Abstract
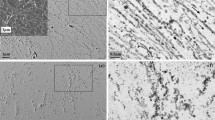
The effects of trace impurities on the adherence of oxides to ultra low carbon steels were investigated. Three steels, of differing chromium, aluminium, silicon, nitrogen and oxygen content, were oxidized at 850 K in 10% CO2-90% N2 gas and then oxidized at 770 K in 10% CO2-10% O2-80% N2 gas. Surface analysers, i.e. a Mössbauer spectrometer, Auger electron spectrometer and/or ion micro analyser, were utilized in the present study because of the very thin layer of oxides formed (1.0 to 2.0 µm). The following results were obtained. The oxide on the Al-containing steel spalled at the outer-inner oxide interface, where aluminium was enriched and many cavities appeared. The inner oxide layer, oxidized by the transport of CO2 or O2 gases along the outer layer grain boundaries or micropores, became thick. This generated a stress at the outer-inner layer interface with the resultant formation of cavities. On the other hand, the oxide on the Cr-containing steel showed good adherence to the metal. The inner layer, enriched with chromium, did not become thick and had no cavities at the interface. The addition of chromium to the Al-containing steel resulted in good oxide adherence because chromium acted as a barrier to the aluminium enrichment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. E. Boggs andR. H. Kachik,J. Electrochem. Soc. 116 (1969) 424.
J. E. Antill, K. A. Peakall andJ. B. Warburton,Corros. Sci. 8 (1968) 689.
G. J. Billigns, M.S. Thesis, “Oxidation and Decarburization Kinetics of Iron-Carbon Alloys in Carbon Dioxide-Carbon Mono-oxide Atmospheres” (McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, 1966).
K. Hauffe, “Oxidation of Metals” (Plenum Press, New York, 1965) p. 102.
R. J. Hussey andM. J. Graham,Corros. Sci. 21 (1981) 255.
P. Berge, C. Ribon andP. Saint Paul,Corrosion 33 (1977) 173.
L. Tomlinson,ibid. 37 (1981) 591.
D. Caplan, R. J. Hussey, G. I. Sproule andM. J. Graham,Corros. Sci. 21 (1981) 689.
D. Caplan andM. Cohen,ibid. 7 (1967) 725.
V. Leroy,Mater. Sci. Eng. 42 (1980) 289.
A. Rahmel andJ. Tobolski,Corros. Sci. 5 (1965) 333.
C. W. Tuck, M. Odgers andK. Sachs,Corros. Sci. 9 (1969) 271.
H. Nakagawa, Y. Ujihira andM. Inaba,Nuct. Instr. Meth. 196 (1982) 573.
B. Tamamushi, “Rikagaku Jiten”, 3rd Edn. (Iwanami Shoten Co., Tokyo, Japan, 1971) p. 515.
T. Honma,Boshyoku Gijutsu 25 (1976) 251.
S. Ohara, “Kinzoku Soshikigaku Gairon” (Asakura Shoten Co., Tokyo, Japan, 1966) p. 144.
O. Kubaschewski andB. E. Hopkins, “Oxidation of Metals and Alloys”, 2nd Edn. (Butterworths, London, 1965) p. 54.
J. E. Harris,Acta Metall. 26 (1978) 1033.
R. H. Bricknell andD. A. Woodford,ibid. 30 (1982) 257.
A. Bruckman,Corros. Sci. 7 (1967) 51.
G. B. Gibbs,Oxillations Met. 7 (1973) 173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inaba, M., Teshima, K., Honma, Y. et al. Effects of trace impurities on the adherence of oxide to ultra low carbon steel. J Mater Sci 21, 917–922 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01117372
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01117372