Abstract
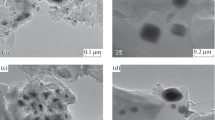
Cobalt-dispersed carbons were synthesized by pressure pyrolysis of cobaltocene-divinylbenzene and phenylallylcobaltocene-divi nylbenzene at 125 MPa below 700° C. The carbons resulting from cobaltocene-divinylbenzene contained uniformly dispersed fine particles, < 20 nm diameter, of metallic cobalt of lower crystallinity, which were composed of ferromagnetic and superparamagnetic particles. Metallic cobalt particles of cubic and hexagonal structures with higher crystallinity were formed during pyrolysis of phenylallylcobaltocene-divinyibenzene. Cobaltucence-divinylbenzene and phanylallylcobaltocene-divinylbenzene changed their magnetic properties from diamagnetism to paramagnetism at 250 and 200° C, respectively. The infrared absorption band of the cyclopentadienyl ring at 995 cm−1 disappeared at 350° C in cobaltocene divinylbenzene and at 300° C in phenylallylcobaltocene-divinylbenzene. Superparamagnetic particles from cobaltocene-divinylbenzene aggregated and crystallized to produce larger particles of diameter 30 to 100 nm, which increased the magnetization during thermomagnetic measurement. The saturation magnetization of cobalt-dispersed carbons from phenylallylcobaltocene-divinylbenzene was higher by about 10% than that from cobaltocene-divinylbenzene. The coercive forces of cobalt-dispersed carbon from phenylallylcobaltocene-divinylbenzen and cqbaltocene-divinylbenzene were 350 and 250 Oe (2.79 × 104 and 1.99 × 104 Am−1), respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. L. Walker Jr, andA. Weinstein,Carbon 5 (1963) 13.
A. S. Kotosonov, V. A. Vinnikov, V. I. Frolor andB. G. Ostronov,Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 185 (1969) 1316.
H. Marsh, F. Dachille, J. Melvin andP. L. Walker Jr,Carbon 9 (1971) 159.
P. W. Whang, F. Dachille andP. L. Walker Jr,High Temp. High Press. 6 (1974) 127.
Idem, ibid. 6 (1974) 137.
S. Hirano, F. Dachille andP. L. Walker Jr,ibid. 5 (1973) 207.
S. Hirano, M. Ozawa andS. Naka,J. Mater. Sci. 16 (1981) 1989.
S. Hirano, T. Pogo, H. Suzuki andS. Naka,ibid. 18 (1983) 2811.
G. Wilkinson, F. A. Cotton andJ. M. Birmingham,J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 2 (1956) 95.
G. E. Herberich andE. Bauer,J. Organometall. Chem. 16 (1969) 301.
J. Drain andA. Michel,Bull. Soc. Chim. France (1951) 517.
V. I. Telnoi andI. B. Rabinovitch,Russ. Chem. Rev. 46 (1977) 689.
H. P. Fritz,Chem. Ber. 92 (1959) 780.
H. P. Myers andW. Sucksmith,Proc. R. Soc. A207 (1951) 427.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, SI., Yogo, T., Nogami, N. et al. Synthesis and properties of cobalt-dispersed carbons by pressure pyrolysis of organocobalt polymers. J Mater Sci 21, 225–229 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01144724
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01144724