Summary
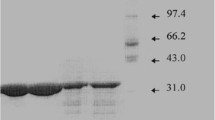
A thermostable protease fromThermoactinomyces thalpophilus was purified to give a single protein band on disc PAGE with a molecular size of 55000 Da. Optimal proteolytic activity of the purified protease was at pH 6.0 and 70°C. The enzyme was maximally stable between pH 5.0 and 8.0 and retained 62% of its original activity at 70°C after 30 min. Temperature stability was not improved in the presence of Ca2+ (1mm). Enzyme activity was inhibited by AG+, Hg2+, Ba2+ and Co2+, partially inhibited byo-phenanthroline but not by diisopropylfluorophosphate (5mm).
Résumé
Une protéase thermostable deThermoactinomyces thalpophilus a été purifiée jusqu'à donner une bande protéique unique sur un disque PAGE avec un poids moléculaire de 55000 daltons. L'activé protéolytique optimum de la protéase purifiée se situe à pH 6.0 at à 70°C. L'enzyme présente son maximum de stabilité entre pH 5.0 et 8.0 et conserve 62% de son activité originelle après 30 min à 70°C. La stabilité à la température n'est pas améliorée en présence de Ca2+ 1mm. L'activité enzymatique est inhibée par Ag+, Hg2+, Ba2+ et Co2+. Elle est partiellement inhibée par l'o-phénanthroline mais elle n'est pas inhibée par le di-iso-propylfluorophosphate 5mm.
Resumen
Se purificó una proteína termoestable deThermoactinomyces thalpophilus que dió una sola banda proteica al someterla a una electroforesis en columna de poliacrilamida (PAGE) y un tamaño molecular de 55.000 Da. La actividad proteolítica de la proteína purificada era óptima a pH 6.0 y 70°C. El enzima tenía máxima estabilidad entre pH 5.0 y 8.0 y retuvo un 62% de su actividad original despues de 30 min at 70°C. La estabilidad térmica no mejoró en presencia de Ca2+ (1mm). La actividad enzimática fue Inhibida por Ag+
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, P. 1964 Estimation of the molecular weight of proteins by Sephadex gel filtration.Biochemical Journal 91, 222–233.
Ansari, M. &Stevens, L. 1983 Purification and properties of two neutral proteinases fromAspergillus nidulans.Journal of General Microbiology 129, 1637–1644.
Cross, T. 1981 The monosporic actinomycetes. InProcaryotes. A Handbook on Habitat, Isolation and Identification of Bacteria. Vol. II. eds. Starr, M.P. Stolp, H., Truper, H.G., Balows, A. and Schlegel, H.G. pp. 2091–2102. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Davis, P.J. 1964 Disc electrophoresis. III. Method and application to human serum proteins:Annals of New York Academy of Science 121, 404–427.
Desai, A.J. &Dhala, S.A. 1969 Purification and properties of proteolytic enzymes from thermophilic actinomycetes.Journal of Bacteriology 100, 149–155.
Kleine, R. &Keitmann, U. 1982 Separation and comparative characterization of the cationic protease and anionic protease from the culture medium ofThermoactinomyces vulgaris.Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift Physiologische-Chemisches 363, 843–853.
Loffler, A. 1986 Proteolytic enzymes: sources and applications.Food Technology 40, 63–70.
Makino, K., Ogaki, J., Nishihara, T., Khidawa, T. &Kanato, M. 1983 Studies on protease from marine bacteria. 2. Properties of extracellular protease from marinePseudomonas sp. 145–2.Microbios 36, 7–20.
Morihara, K., Ota, T. Tsuzuki, H. 1967 Multiple proteolytic enzymes ofStreptomyces fradiae. Production, isolation and preliminary characterization.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 139, 382–397.
Obi, S.K.C. &Odibo, F.J.C. 1984 Some properties of a highly thermostable α-amylase from aThermoactinomyces sp.Canadian Journal of Microbiology 30, 780–785.
Sidler, W. &Zuber, H. 1980 Isolation procedures for thermostable neutral proteinase produced byBacillus stearothermophilus.European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 10, 197–209.
Upton, M.E. &Fogarty, W.M. 1977 Production and purification of thermostable amylase and protease ofThermomonospora viridis.Applied and Environmental Microbiology 33, 59–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odibo, F.J.C., Obi, S.K.C. Purification and some properties of a thermostable protease ofThermoactinomyces thalpophilus . Mircen Journal 4, 327–332 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01096137
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01096137