Abstract
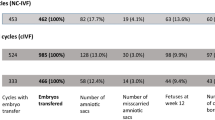
The effect of increasing doses of exogenous gonadotropin stimulation for ovarian hyperstimulation was studied utilizing mouse embryos fertilized in vivo or in vitro. Increased rates of embryo degeneration, fragmentation, and triploidy, increased sister-chomatid exchange, and decreased fertilization rates were observed in high-dose stimulation groups. It appears, therefore, that oocyte and/or embryo quality may be affected by increased amounts of exogeneous gonadotropin stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marrs RP, March CM, Mishell DR Jr: A comparison of clinical and laboratory methods in monitoring human menopausal gonadotropin therapy. Fertil Steril 1980;34:542
Marrs RP, Vargyas JV, March CM: Correlation of ultrasonic and endocrinologic measurements in human menopausal gonadotropin therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1983;145:417
Vargyas JM, Morente C, Shangold G, Marrs RP: The effect of different methods of ovarian stimulation for human in vitro fertilization and embryo replacement. Fertil Steril 1984;42:745
Jones GS: Uptade on in vitro fertilization. Endocrine Rev 1984;5:62
Beaumont HM, Smith AF: Embryonic mortality during the pre- and postimplantation periods of pregnancy in mature mice after superovulation. J Reprod Fertil 1975;3:437
Maudlin I, Fraser IR: The effect of PMSG dose on the incidence of chromosomal anomalies in mouse embryos fertilizedin vitro. J Reprod Fertil 1977;50:275
Fraser LR, Zanellotti HM, Paton GR, Drury LM: Increased incidence of triploidy in embryos derived from mouse eggs fertilizedin vitro. Nature 1976;260:39
Takagi N, Sasaki M: Digynic triploidy after superovulation in mice. Nature 1976;264:278
Fujimoto S, Pahlavan N, Dukelow WR: Chromosome abnormalities in rabbit preimplantation blastocysts induced by superovulation. J Reprod Fertil 1974;40:177
Walton EA, Evans G, Armstrong DT: Ovulation response and fertilization failure in immature rats induced to superovulate. J Reprod Fert 1983;67:91
Gray MH, Chrisman CL: The effect of pregnant mare serum gonadotropin on mouse oocytes as monitored at metaphase II. Theriogenology 1979;13:165
Boue JG, Boue A: Increased frequency of chromosomal anomalies in abortions after induced ovulation. Lancet 1973;1:679
Latt SA: Sister chromatid exchanges, indices of human chromosome damage and repair: Detection by fluorescence and induction by mitomycin C: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1974;71:3162
Perry P, Evans HG: Cytological detection of mutagen-carcinogen exposure by sister chromatid exchange. Nature 1975;258:121
Carrano AV, Thompson LH, Lindl PA, Minkler JL: Sister chromatid exchange as an indicator of mutagenesis. Nature 1978;2781:551
Saito H, Berger T, Mishell DR Jr, Marrs RP: The effect of serum fractions on embryo growth. Fertil Steril 1984;41:761
Tarkowski AK: An air-drying method for chromosome preparation from mouse eggs. Cytogenetics 1966;5:394
Perry P, Wolff S: New Method for differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature 1974;258:156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, F., Marrs, R.P. The effect of pregnant mare serum gonadotropin on mouse embryos fertilized in vivo or in vitro. J Assist Reprod Genet 3, 353–357 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01133247
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01133247