Abstract
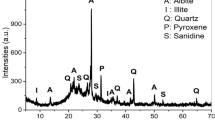
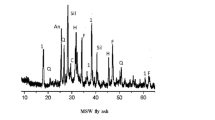
The possibility of production of ceramic floor tile based on kaolin from the Angrenskoe Deposit and flotation waste from a lead-zinc plant (SOF) is studied. The main physicochemical properties of ceramic specimens sintered from mixtures with different contents of kaolin and SOF are described. An optimum temperature regime for the firing process is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. T. Mukhamedzhanova, A. P. Irkakhodzhaeva, and N. A. Sirazhiddinov, “A study of the physicomechanical properties of materials based on kaolin, gliege, and loess melt,”Uzb. Khim. Zh., No. 4, 3 (1982).
V. I. Potapov and Kh. T. Tulyaganov,Mineral Raw Resources of Uzbekistan [in Russian], Fan, Tashkent (1977).
A. G. Nimchik, Kh. L. Usmanov, and N. A. Sirazhiddinov, “Effect of silica-containing flotation waste on the decomposition of calcium carbonate,”Uzb. Khim. Zh., No. 2, 73–75 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 10, pp. 21–23, October, 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhamedzhanova, M.T. Flotation waste from a lead-zinc plant in tile compositions. Glass Ceram 53, 306–308 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01130797
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01130797