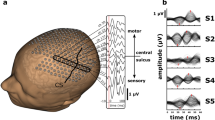
Summary
Thirteen patients with clinically and radiographically defined right middle cerebral artery infarction were studied using EEG, quantitative electroencephalographic (QEEG) spectra, and multi-channel evoked potentials. The purpose of this effort was to develop QEEG rules that related to the patient's neurologic status. Three QEEG relative delta spectral patterns were identified in the right hemisphere which related to neurologic residua. These include limited perisylvian involvement, mixed involvement of perisylvian and extrasylvian regions, and extrasylvian involvement only. While there were parallels between QEEG spectral patterns and auditory, visual and somatosensory evoked potentials, there were modality specific features consistent with functional differences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Electroencephalographic Society Guidelines in EEG-1976. In: D.W. Klass and D.D. Daly (Eds.), Current Practice of Clinical Electroencephalography. Raven Press, New York, 1979: 481–498.
Chapman, S.B., Pool, K.D., Finitzo, T. and Hong, C.T. Comparison of language profiles and electrocortical dysfunction in aphasia. In T.E. Prescott (Ed.), Clinical Aphasiology, Vol 18, College Hill Press, Boston, 1989: 41–59.
Chiappa, K.H., Burke, S.R. and Young, B.R. Results of EEG monitoring during 367 carotid endarterectomies. Use of a dedicated microcomputer. Stroke, 1979, 41: 379–386.
De Weerd, A.W., Veldhuizen, R.J., Veering, M.M., Poortvliet, D.C.J. and Jonkman, E.J. Recovery form cerebral ischaemia. EEG, cerebral blood flow and clinical symptomatology in the first three years after a stroke. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1988, 70: 197–204.
Faught, E., Mitchem, H.L., Conger, K.A., Garcia, J.h. and Halsey, J.H Jr. Patterns of EEG frequency content during experimental transient ischaemia in subhuman primates. Neurological research, 1988, 10: 184–191.
Ferguson, G.A. Statistical analysis in psychology and education. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, 1971.
Finitzo, T., Pool, K.D. and Chapman, S.B. Quantitative electroencephalography and anatamo-clinical principles of aphasia: A validation study. In R.A Zapulla (Ed.), Windows on the brain: Neuropsychology's Technological Frontiers. New York, Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 620: 1991.
Gummow, L.J., Dustman, R.E. and Keaney, R.P. Remote effects of cerebrovascular accidents: Visual evoked potentials and electrophysiological coupling. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1984, 58: 408–417.
Jones, H.R. and Millikan, C.H. Temporal profile (clinical course) of acute carotid system cerebral infarction. Stroke, 1976, 7: 64–71.
Jonkman, E.J., Poortvliet, D.C.J., Veering, M.M. De Weerd, A.W. and Jow, E.R. The use of neurometrics in the study of patients with cerebral ischaemia. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1985, 61: 333–341.
Kayser-Gatchalian, M.C and Neundorfer, B. The prognostic value of EEG in ischaemic cerebral insults. EEG and clin. Neurophys., 1980, 49: 608–617.
Lennox, W.G, Gibbs, F.A. and Gibbs, E.L. The relationship in man of cerebral activity to blood flow and to blood constituents. J. Neurol. Psychiat., 1938, 1: 211–225.
Nuwer, M.R, Jordan, S.E. and Ahn, S.S. Evaluation of stroke using EEG frequency analysis and topographic mapping. Neurology, 1987, 37: 1153–1159.
Papanicolaou, A.C, Levin, H.S and Eisenberg, H.M. Evoked potential correlates of recovery from aphasia after focal left hemisphere injury in adults. Neurosurg., 1984, 14: 412–415.
Pool, K.S, Finitzo, T., Hong, C.T., Rogers, J. and Pickett, R.B. Infarction of the superior temporal gyrus: A description of auditory evoked potential latency and amplitude topology. Ear hearing, 1989, 10: 144–152.
Report of the American Academy of Neurology, Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee. Assessment: EEG brain mapping. Neurology, 1989, 39: 1100–1101.
Roseman, E., Schmidt, R.P. and Foltz, E.L. Serial electroencephalography in vascular lesions of the brain. Neurology, 1952, 2: 311–331.
Sainio, K., Stenberg, D., Kesimaki, I., Muuronen, A. and Kaste, M. Visual and spectral EEG analysis in the evaluation of the outcome in patients with ischemic brain infarction. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1983, 56: 117–124.
Selnes, O.A., Knopman, D.S., Niccum, N., Rubens, A.B. and Larson, D. Computed tomographic scan correlates of auditory comprehension deficits in aphasia: A prospective recovery study. Ann. Neurol., 1983, 13: 558–566.
Sugar, O. and Gerard O.W. Anoxia and brain potentials. Stroke, 1938, 1: 558–572.
Vaughan, H.G., Katzman, R. and Taylor, J. Alterations of visual evoked response in the presence of homonymous visual defects. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1963, 15: 737–746.
Wong, P.K.H., Lombroso, C.T. and Matsumiya, Y. Somatosensory evoked potentials: variability analysis in unilateral hemispheric disease. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol., 1982, 54: 266–274.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Acknowledgements: We wish to thank Dr. Ed Faught for his insights regarding EEG and metabolism and Dr. Frank Morrison for patient referral. Reidun Pickett, R.EEG, R.EP collected the data with her usual meticulous attention to detail. Our doctoral students, Alan Rampy, Susan Reamy Rampy, Beth Wallace and Jackie Clark assisted us in data and manuscript preparation. Partial funding for this research was provided by NIH grant NS 18276-06.
A preliminary report of this study was presented at the 113th American Neurological Association, October 2–5, 1988.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pool, K.D., Finitzo, T. & Hong, CT. Quantitative topographic electrophysiology and functional neurologic status in right middle cerebral artery infarction. Brain Topogr 3, 321–328 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01135441
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01135441