estudo ao microscopio eletrônico de nodulos emPhaseolus vulgaris L. causados por uma estripe inefetiva deRhizobium. Turrialba29, 93–96
Pankhurst, C.E. (1974) IneffectiveRhizobium trifolii mutants examined by immune-diffusion, gel-electrophoresis and electron microscopy. J. Gen. Microbiol.82, 405–413
Ronson, C.W., Lyttleton, P., Robertson, J.G. (1981) C4-dicarboxylate transport mutants ofRhizobium trifolii form ineffective nodules onTrifolium repens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA78, 4284–4288
Selvaraj, G., Hooper, I., Shantharam, S., Iyer, V.N., Barran, L., Wheatcroft, R., Watson, R.J. (1987) Derivation and molecular characterization of symbiotically deficient mutants ofRhizobium meliloti. Can. J. Microbiol.33, 739–747
Van den Bosch, K.A., Noël, K.D., Kaneko, Y., Newcomb, E.H. (1985) Nodule initiation elicited by noninfective mutants ofRhizobium phaseoli. J. Bacteriol.162, 950–959
Watson, R.J., Chan, Y.-K., Wheatcroft, R., Yang, A.-F., Han, S. (1988)Rhizobium meliloti genes required for C4-dicarboxylate transport and symbiotic nitrogen fixation are located on a megaplasmid. J. Bacteriol.170, 927–934
Webb, M.A., Newcomb, E.H. (1987) Cellular compartimentation of ureide biogenesis in root nodules of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.). Planta172, 162–175
Werner, D., Mörschel, E. (1978) Differentiation of nodules ofGlycine max. Ultrastructural studies of plant cells and bacteroids. Planta141, 169–177
Werner, D., Mörschel, E., Kort, R., Mellor, R.B., Bassarab, S. (1984) Lysis of bacteroids in the vicinity of the host cell nucleus in an ineffective (fix−) root nodule of soybean (Glycine max). Planta162, 8–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada to H. Antoun and N. Benhamou. The authors are grateful to Dr. E.H. Newcomb, Department of Botany, University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA, for helpful comments on the interpretation of the micrographs. We also wish to thank S. Noël and H. Bissonnette for excellent technical assistance, Mrs. M. Pelchat for typing this manuscript, and Dr. G.B. Ouellette, Centre Forestier des Laurentides, Agriculture Canada, Sainte-Foy, Que., Canada, for the use of his light microscope. Printing for this paper was supported by the Conseil des recherches et services agricoles du Québec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lafontaine, P.J., Benhamou, N. & Antoun, H. The occurrence of unusual laminated structures rich in β-1,4-glucans in plastids ofPhaseolus vulgaris root-nodule cells infected by an ineffective C4-dicarboxylic-acid mutant ofRhizobium leguminosarum bv.phaseoli . Planta 180, 312–323 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01160386
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01160386