Abstract
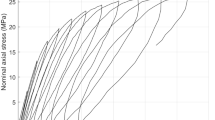
Fracture initiation of short glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic polyester was characterized by theJ-integral measurement based on the energy release rate interpretation ofJ. The criticalJ value (J c) is shown to be a fracture characterizing parameter for the onset of the crack initiation in the injection moulded short glass fibre reinforced composite material. TheJ c value of the composite is estimated by be 6.0kJ m−2. This value is in good agreement with the linear elastic strain energy release rate (G c), since the composite exhibited a fairly linear stress-strain relationship. The estimated ratios ofJ c to the total energy absorbed per unit uncracked area are in good agreement with the analytically obtained values after the remote energy dissipation due to fibre and matrix interaction away from the crack tip has been subtracted from the total energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- J :
-
J-integral
- J c :
-
The criticalJ
- G :
-
Elastic strain energy release rate
- G c :
-
The criticalG
- K l :
-
Opening mode stress intensity factor
- \(K_{I_C } \) :
-
The criticalK l
- P :
-
Applied load
- x :
-
Load-point displacement
- B :
-
Specimen thickness
- E :
-
Young's modulus
- v :
-
Poisson's ratio
- F :
-
Force
- Y :
-
Central deflection
- a/W :
-
Ratio of the crack length to the specimen width
- σ y :
-
Yield stress
- U t :
-
Total strain energy in loading a specimen
- U d :
-
Remotely dissipated strain energy after unloading
- U t−d :
-
U t−U d
- φ t :
-
Ratio ofJ c toU t per unit uncracked ligament
- φ t−d :
-
Ratio ofJ c toU t−d per unit uncracked ligament.
References
B. D. Agarwal, B. S. Pastro andP. Kumar,Eng. Fracture Mechanics 19 (1984) 675.
B. D. Agarwal, P. Kumar andS. K. Khanna,Compos. sci. tech. 25 (1986) 311.
J. R. Rice,J. Appl. Mech. 35 (1968) 379.
J. A. Begley andJ. D. Landes, ASTM STP 514 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1972) pp. 1–20.
J. D. Landes andJ. A. Begley,ibid. pp. 24–39.
B. H. Kim andC. R. Joe,Eng. Fracture Mechanics 30(4) (1988) 493.
Idem, Polymer testing,7 (1987) 355.
Idem, Int. J. Fracture 34 (1987) R57.
J. R. Rice, P. C. Paris andJ. G. Merkle, ASTM STP 536 (1973) pp. 231–245.
J. D. G. Sumpter andC. E. Turner, ASTM STP 601 (1976) pp. 3–18.
J. E. Srawley,Int. J. Fracture 12 (1976) 475.
B. H. Kim andC. H. Joe,Eng. Fracture Mechanics, in press.
J. E. Srawley,Int. J. Fracture 12 (1976) pp. 470–474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.H., Kim, H.S. Fracture characterization of short glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic polyester by theJ-integral. J Mater Sci 24, 921–925 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148779
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148779