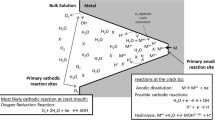
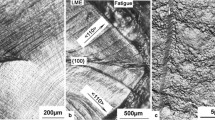
Abstract
Fatigue crack initiation in engineering materials has been the subject of considerable research. Most of these investigations focused on gaseous environment effects, and extensive review articles have appeared in recent times discussing the role of gaseous environments on crack initiation. Because of experimental difficulties, the effect of aqueous environments on mechanisms of fatigue crack initiation has received little attention, despite their unquestionable importance from an engineering standpoint. In this review, several of the fatigue crack initiation models are examined in detail and their anomalies discussed. The physics and micromechanisms of crack initiation during cyclic deformation in aqueous environments which are highly corrosive in nature are examined. The characteristics of the crack initiation process in aqueous environments are critically reviewed in the light of the specific role of several concurrent factors involving the nature of the aqueous medium, corrosion interactions, alloy chemistry, processing treatments, intrinsic microstructural effects and test variables.[/p]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. E. Fine,Met. Trans. 11A (1980) 365.
S. Suresh andR. O. Ritchie,Int. Metals Rev. 29(6) (1984).
N. Thompson andN. J. Wadsworth,Metal Fatigue Adv. Metal Phys. (Phil. Mag. Suppl.) 7 (1958) 72.
T. H. Alden, Report no. 62-RL-2923, General Electric Research Laboratory (1962).
D. H. Avery andW. A. Backofen, “Fracture of Solids”, edited by D. C. Drucker and J. C. Gilman (Interscience, New York, 1963) p. 339.
J. C. Grosskreutz,J. Appl. Phys. 34 (1963) 372.
J. C. Grosskreutz andP. Waldow,Acta Metall. 11 (1963) 717.
K. U. Snowden,ibid. 11 (1963) 675.
C. Laird andG. C. Smith,Philos. Mag. 8 (1963) 1945.
M. J. May andR. W. K. Honeycombe,J. Inst. Metals 92 (1963–64) 41.
J. C. Grosskreutz, Sagamore Conference, Fatigue—An Interdisciplinary Approach, edited by J. J. Burke, N. L. Reed and V. Weis (Syracuse University Press, 1964) p. 27.
B. L. Ritter andN. L. Grant, “Thermal and High Strain Fatigue” (Institute of Metals, London, 1967) p. 80.
J. C. Grosskreutz andG. G. Shaw, “Fracture 1969” Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Fracture, Brighton, 1969 (Chapman and Hall, London, 1969) p. 602.
W. J. Plumbridge andD. A. Ryder,Metall. Rev. 136 (1969) 119.
J. C. Grosskreutz,Phys. Status Solidi (1970).
D. J. Duquette, “Corrosion Fatigue — Chemistry Mechanics and Microstructure”, NACE-2, edited by O. F Devereuxet al. (1972) p. 12.
“Corrosion Fatigue”, University of Newcastle,Met. Sci. 13 (1979).
H. Mughrabi, R. Wang, K. Differt andU. Essmar, “Fatigue Crack Initiation by Cyclic Slip Irreversibility in High Cycle Fatigue”, International Conference in Quantitative Measurement of Fatigue Damage, Dearborn, Michigan (1982).
Z. S. Basinski, R. Pascual andS. J. Basinski,Acta Metall. 31 (1983) 591.
M. E. Fine andR. O. Ritchie, Fatigue and Microstructure, edited by M. Meshii (American Society of Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1979) p. 245.
P. H. Frith,J. Iron Steel Inst. 159 (1948) 385.
W. A. Wood, “Fatigue in Aircraft Structuresrd (Academic, New York, 1956).
H. E.Frankel, A. Bennett andW. A. Pennington,Trans. ASM 52 (1960) 257.
W. A. Wood, S. Coustand andK. R. Sargart,Acta Metall. 11 (1963) 643.
P. R. Swann, F. P. Ford andA. R. C. Westwood, (eds) “Mechanisms of Environment Sensitive Cracking of Materials” (Metals Society, UK, 1977).
