Summary
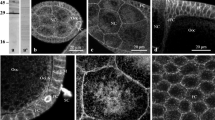
Oocyte-follicle cell gap junctions inTribolium occur in all oogenetic stages studied. During early previtellogenesis the junctions are found exclusively between lateral membranes of oocyte microvilli and the membrane of prefollicle cells. In late previtellogenesis and vitellogenesis the junctions are located between the tips of oocyte microvilli and the flat membranes of the follicle cells. During previtellogenesis gap junctions are infrequent, whereas in the phase of yolk accumulation their number increases considerably, exceeding 17 junctions/μm2 of the follicle cell membrane. It could be shown by microinjection of a fluorescent dye that gap junctions are in a functional state during vitellogenesis. Possible roles of heterologous gap junctions in oogenesis are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amsterdam A, Josephs R, Lieberman ME, Lindner HR (1976) Organization of intramembrane particles in freeze-cleaved gap junctions of rat Graafian follicles: optical diffraction analysis. J Cell Sci 21:93–105
Anderson E, Albertini DF (1976) Gap junctions between the oocyte and companion follicle cells in the mammalian ovary. J Cell Biol 71:680–686
Anderson E, Albertini DF, Wilkinson RF (1977) Cytological differentiation of the female gamete. In: Brinkley BR, Porter KR (eds) International cell biology. Rockefeller University Press, New York, pp 561–568
Biliński S, Klag J (1982) Gap junctions between oocyte and follicle cells inAcerentomon sp. (Insecta, Protura). Int J Inv Reprod 5:331–335
Branton D, Bullivant S, Gilula NB, Karnovsky MJ, Moor H, Mühlethaler K, Northcote DH, Packer L, Satir B, Satir P, Speth V, Staehelin LA, Steere RL, Weinstein RS (1975) Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science 190:54–56
Brower PT, Schultz RM (1982) Intercellular communication between granulosa cells and mouse oocytes: existence and possible nutritional role during oocyte growth. Dev Biol 90:144–153
Caveney S, Berdan R (1982) Selectivity in junctional couping between cells of insect tissurs. In: King RC, Akai H (eds) Insect ultrastructure, vol I. Plenum Press, New York, pp 434–465
Chaminade M, Laverdure A (1980) La vitellogenèse endogène chezTenebrio molitor (Coleoptère). Bull Soc Zool 105:437–444
Gilula NB, Epstein ML, Beers WH (1978) Cell-to-cell communication and ovulation: a study of the cumulus-oocyte complex. J Cell Biol 78:58–75
Heller DT, Schultz RM (1980) Ribonucleoside metabolism by mouse oocytes: metabolic cooperativity between the fully grown oocyte and cumulus cells. J Exp Zool 124:355–364
Heller DT, Cahill DM, Schultz RM (1981) Biochemical studies of mammalian oogenesis: metabolic cooperativity between granulosa cells and growing mouse oocytes. Dev Biol 84:455–464
van den Hoef MHF, Dictus WJAG, Hage WJ, Bluemink JG (1984) The ultrastructural organization of gap junctions between follicle cells and the oocyte inXenopus laevis. Eur J Cell Biol 33:242–247
Huebner E (1981) Oocyte-follicle cell interaction during normal oogenesis and atresia in an insect. J Ultrastruct Res 74:95–104
Schroeder TE (1981) Microfilament-mediated surface change in starfish oocytes in response to 1-methyladenine: implications for identifying the pathway and receptor sites for maturation inducing hormones. J Cell Biol 90:362–371
Stewart WW (1978) Functional connections between cell as revealed by dye coupling with a highly fluorescent naphthalimide tracer. J Cell Biol 14:741–759
Telfer WH, Huebner E, Smith DS (1982) The cell biology of vitellogenic follicles inHyalophora andRhodnius. In: King RC, Akai H (eds) Insect ultrastructure, vol. I. Plenum Press, New York, pp 118–149
Ullmann SL (1973) Oogenesis inTenebrio molitor: histological and autoradiographical observations on pupal and adult ovaries. J Embryol Exp Morphol 30:179–217
Wollberg Z, Cohen E, Kalina M (1976) Electrical properties of developing oocytes of the migratory locust,Locusta migratoria. J Cell Physiol 88:145–158
Woodruff RI (1979) Electrotonic junctions inCecropia moth ovaries. Dev Biol 69:281–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biliński, S.M., Hage, W.J. & Bluemink, J.G. Gap junctions between the follicle cells and the oocyte during oogenesis in an insect,Tribolium destructor/Coleoptera. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv 194, 296–300 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01152175
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01152175