Abstract
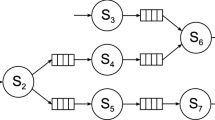
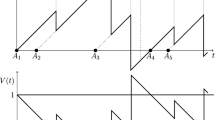
In small-lot, multi-product, multi-level assembly systems, kitting (or accumulating) components required for assembly plays a crucial role in determining system performance, especially when the system operates in a stochastic environment. This paper analyzes the kitting process of a stochastic assembly system, treating it as an assembly-like queue. If components arrive according to Poisson processes, we show that the output stream departing the kitting operation is a Markov renewal process. The distribution of time between kit completions is also derived. Under the special condition of identical component arrival streams having the same Poisson parameter, we show that the output stream of kits approximates a Poisson process with parameter equal to that of the input stream. This approximately decouples assembly from kitting, allowing the assembly operation to be analyzed separately.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U.N. Bhat, A controlled transportation queueing process, Manag. Sci. 16(1970)446–452.
U.N. Bhat, Finite capacity assembly queues, Queueing Syst. 1(1986)85.
R.L. Disney and P.C. Kiessler,Traffic Processes Queuing Networks: A Markov Renewal Approach (Johns Hopkins Univ. Press. 1987).
R.L. Disney and D. Konig, Queueing networks: A survey of their random processes, SIAM Rev. 27 (1985) 335–403.
J.M. Dobbie, A double-ended queueing problem of Kendall, Oper. Res. 9 (1961) 755–757.
J.M. Harrison, Assembly-like queues, J. Appl. Prob. 10 (1973) 354–367.
W.J. Hopp and J.T. Simon, Bounds and heuristics for assembly-like queues, Queueing Syst. 4 (1989) 137–156.
B.R.K. Kashyap, A double-ended queueing system with limited waiting space, Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. (India) 31 (1965) 559–570.
B.R. Kashyap and M.L. Chaudhury,An Introduction to Queuing Theory (A&A Publ., Kingston, Ontario, Canada, 1988).
G. Latouche, Queues with paired customers, J. Appl. Prob. 18 (1981) 684–696.
S. Saboo and W.E. Wilhelm, An approach for modeling small-lot assembly networks, IIE Trans. (Dec. 1986) 322–334.
P. Som and W.E. Wilhelm, Analysis of a stochastic assembly system — A Markov renewal approach, Working Paper, Texas A&M University (1992).
W.E. Wilhelm, P. Som and B. Carroll, A model for implementing a paradigm of time-managed, material flow control in certain assembly systems, Int. J. Prod. Res. 30 (1992) 2063–2086.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Som, P., Wilhelm, W.E. & Disney, R.L. Kitting process in a stochastic assembly system. Queueing Syst 17, 471–490 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01158705
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01158705