H. H. Atkins0n,J. Appl. Phys. 30 (1959) 637.
J. C. Grosskreutz,Phys. Status Solidi 47 (1971) 11.
C. Laird andD. J. Duquette, “Corrosion Fatigue —Chemistry, Mechanisms and Microstructure”, NACE-2, edited by O. F. Devereuxet al. (1971) p. 88.
N. Thompson, N. J. Wadsworth andN. Louat,Philos. Mag. 1 (1956) 113.
J. V. Sharp,ibid. 16 (1963) 77.
P. J. E. Forsyth andC. A. Stubbington,J. Inst. Metals 83 (1954–55) 395.
Idem, ibid. 86 (1956–57) 339.
Idem, ibid. 86 (1957–58) 90.
A. H. Cottrell andD. Hull,Proc. R. Soc. A242 (1957) 211.
W. A. Wood andR. L. Segall,Bull. Inst. Metall. 3 (1957) 160.
J. M. Finney andC. Laird,Philos. Mag. 31 (1975) 339.
D. Hull,J. Inst. Metals 86 (1958) 425.
R. C. Boettner, A. J. McEvily, Jr andY. C. Lin,Philos. Mag. 10 (1964) 95.
D. I. Golland andP. L. James,Acta Metall. 15 (1967) 1889.
N. F. Mott,ibid. 6 (1958) 195.
A. J. McEvily, Jr andE. S. Machlin, “Fracture” (Wiley, 1959) p. 450.
A. J. Kennedy,Philos. Mag. 6 (1961) 49.
P. G. Patridge,Acta Metall. 13 (1965) 517.
D. F. Watt,Philos. Mag. 14 (1966) 87.
P. Neumann,Acta Metall. 17 (1969) 1219.
A. N. May,Nature 185 (1960) 303.
Idem, ibid. 186 (1960) 573.
C. Roberts andA. P. Greenough,Philos. Mag. 12 (1965) 81.
D. F. Watt, J. D. Embury andR. K. Ham,ibid. 17 (1968) 199.
M. P. E. Desvaux,Z. Metallkde 61 (1970) 206.
M. P. E. Desvaux andP. Charsley,Mater. Sci. Engng 4 (1969) 221.
cJ. C. Grosskreutz,J. Electrochem. Soc. 7 (1970) 940.
C. Laird, “Metallurgical Treatises”, edited by J. K. Tien and J. F. Elliott (Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1981).
M. R. Lin, M. E. Fine andT. Mura,Acta Metall. 34 (1986) 619.
J. D. Eshelby,Proc. R. Soc. 241A (1957) 376.
Idem, ibid. 252A (1959) 561.
C. Laird andA. R. Krause, “Inelastic Behavior of Solids”, edited by M. F. Kanninen, W. F. Adler and A. R. Rosenfield, (McGraw Hill, 1970) p. 691.
W. H. Kim andC. Laird,Acta Metall. 26 (1978) 241.
D. S. Kemsley,J. Inst. Metals 85 (1956) 420.
J. Porter andJ. C. Levy,ibid. 89 (1960) 86.
R. C. Boettner, C. Lair andA. J. McEvily, Jr,Trans. ASME 233 (1965) 379.
E. A.Starke, Jr andG. Lutjering, “Fatigue and Microstructure”, edited by M. Meshii (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1979) p. 275.
R. C. Boettner, A. J. McEvily, Jr andY. C. Liu,Philos. Mag. 10 (1984) 95.
T. S. Sudarshan andM. R. Louthan, Jr,Int. Metals Rev. 32 (3) (1987) 121.
B. P. Haigh,J. Inst. Metals 18 (1917) 55.
D. J. McAdam, Jr,Proc. ASTM 26 (1926) 224.
D. Whitman andU. R. Evans,J. Iron Steel Inst. 165 (1950) 79.
D. J. Duquette, “Fatigue and Microstructure”, edited by M. Meshii (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1979) p. 336.
R. Johnson, A. McMinn andB. Tomkins, “Proceedings Third International Conference on Mechanical Behavior of Materials” University of Cambridge (Pergamon, Oxford, 1979) p. 371.
