Abstract
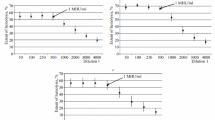
Two mouse monoclonal antibodies against the human complement control protein, Factor H (β1H) , are described. The antibodies are both IgG − γ1 - subclasses and are directed against different epitopes on the human Factor H molecule. One of the antibodies, MRC OX 24, increases the cofactor activity of Factor H in Factor I-mediated cleavage of soluble C3b. The second antibody, MRC OX 23, which has no effect alone, reduces the increase in cofactor activity observed in the presence of the first antibody. However, MRC OX 24 inhibits the binding of125I-labelled Factor H to surface-bound C3b (EAC3b). Again MRC OX 23 alone does not have any effect but decreases the inhibition in125I-Labelled Factor H binding to EAC3b observed with MRC OX 24. These studies show clearly that the interaction of Factor H with soluble C3b is different to its interaction with surface-bound C3b. In an indirect immunoprecipitation system using these monoclonal antibodies, single-chain molecules of 150 000 mol.wt. are specifically precipitated from human serum and also from the sera of other primates - rhesus monkey, cynomolgus monkey, and African green monkey. There was no precipitation from sera of cow, pig, sheep, chick, or rabbit. Using a radioimmunoassay with radiolabelled monoclonal MRC OX 23, the concentration of Factor H in human plasma was determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitter-Suermann D, Burger R & Hadding U (1981) Activation of the alternative pathway of complement: efficient fluid phase amplification by blockade of the regulatory complement protein, γ1H, through sulfated polyanions. Eur. J. Immunol.11, 291.
Cuatrecasas P (1970) Protein purification by affinity chromatography. J. Biol. Chem.245, 3059.
Daha MR & Van Es LA (1982) Isolation, characterization and mechanism of action of rat γ1H. J. Immunol128, 1839.
DiScipio RG & Hugli TE (1982) Circular dichroism of factor H — a regulatory component of the complement system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta709, 58.
Ey PL, Prowse SJ & Jenkin CR (1978) Isolation of pure IgGl, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using Protein A-Sepharose. Imunochemistry15, 429.
Fairbanks G, Steck TL & Wallach DFH (1971) Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erthrocyte membrane. Biochemistry10, 2606.
Fearon DT (1979) Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.76, 5867.
Galfre G, Howe SC, Milstein C, Butcher GW & Howard JC (1977) Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature, 266, 550.
Hong K, Kinoshita T, Dohi Y & Inoue K (1982) Effect of trypsinization of the activity of factor H. J. Immunol.129, 647.
Hsiung L-M, Barclay AN, Brandon MR, Sim E & Porter RR (1982) Purification of human C3bINA by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography. Biochem. J.203, 293.
McMahan MR (1982) Complement components C3, C4 and Bf in 6 nonhuman primate species. Lab. Animal Science32, 57.
Prahl JW & Porter RR (1968) Allotype-related sequence variation of the heavy chain of rabbit IgG. Biochem. J.107, 753.
Reid KBM (1983) Proteins involved in the activation and control of the two pathways of human complement. Biochem. Soc. Trans.11, 1.
Rommel FA, Bendure DW & Kalter SS (1980) Haemolytic complement in nonhuman primates. Lab. Animal Science30, 1026.
Sim E & Sim RB (1981) Binding of fluid phase complement component C3 and C3b to human lymphocytes. Biochem. J.198, 509.
Sim E & Sim RB (1983) Enzymic assay of C3b receptor on intact cells and solubilised cells. Biochem. J.210, 567.
Sim E, Wood AB, Hsiung L-M & Sim RB (1981) Pattern of degradation of human complement fragment C3b. FEBS Lett.132, 55.
Sim RB & DiScipio RG (1982) Purification and structural studies on the complement system control protein γ1H (Factor H). Biochem. J.205, 285.
Sim RB, Twose TM, Paterson DS & Sim E (1981) The covalent binding reaction of complement component C3. Biochem. J.193, 115.
Whaley K & Ruddy S (1976) Modulation of the alternative complement pathway by γ1H globulin. J. Exp. Med.144, 1147.
Whaley K, Widener H & Ruddy S (1978) Modulation of the alternative pathway amplification loop in rheumatic disease, in: Clinical Aspects of the Complement System (Operferkuch W, Rother K & Schulz DR, eds), pp 99–112. G. Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, W. Germany.
World Health Organization (1981) Nomenclature for the components of the alternative pathway of complement. Bull. W.H.O.59, 489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Note: The nomenclature of the complement-system proteins used here is in accordance with the recommendations of the World Health Organization (1981).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sim, E., Palmer, M.S., Puklavec, M. et al. Monoclonal antibodies against the complement control protein Factor H (β1 H). Biosci Rep 3, 1119–1131 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01120205
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01120205