Abstract
This study examines the validity and accuracy of the commonly used diffuse, specular, and diffuse-specular constant property models for predicting radiant interchange among real surfaces by comparing analytical predictions with experimental data. The materials tested were sandblasted stainless steel, electropolished stainless steel, rough electroplated gold, and smooth electroplated gold. Measurements were made over the temperature range from 310.4 ‡K to 644.0 ‡K. The data indicates that the simple diffuse model yields reasonably accurate radiant heat exchange predictions. The variation in the radiative surface characteristics with direction should be accounted for in some manner, particularly for specular or nearly specularly reflecting surfaces.
Zusammenfassung
Die vorliegende Untersuchung beschÄftigt sich mit dem Gültigkeitsbereich und der Genauigkeit der unter der Annahme diffuser, spiegelnder und diffus-spiegelnder OberflÄchen bei konstanten Zustandsgrö\en im allgemeinen benutzten Modelle zur Berechnung des Strahlungsaustausches zwischen technischen OberflÄchen. Analytisch ermittelte Ergebnisse werden mit experimentellen verglichen. Die untersuchten Materialien waren sandgestrahlter Edelstahl, elektropolierter Edelstahl, rauhes elektroplattiertes Gold und glattes elektroplattiertes Gold. Die Messungen wurden im Temperatur-bereich von 310,4 ‡K bis 644,0 ‡K vorgenommen. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, daβ sich der Wärmeaustausch durch Strahlung mit Hilfe des einfachen Modells diffuser Reflektion verhÄltnismÄ\ig genau beschreiben lÄ\t. Der Einflu\ der Richtungs-charakteristiken der strahlenden OberflÄche sollte insbesondere für spiegelnde oder fast spiegelnde reflektierende OberflÄchen mit in Betracht gezogen werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area
- E Ai-Aj :
-
Exchange factor
- F Ai-Aj :
-
Configuration factor
- G :
-
Irradiation (incident radiant energy flux)
- G* :
-
Dimensionless irradiation,G/ε h σT 4h
- H :
-
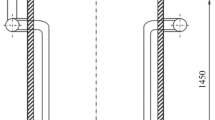
Plate separation distance, Fig. 1
- J :
-
Radiosity (diffusely leaving radiant energy flux)
- L :
-
Plate width, Fig. 1
- q :
-
Local heat flux
- T :
-
Temperature
- x :
-
Coordinate distance, Fig. 1
- y :
-
Coordinate distance, Fig. 1
- z :
-
Coordinate distance, Fig. 1
- α :
-
Absorptance
- γ :
-
Plate separation to width ratio,H/L
- ε :
-
Emittance
- ζ:
-
⧀mensionless coordinate,z/H
- η :
-
Dimensionless coordinate,y/L
- θ′ :
-
Polar angle of incidence
- λ :
-
Wavelength
- λ m :
-
Wavelength of the mean blackbody radiant energy
- λ max :
-
Wavelength of the maximum blackbody radiant energy
- ξ :
-
Dimensionless coordinate,x/L
- ϱ :
-
Reflectance
- ϱ (θ′):
-
Reflectance of an optically smooth surface predicted from Fresnel's equations
- σ :
-
Stefan Boltzmann constant
- σ o :
-
Optical rms roughness
- σm :
-
Mechanical rms roughness
- Φ′ :
-
Azimuthal angle of incidence
- c:
-
Refers to cold surface
- h:
-
Refers to hot surface
References
Sparrow, E. M., andR. D. Cess: Radiation Heat Transfer. Belmont, Calif.: Brooks/Cole Publishing Company 1966.
Schornhorst, J. R.: An Analytical and Experimental Investigation of Radiant Heat Exchange Between Simply Arranged Surfaces. Ph. D. Thesis, Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana (1967):
Schornhorst, J. R., andR. Viskanta: Trans. ASME, Series C, J. Heat Transfer 90 (1968) pp. 429/436.
Engstrom, P. M.: An Investigation of Radiant Heat Exchange Between Plane Surfaces. M. S. Thesis, Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana (1968).
Sparrow, E. M., E. R. G. Eckert andV. K. Jonnson: Trans. ASME, Series C, J. Heat Transfer 84 (1962) pp. 294/300.
Hilderband, F. B.: Methods of Applied Mathematics. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall 1952.
Wade, W. R., and W. S.Slemp: Measurements of Total Emittance of Several Refractory Oxides, Cements, and Ceramics for Temperatures from 600 ‡R to 2000 ‡R. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Technical Note D-998 (1961).
Edwards, D. K., andI. Catton: Radiation Characteristics of Rough. Oxidized Metals, in: Advances in Thermophysical Properties at Extreme Temperatures and Pressures, pp. 189/199. New York: ASME 1965.
Love, T. J., and R. E.Francis: Experimental Determination of Reflectance Function for Type 302 Stainless Steel. AIAA Paper No. 67–321 (1967).
Took, J. S.: Radiant Heat Transfer Analysis Among Surfaces Having Direction Dependent Properties by the Monte Carlo Method. M. S. Thesis, Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana (1967)
Toor, S. J., andR. Viskanta: Intern. J. Heat Mass Transfer 11 (1968) pp. 883/897.
Wiebelt, J. A.: Engineering Radiation Heat Transfer. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston Publ. 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engstrom, P.M., Viskanta, R. & Toor, J.S. Study of radiation interchange in an enclosure consisting of plane isothermal and adiabatic surfaces. Warme- und Stoffubertragung 3, 63–69 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01108026
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01108026