B. D. Westcott,Mech. Eng. 60 (1938) 813.
R. N. Parkins, “Corrosion Fatigue” edited by R. N. Parkins and Y. M. Kolotyokin (Metals Society, UK, 1980) p. 36.
D. J. Duquette andH. H. Uhlig,Trans. ASM 61 (1968) 449.
H. Spann, “Corrosion Fatigue”, NACE-2 (1972) p. 40.
H. Kitagawa, T. Fujita andK. Miyazawa, “Corrosion Fatigue Technology”, ASTM STP 642 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1978) p. 98.
K. Endo, K. Komai andP. Imashiro,Bull. J. SME 20 (1977) 513.
J. Cornet andS. Golan,Corrosion 15 (1959) 262.
G. D. Lehmann,Engineering 122 (1926) 837.
A. M. Binnie,ibid. 128 (1929) 190.
P. Mehdizadeh, R. L. McGlasson andJ. E. Landers,Corrosion 22 (1966) 325.
H. P. Chu andJ. G. Macco, “Corrosion Fatigue Technology”, ASTM STP 642 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1978) p. 223.
M. Levy andJ. L. Morrossi,ibid.“, p. 300.
R. Ebara, T. Kai andK. Inoue,ibid.“, p. 155.
H. Masuda andD. J. Duquette,Met. Trans. 6A (1975) 87.
E. F. Smith III, R. Jacko andD. J. Duquette, in “Effect of Hydrogen on Behavior of Materials”, edited by I. M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson (Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1976) p. 218.
D. J. McAdam Jr andG. W. Geil,Proc. ASTM 41 (1928) 696.
M. T. C. Simnad andU. R. Evans,J. Iron Steel Inst. 156 (1947).
U. R. Evans andM. Simnad,Proc. R. Soc. Ser. 188A (1947) 372.
R. N. Parkins, “Corrosion Fatigue”, Proceedings of the First USSR-UK Seminar on Corrosion Fatigue of Metals, edited by R. N. Parkins and Y. H. Kolotkyku, Lvov, USSR (The Metals Society, London, 1984).
A. J. Gould andU. R. Evans,J. Iron Steel Inst. 156 (1947) 531.
O. F. Deveraeux, J. Dresty andB. Kovacs,Met. Trans. 2A (1971) 3225.
H. N. Hahn andD. J. Duquette,ibid. 10A (1979) 1453.
D. J. Duquette andH. H. Uhlig,Trans. ASM 62 (1969) 839.
D. Whitman andU. R. Evans,J. Iron Steel Inst. 165 (1950) 72.
R. W. Staehle, in “Mechanical Behavior of Materials”, edited by K. J. Miller and R. F. Smith, Vol. I (Pergamon, Oxford, 1980) p. 93.
E. D. Hondros andC. Lea,Nature 289 (1981) 663.
J. C. Scully, “The Fundamentals of Corrosion”, 2nd Edn (Pergamon, Oxford, 1975).
D. P. Harvey II, T. S. Sudarshan, M. R.Louthan Jr andR. E. Swanson,J. Mater. Energy Systems 7 (1985) 269.
P. A. Rebinder andE. K. Venstrem,Z. Fiz. Khim. 26 (1952) 12.
V. Liktman, E. Shchukin and P. A. Rebinder, “Physicochemical Mechanisms of Metals” (Academy of Sciences, Jerusalem, 1963) p. 12.
S. P. Lynch, “Mechanisms of Environment Sensitive Cracking of Materials” (The Metals Society, London, 1977) p. 201.
R. E. Stoltz andR. M. Pelloux,Met. Trans. 3A (1972) 2433.
D. Phillips andN. Thompson,Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 63B (1950) 39.
S. Harper andA. Cottrell,ibid. 63B (1950) 331.
R. Roscoe,Nature 133 (1934) 912.
I. Kramer andL. Demer,Prog. Mater. Sci. 9(3) (1961) 195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivatsan, S., Sudarshan, T.S. Mechanisms of fatigue crack initiation in metals: role of aqueous environments. J Mater Sci 23, 1521–1533 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01115686
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01115686