Abstract
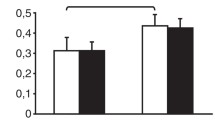
We studied platelet number and function in nine anaemic children with end-stage renal disease during a clinical trial with recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO). All the children showed a correction in both haematocrit and haemoglobin levels which was followed by a significant reduction in bleeding time. We also observed a significant increasse in platelet count after both 6 and 12 weeks of therapy; at the same time mean platelet volume decreased and a normal platelet mass was maintained. The mean baseline platelet aggregation response to ADP was normal, but was decreased to collagen (P<0.05 vs normal control). Platelet production of thromboxane B2 in serum was also lower than normal controls. After correction of anaemia with rHu-EPO, platelet aggregation improved in patients with a decreased baseline response, and mean levels of thromboxane B2 became normal. In conclusion, the treatment with rHu-EPO improved haemostatic balance not only by correcting anaemia, but also by increasing platelet count and function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eschbach JW (1989) The anaemia of chronic renal failure, pathophysilogy and the effects of recombinant human erythropoietin. Kidney Int 35: 134–148
Eschbach JW, Egrie JG, Dowing MR, Browne JK, Adamson JW (1987) Correction of anaemia of end-stage renal disease with recombinant human erythropoietin: results of combined stage I and II clinical trial. N Engl J Med 316: 73–78
Livio M, Gotti E, Marchesi D, Mecca G, Remuzzi G, De Gaetano G (1982) Uremic bleeding: role of anaemia and beneficial effect of red-cell transfusions. Lancet II: 1013–1015
Moia M, Vizzotto L, Cattaneo M, Mannucci PM, Casati S, Ponticelli C (1987) Improvement in the haemosstatic defect of uremia after treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin in anaemic patients on hemodialysis. Lancet I: 73–78
Steiner RW, Coggins C, Carvalho ACA (1979) Bleeding time in uremia: a useful test to assess clinical bleeeding. Am J Hematol 17: 107–117
Woolley AC (1987) Platelet dysfunction in uremia. Kidney 19: 15–19
Remuzzi G (1988) Bleeding in renal failure. Lancet I: 1205–1208
Di Minno S, Martinez J, McKean ML, De La Rosa J, Burke JF, Murphy S (1985) Platelet dysfunction in uremia. Multifaceted defect partially corrected by dialysis. Am J Med 79: 552–559
Fabris F, Randi ML, Sbrojavacca R, Casonato A, Girolami A (1981) The possible value of platelet aggregation studies in patients with increased platelet number. Blut 43: 279–285
Luzzatto G, Fabris F, Mazzucato M, Girolami A (1985) PF4 versus BTG as evidence for platelet activation in myeloproliferative disorders. Scand J Haematol 35: 299–304
Luzzato G, De Franchis G, Fabris F, Gerunda GE, Girolami A (1985) Increased proportion of giant platelets and platelet distribution width are better indicators of altered platelet homeostasis than mean platelet volume in liver cirrhosis. Folia Haematol (Leipz) 5: 719–726
Remuzzi G, Benigni A, Dodesini P, Patrono C (1983) Reduced platelet thromboxane formation in uremia. Evidence for a functional cyclooxygenase defect. J Clin Invest 71: 762–768
Remuzzi G, Cavenaghi AE, Mecca G, Donati MB, De Gaetano G (1977) Prostacyclin-like activity and bleeding in renal failure. Lancet II: 1195–1197
Winearls CG, Oliver DO, Pippard MJ, Cotes PM (1986) Effects of human erythropoietin derived from recombinant DNA on the anemia of the patients maintained by chronic haemodialysis. Lancet I: 1176–1178
Rabiner SF (1972) The effect of dialysis on platelet function of Patients with renal failere. