Abstract
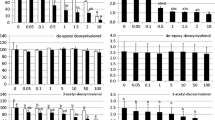
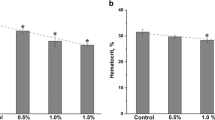
Peripheral blood lymphocytes were isolated from broiler chicks that had ingested feed amended with autoclavedFusarium proliferatum culture material containing fumonisin B1 (FB1), fumonisin B2 (FB2) and moniliformin. Lymphocyte viability was determined for birds that were placed on amended rations at day 1 or day 7 of age at three different levels of mycotoxins, ranging from 61–546 ppm FB1, 14–94 ppm FB2 and 66–367 ppm moniliformin. Reduction of the tetrazolium salt, MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide], to yield MTT formazan, based on mitochondrial metabolic activity, was used to assess cell viability. Lymphocyte cytotoxic effects were observed in all treatment groups on day 21; chicks that started on amended feed at day 1 of age were affected more than those that started at day 7. Abnormal erythrocytes resembling early stages of erythroblasts were observed in peripheral blood from test chicks. Abnormally shaped red cells (poikilocytes) having a spindle-shape with one or both ends pointed were present. Some red cells appeared to be undergoing mitosis. Both reduced lymphocyte viability and abnormal erythrogenesis occurred in chicks given feed amended withF. proliferatum culture material containing FB1, FB2 and moniliformin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marasas WFO, Nelson PE, Toussoun TA. ToxigenicFusarium species: Identity and mycotoxicology. University Park, PA: The Pennsylvania State University Press, 1984.
Ross PF, Nelson PE, Richard JL, Osweiler GD, Rice LG, Plattner RD, Wilson TM. Production of fumonisins byFusarium moniliforme andFusarium proliferatum isolates associated with equine leukoencephalomalacia and a pulmonary edema syndrome in swine. Appl Environ Microbiol 1990; 56: 3225–26.
Thiel PG, Marasas WFO, Sydenham EW, Shephard GS, Gelderblom WCA, Nieuwenhuis JJ. Survey of fumonisin production byFusarium species. Appl Environ Microbiol 1991; 57: 1089–93.
Nelson PE, Plattner RD, Shackelford DD, Desjardins AE. Fumonisin B1 production byFusarium species other thanF. moniliforme in sectionLiseola and by some related species. Appl Environ Microbiol 1992; 58: 984–89.
Ross PF, Rice LG, Reagor JC, Osweiler GD, Wilson TM, Nelson HA, Owens DL, Plattner RD, Harlin KA, Richard JL, Colvin BM, Banton MI. Fumonisin B1 concentrations in feeds from 45 confirmed equine leukoencephalomalacia cases. J Vet Diagn Invest 1991; 3: 238–41.
Ross PF, Rice LG, Plattner RD, Osweiler GD, Wilson TM, Owens DL, Nelson HA, Richard JL. Concentrations of fumonisin B1 in feed associated with animal health problems. Mycopathologia 1991; 114: 129–35.
Thiel PG, Shephard GS, Sydenham EW, Marasas WFO, Nelson PE, Wilson TM. Levels of fumonisins B1 and B2 in feeds associated with confirmed cases of equine leukoencephalomalacia. J Agric Food Chem 1991; 39: 109–11.
Gelderblom WCA, Kriek NPJ, Marasas WFO, Thiel PG. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of theFusarium moniliforme metabolite, fumonisin B1, in rats. Carcinogenesis 1991; 12: 1247–51.
Sydenham EW, Gelderblom WCA, Thiel PG, Marasas WFO. Evidence for the natural occurrence of fumonisin B1, a mycotoxin produced byFusarium moniliforme, in corn. J Agric Food Chem 1990; 38: 285–90.
Gelderblom WCA, Jaskiewicz K, Marasas WFO, Thiel PG, Horak RM, Vleggaar R, Kriek NPJ. Fumonisinsnovel mycotoxins with cancer-promoting activity produced byFusarium moniliforme. Appl Environ Microbiol 1988; 54: 1806–11.
Bezuidenhout SC, Gelderblom WCA, Gorst-Allman CP, Horak RM, Marasas WFO, Spiteller G, Vleggaar R. Structure elucidation of the fumonisins, mycotoxins fromFusarium moniliforme J Chem Soc Chem Commun 1988; 743–45.
Brown TP, Brunet PY, Odor EM, Murphy DW, Mallinson ET. Microscopic lesions of naturally occurring and experimental ‘spiking mortality’ in young broiler chickens. Avian Dis 1991; 35: 481–486.
Marasas WFO, Thiel PG, Rabie CJ. Moniliformin production inFusarium sectionLiseola. Mycologia 1986; 78: 242–47.
Engelhardt JA, Carlton WW, Tuite JF. Toxicity ofFusarium moniliforme var.subglutinans for chicks, ducklings, and turkey poults. Avian Dis 1989; 33: 357–60.
Javed T, Bennett GA, Richard JL, Dombrink-Kurtzman MA, Côté LM, Buck WB. Mortality in broiler chicks on feed amended withFusarium proliferatum culture material or with purified fumonisin B1 and moniliformin. Mycopathologia 1993; 123: 171–184.
Slater TF, Sawyer B, Strauli U. Studies on succinatetetrazolium reductase systems. III. Points of coupling of four different tetrazolium salts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1963; 77: 383–93.
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Meth 1983; 65: 55–63.
Holt PS, Buckley S, DeLoach JR. Detection of the lethal effects of T-2 mycotoxin on cells using a rapid colorimetric viability assay. Toxicol Lett 1987; 39: 301–12.
Reubel GH, Gareis M, Amselgruber WM. Cytotoxicity evaluation of mycotoxins by an MTT-bioassay. Mycotoxin Res 1987; 3: 85–96.
Visconti A, Minervini F, Lucivero G, Gambatesa V. Cytotoxic and immunotoxic effects ofFusarium mycotoxins using a rapid colorimetric bioassay. Mycopathologia 1991; 113: 181–86.
Shier WT, Abbas HK, Mirocha CJ. Toxicity of the mycotoxins fumonisins B1 and B2 andAlternaria alternata f. sp.Lycopersici toxin (AAL) in cultured mammalian cells. Mycopathologia 1991; 116: 97–104.
Lucas AM, Jamroz C. Atlas of Avian Hematology, Washington, DC: US Department of Agriculture, 1961 (Agriculture Monograph 25).
Dombrink-Kurtzman MA, Bennett GA, Richard JL. Avian lymphocytes as in vitro models to predict fumonisin cytotoxicity. FASEB J 1992; 6: A2007.
Wang E, Norred WP, Bacon CW, Riley RT, Merrill AH, Jr. Inhibition of sphingolipid biosynthesis by fumonisins. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 14486–90.
Klein J. Immunology: The science of self-nonself discrimination. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dombrink-Kurtzman, M.A., Javed, T., Bennett, G.A. et al. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity and erythrocytic abnormalities induced in broiler chicks by fumonisins B1 and B2 and moniliformin fromFusarium proliferatum . Mycopathologia 124, 47–54 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103056
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103056