Abstract
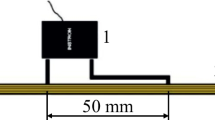
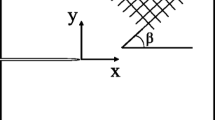
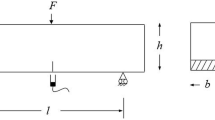
The characterization of crack growth (Mode I) in glass fibre-reinforced materials is difficult because neither the crack length nor the crack tip can be assessed with sufficient accuracy because of delamination and bridging of broken and unbroken fibres. Hence linear elastic fracture mechanics cannot be employed. A new testing technique is reported, to characterize the crack growth in Mode I under quasistatic loading conditions in terms of fracture mechanics. The tests and evaluation procedures are based on the fracture energy concept, which does not require knowledge of the exact crack length. Experiments were performed at room temperature and 77 K, on a two-dimensionally glass fibre-reinforced epoxy (ISOVAL 10). The splitting test method proposed in the present work is experimentally simple; the loading device and the sample geometry are small and well suited for measurements at low temperatures on both unirradiated or irradiated samples. Results of acoustic emission and fractographic examinations, as well as investigations on the specimen-size dependence of the measured fracture mechanical quantities, are presented. Advantages and disadvantages of the new technique are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Lau, H. H. Abdelmohsen andM. K. Abdelsalam,Adv. Cryog. Engng 34 (1988) 83.
S. M. Lee,J. Compos. Mater. 20 (1986) 185.
S. Hashemi, A. J. Kinloch andJ. G. Williams,Compos. Sci. Tech. 37 (1990) 429.
Idem, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 427 (1990) 173.
A. C. Garg,Engng Fract. Mech. 23 (1986) 719.
A. C. Garg andO. Ishai,ibid. 22 (1985) 413.
Idem, ibid. 22 (1985) 595.
Y. Kagawa, E. Nakata andS. Yoshida, ASTM STP 864 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1985) p. 27.
A. Daimaru, T. Hata andM. Taya,ibid. p. 505.
S. M. Jeng, J. M. Yang andC. J. Yang,Mater. Sci. Engng A 138 (1991) 181.
C. G. Aronsson andJ. Bäcklund,J. Compos. Mater. 20 (1986) 287.
Idem, ASTM STP 907 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1986) p. 134.
A. Hillerborg, in Proceedings of “Fracture Mechanics of Concrete, Developments in Civil Engineering”, Vol. 7 edited by F. Wittmann (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1983) p. 223.
Idem, Mater. Construct. 18 (1985) 25.
P. E. Roelfstra, Thesis, Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausane (1989).
B. Hillemeier, Thesis, University of Karlsruhe (1976).
E. K. Tschegg, Aust. Pat. 233/86, 390 328 (1986).
Idem, Mater. Test.33 (1991) 338.
E. K. Tschegg, K. Humer andH. W. Weber,Adv. Cryog. Engng 38A (1992) 355.
H. N. Linsbauer andE. K. Tschegg: Final report A1, COST 502, No. HNL-01-89 (1989).
E. K. Tschegg,ASTM J. Test. Eval. (1991) submitted.
E. K. Tschegg, K. Humer andH. W. Weber,Cryogenics 31 (1991) 312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tschegg, E.K., Humer, K. & Weber, H.W. Fracture tests in Mode I on fibre-reinforced plastics. J Mater Sci 28, 2471–2480 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01151682
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01151682