Abstract
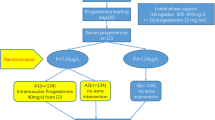
Exogenous progesterone (P) was supplemented to gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) patients to determine the optimal timing to start P supplementation and the role of isthmic block in GIFT. Patients were alternatively divided into two groups. In the immediate group, exogenous P was supplied from the day of surgery. In the delayed group, P was supplied 4 days after the surgery, the day the fertilized ovum is supposed to arrive in the uterine cavity. Except for higher serum P levels on luteal day 3 in the immediate group, no significant differences were found in serum P levels during the early luteal phase, the pregnancy rate, and the abortion rate between the two groups. It is possible that in stimulated cycles, higher serum P levels during the early luteal phase render the endometrium receptive for embryo implantation, albeit unlock the isthmic block. It may not be crucial to start exogenous P supplementation either before or after a fertilized egg(s) arrives in the uterine cavity. The role of isthmic block in GIFT needs further evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang KE, Muechler EK, Schwartz KR, Goggin M, Graham MC: Serum progesterone levels in women treated with human menopausal gonadotropin and human chorionic gonadotropin for in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 1986;46:903–906
Kemeter P, Feichtinger W, Neumark J, Szalay S, Bieglmayer C, Jenish H: Influence of laparoscopic follicular aspiration under general anesthesia on corpus luteum progesterone secretion in normal and clomiphene-stimulated cycles. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1982;89:948–950
Wramsby H, Kullander S, Liedholm P, Ronnevik G, Sundstrom P, Thorell J: The success rate on in vitro fertilization of human oocytes in relation to the concentration of different hormones in follicular fluid and peripheral plasma. Fertil Steril 1981;36:448–454
Jansen RPS: Endocrine response in the fallopian tube. Endocr Rev 1984;5:525–551
Croxatto HB, Qrtiz ME, Diaz S, Hess R, Balmaceda J, Croxatto D: Studies on the duration of egg transport by the human oviduct. II. Ovum location at various intervals following luteinizing hormone peak. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1978;132:629–634
Jansen RPS: Abortion incidence following fallopian tube repair. Obstet Gynecol 1980;56:499–502
Jansen RPS: Spontaneous abortion incidence in the treatment of infertility. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982;143:451–473
Laatikainen T, Kurummaki H, Koskimies A: A short luteal phase in cycles stimulated with clomiphene and human menopausal gonadotropin for in vitro fertilization. J Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1988;5:15–17
Ferraretti AP, Gianaroli L, Razzani D, Franceschetti F, Bolelli F, Flamigni C: Short luteal phase after multiple ovarian induction. Fourth World Conference of In Vitro Fertilization. Melbourne, Australia, November 18–22, 1985
Frydman R, Testart J, Giacomini P, Imbert MC, Martin E, Nahoul K: Hormonal and histological study of the luteal phase in women following aspiration of the preovulatory follicle. Fertil Steril 1982;38:312–317
Garcia JE, Acosta AA, Hsiu J, Jones HW Jr: Advanced endometrial maturation after ovulation induction with human menopausal gonadotropin/human chorionic gonadotropin for in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 1984;41:31–35
Cohn JJ, Debache C, Pigeau F, Mandelhaum J, Plachot M, de Brux J: Sequential use of clomiphene citrate, human menopausal gonadotropin and human chorionic gonadotropin in human IVF. II. Study of luteal phase adequacy following aspiration of the preovulatory follicles. Fertil Steril 1984;42:360–363
Salut-Baroux J, Giacomini P, Cornet D: Study of the luteal phase after ovulation and in vitro fertilization (Abstr). Fertil Steril 41:166, 1984 Joint annual meeting of the Canadian fertility and andrology society and British fertility society. Vancouver, Canada, September 6–8, 1984
Graf MJ, Reyniak JV, Battle-Mutter P, Laufer N: Histologic evaluation of the luteal phase in women following follicle aspiration for oocyte retrieval. Fertil Steril 1988;49:616–619
Sterzik K, Sasse V, Dallenbach C, Dallenbach-Hellweg G, Schneider V: In vitro fertilization: The degree of endometrial insufficiency varies with the type of ovarian stimulation. Fertil Steril 1988;50:457–462
Speroff L, Glass RH, Kase NG: Sperm and egg transport, fertilization, and implantation.In Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility, L Speroff, RH Glass, NG Kase (eds). Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1989, pp 499–512
Glass RH: Fate of rabbit eggs fertilized in the uterus. J Reprod Fertil 1972;31:139–141
Adams CE: Consequences of accelerated ovum transport, including a reevaluation of Estes' operation. J Reprod Fertil 1979;55:239–246
Ikle FA: Pregnancy after implantation of the ovary into the uterus. Gynecologia 1961;151:95–99
Rosenwak Z: Donor eggs: Their application in modern reproductive technologies. Fertil Steril 1987;47:895–909
Garcia JE, Acosta AA, Hsiu JG, Jones HW Jr: Advanced endometrial maturation after ovulation induction with human menopausal gonadotropin/human choronic gonadotropin for in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 1984;41:31–35
Forman RG, Eychenne B, Nessmann C, Frydman R, Robel P: Assessing the early luteal phase in in vitro fertilization cycles: Relationships between plasma steroids, endometrial receptors, and endometrial histology. Fertil Steril 1989;51:310–316
McNeely MJ, Soules MR: The diagnosis of luteal phase deficiency: a critical review. Fertil Steril 1988;50:1–15
Rosenberg SM, Luciano AA, Riddick DH: The luteal phase defect: The relative frequency of, and encouraging response to, treatment with vaginal progesterone. Fertil Steril 1980; 34:17–20
Andrews WC: Luteal phase defects. Fertil Steril 1979;32:501–509
Balsch J, Vanrell JA, Marquez M, Burzaco I, Gonzalaz-Merlo J: Dehydrogesterone versus vaginal progesterone in the treatment of the endometrial luteal phase deficiency. Fertil Steril 1982;37:751–754
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, SY., Soong, YK., Chang, MY. et al. Immediate versus delayed progesterone supplementation in gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT). J Assist Reprod Genet 6, 275–279 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01139181
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01139181