Abstract
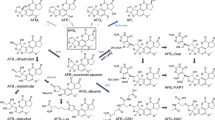
We studied thein vitro activation of aflatoxin B1 (B1) by microsomes and its inactivation by the cytosol of various quail and hamster organs, using B1-DNA binding as an index. The microsomal activity of the liver to bind B1 to DNA was not largely different between the two species and was higher than that of the other organs examined in either species. The microsomal activity of the kidney and lung was very low in the quail compared with the hamster, indicating the very small contribution of the lung and kidney microsomes to the activation of B1 in birds. Only the hamster liver cytosol showed strong inhibition of microsome-mediated B1-DNA binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garner RC. Microsome-dependent binding of aflatoxin B1 to DNA, RNA, polyribonucleotides and proteinin vitro. Chemico-biological Interactions 1973; 6: 125–129.
Swenson DH, Miller JA, Miller EC. 2,3-Dihydro-2,3-dihydroxy-aflatoxin B1: An acid hydrosis product of an RNA-aflatoxin B1 adduct formed by hamster and rat liver microsomesin vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1973; 53: 1260–1267.
Busby WF, Wogan GN. Aflatoxin. In Searle CE (ed), Chemical Carcinogens, 2nd edn. Washington DC: American Chemical Society, 1984; 945–1136.
Croy RG, Wogan GN. Quantitative comparison of covalent aflatoxin-DNA adducts formed in rat and mouse livers and kidneys. J Natl Cancer Inst 1981; 66: 761–768.
Daniels JM, Liu L, Stewart RK, Massey TE. Biotransformation of aflatoxin B1 in rabbit lung and liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 1990; 11: 823–827.
Liu L, Massey TE. Bioactivation of aflatoxins B1 by lipoxygenase, prostaglandin H synthase and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase in guinea-pig tissues. Carcinogenesis 1992; 13: 533–539.
Degen GH, Neumann H-G. Differences in aflatoxin B1-susceptibility of rat and mouse are correlated with the capabilityin vitro to inactivate aflatoxin B1-oxide. Carcinogenesis 1981; 2: 299–306.
O'Brien K, Moss E, Judah D, Neal G. Metabolic basis of the species difference to aflatoxin B1 induced hepatotoxicity. Biochem Biophysic Res Comm. 1983; 114: 813–821.
Lotlikar PD, Jhee EC, Insetta SM, Clearfield MS. Modulation of microsome-mediated aflatoxin B1 binding to exogenous and endogenous DNA by cytosolic glutathione S-transferase in rat and hamster livers. Carcinogenesis 1984; 5: 269–276.
Ramsdell HS, Eaton D. Species susceptibility to aflatoxin B1 carcinogenesis: Comparative kinetics of microsomal biotransformation. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 615–620.
Tarloff JB, Goldstein RS, Sozio RS, Hook JB. Hepatic and renal conjugation (phase II) enzyme activities in young adult, middle-aged, and senescent male Sprague-Dawley rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1991; 197: 297–303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kono, M., Kumagai, S. In vitro microsome-mediated aflatoxin B1-DNA binding and its inhibition by cytosol of various organs of the hamster and quail. Mycopathologia 132, 117–119 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103784
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103784