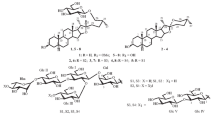
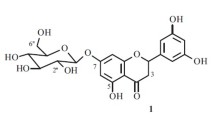
Abstract
The unripe fruits ofSolanum pseudomeum were found to contain two glyco-alkaloids, identified as solamargine and solasonine. The glyco-alkaloids fraction afforded after hydrolysis one steroidal alkaloid, identified as solasodine. The neutral glycoside fraction, gave after hydrolysis a steroid sapogenin: chlorogenin. Three phytosterols were isolated from the unsaponifiable matter of the lipid fraction, identified as β-sitosterol, campesterol and stigmasterol.
Zusammenfassung
Man fand, daß die unreifen Früchte vonSolanum pseudomeum zwei Glyco-Alkaloide, nämlich Solamargin und Solasonin, enthalten. Die Fraktion der Glyco-Alkaloide ergab nach der Hydrolyse ein Steroid-Alkaloid, dieses wurde als Solasodin identifiziert. Die neutrale Glykosid-Fraktion ergab nach der Hydrolyse das Steroid-Sapogenin Chlorogenin. Die Auftrennung des unverseifbaren Anteils der Lipid-Fraktion ergab drei Phytosterine, die als β-Sitosterin, Campesterin und Stigmasterin identifiziert wurden.
Résumé
Les fruits verts (non mûrs) duSolanum pseudomeum, contiennent deux glycoalcaloides, identifiés comme suit: solamargine et solasonine. Un alcaloide stéroidique a été obtenu par hydrolyse de la fraction glyco-alcaloides; et identifié comme suit: solasodine. La fraction glycosidique neutre, a donné après hydrolyse un sapogenin stéroidique chlorogenin. Trois phytosterols ont été isolés de la masse non-saponifiable de la fraction lipide et identifiés comme suit; β-sitosterol, campesterol et stigmasterol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boit, H. G. (1961). Ergebnisse der Alkaloid-Chemie bis 1960. Academie, Verlag-Berlin.
Copius-Peereboom, J. W. (1964).Anal. Chem. 205:325.
Cromwell, B. T. cited in Peach, K. & Tracy, M. V. (1955). Modern Methods of Plant Analysis, vgl. 4, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg.
Fayez, M. B. E. & Saleh, A. A. (1967a).Planta Medica 15:430.
Fayez, M. B. E. & Saleh, A. A. (1967b).Phytochemistry, 6:433.
Guseva, A. R. (1965).Biokimiya 30:260.
Maiti, P. C., Mookerjea, S. & Mathew, R. (1965).J. Pharm, Sci. 54:1828.
Rizk, A. M. & Abou-Zied, E. N. (1970).Planta Medica 18:4.
Saini, A. D., Mukherjee, M. & Biswas, R. C. (1965).Indian J. Plant. Physiology, 8:103.
Taylor, D. A. H. (1958).J. Chem. Soc. 4216.
Wall, M. E. & Wallens, H. A. (1955).J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77:5661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, M., Ahmed, S.S. The steroidal constituents of Solanum pseudomeum L.. Plant Food Hum Nutr 22, 133–136 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01100680
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01100680