Summary
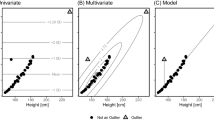
The accuracy and precision of topographic maps depicting scalp potentials and scalp potentials squared have been examined. Electrode placement was that specified by the International 10–20 System and the methods of interpolation bilinear and bicubic splines. The results indicate that, for these interpolation methods, the maximum error expected between the measured scalp quantities and those predicted by interpolation is positively correlated to the root-mean-square value of the measured quantity. Both interpolation methods produce accurate estimates of the interelectrode quantities. Both methods produce precise estimates of the scalp potential in the delta, theta and alpha frequency bands but only poor estimates in the beta band. The precision of the estimates of the scalp potentials squared is poor in all frequency bands. This result indicates that another look at the now common practice of topographically mapping the power-spectral components of the EEG is in order. In general, the bilinear and bicubic spline methods of interpolation perform about equally. This result is used to suggest that because of its additional computational complexity, use of the bicubic method for potential mapping may not be warranted. Advantages of the bicubic method, particularly in radial-current mapping, are however discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashida, H., Tatsuno, J., Okamoto, J. and Maru, E. Field mapping of EEG by unbiased polynomial interpolation. Comput. Biomed. Res., 1984, 17: 267–276.
Buchsbaum, M.S., Rigal, F., Coppola, R., Cappelletti, J., King, C. and Johnson, J. A new system for gray-level surface distribution maps of electrical activity. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1982, 53: 237–242.
Duffy, F.H. Topographic display of evoked potentials: clinical applications of brain electrical activity mapping (BEAM). Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 1982, 388: 183–196.
Duffy, F.H. (Ed.), Topographic Mapping and Brain Electrical Activity. Butterworths, 1986.
Duffy, F.H., Burchfiel, J.L. and Lombroso, C.T. Brain electrical activity mapping (BEAM): a method for extending the clinical utility of EEG and evoked potential data. Ann. Neurol., 1979, 5: 309–321.
Epstein, C.M. and Brickley, G.P. Interelectrode distance and the amplitude of the scalp EEG. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1985, 60: 287–292.
Gevins, A.S. Analysis of the electromagnetic signals of the human brain: milestones, obstacles and goals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 1984, BME-31: 833–850.
Koles, Z.J., Kasmia, A., Paranjape, R.B. and McLean, D.R. Computed radial- current topography of the brain: patterns associated with the normal and abnormal EEG. In press: Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.
Naitoh, P. and Walter, D.O. Simple manual plotting of contours as a means of EEG analysis. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1969, 26: 424–428.
Perrin, F., Bertrand, O. and Pernier, J. Scalp current density mapping: value and estimation from potential data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 1987, BME-34: 283–288.
Perrin, F., Pernier, J., Bertrand, O., Giard, M.H. and Echallier, J.F. Mapping of scalp potentials by surface spline interpolation. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol., 1987, 66: 75–81.
Spath, H. Spline algorithms for curves and surfaces. Utilitas Mathematica Publishing Inc. Winnipeg, 1974.
Ueno, S. and Matsuoka, S. Topographic computer display of abnormal EEG activities in patients with brain lesions. In: Digest of the 11th International Conference on Medical and Bological Engineering, Ottawa, 1976, 218–219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research is supported by the National Health Research and Development Program, Government of Canada and the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koles, Z.J., Paranjape, R.B. Topographic mapping of the EEG: An examination of accuracy and precision. Brain Topogr 1, 87–95 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01129173
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01129173