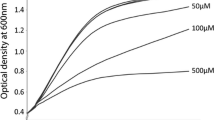
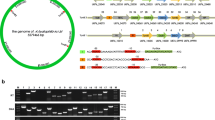
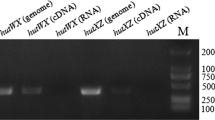
Summary
Iron is essential for bacterial growth and metabolism. In vertebrates this metal is complexed by high-affinity iron-binding proteins, such as transferrin in serum. The fish pathogenVibrio anguillarum possesses a very efficient iron-uptake system which is encoded in the virulence plasmid pJMI. This allows the bacterium to utilize the otherwise unavailable iron in the fish host, resulting in the septicemic disease vibriosis. This system includes the siderophore anguibactin and transport components. We have cloned this iron-utpake system and have defined several genetic units by transposition mutagenesis. Nucleotide sequence analysis identified four open reading frames in the transport region, one of these corresponding to the gene for the outer membrane protein OM2 and another to a 40-kDa polypeptide. Complementation analysis indicated that products from all four reading frames are required for the transport of iron-anguibactin complexes. We have also identified positive and negative-acting regulatory elements that modulate in concert the expression of anguibactin biosynthetic genes and iron transport. The deletion or mutation of the positive-acting regulatory genes results in an iron-uptake-deficient phenotype and leads to an attenuation of virulence, underscoring the importance of this iron-uptake system as a virulence attribute ofV. anguillarum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Actis L, Potter S, Crosa JH (1985) Iron-regulated outer membrane protein OM2 ofVibrio anguillarum is encoded by virulence plasmid pJM1. J Bacteriol 161:736–742
Actis L, Tolmasky M, Crosa JH (1988) Genetic and molecular characterization of essential components of theVibrio anguillarum plasmid-mediated iron-transport system. J Biol Chem 263:2853–2860
Crosa JH (1980) A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogenVibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature 284:566–568
Crosa JH (1989) Genetics and molecular biology of siderophore-mediated iron transport in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 53:517–530
Crosa JH, Hodges L, Schiewe MH (1980) Curing of a plasmid is correlated with an attenuation of the virulence in the marine fish pathogenVibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun 27:897–902
Farrell D, Mikesell P, Actis LA, Crosa JH (1990) A regulatory gene,angR, of the iron-uptake system ofVibrio anguillarum: similarity with phage P22cro and regulation by iron. Gene 86:45–51
Jalal M, Hossain D, van der Helm J, Sanders-Ioerh J, Actis LA, Crosa JH (1989) Structure of anguibactin, a unique plasmid-related bacterial siderophore from the fish pathogenVibrio anguillarum. J Am Chem Soc 111:292–296
Poteete A, Hehir K, Sauer R (1986) Bacteriophage P22 Cro protein: sequence, purification and properties. Biochemistry 25:251–256
Salinas P, Tolmasky ME, Crosa JH (1989) Regulation of the iron-uptake system inVibrio anguillarum: evidence for a cooperative effect between two transcriptional activators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3529–3533
Sauer R, Yocum R, Doolittle R, Lewis R, Pabo C (1982) Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature 298:447–451
Stachel S, An G, Flores C, Nester EW (1985) A Tn3lacZ transposon for the random generation ofβ-galactosidase gene fusions: application to the analysis of gene expression inAgrobacterium. EMBO J 4:891–898
Tolmasky ME, Crosa JH (1984) Molecular cloning and expression of genetic determinants for the iron-uptake system mediated by theVibrio anguillarum plasmid pJMl. J Bacteriol 160:860–866
Tolmasky ME, Actis LA, Crosa JH (1988a) Genetic analysis of the iron uptake region of theVibrio anguillarum plasmid: molecular cloning of genetic determinants encoding a noveltrans-activator of siderophore biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 170:1913–1919
Tolmasky ME, Salinas P, Actis LA, Crosa JH (1988b) Increased production of the siderophore anguibactin mediated by pJM1-like plasmids inVibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun 56:1608–1614
Walter M, Potter S, Crosa JH (1983) Iron-uptake system mediated byVibrio anguillarum plasmid pJM1. J Bacteriol 156:880–887
Weinberg ED (1978) Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev 42:45–66
Weinberg ED (1984) Iron withholding: a defense against infection and disease. Physiol Rev 64:65–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolmasky, M.E., Crosa, J.H. Regulation of plasmid-mediated iron transport and virulence inVibrio anguillarum . Biol Metals 4, 33–35 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01135554
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01135554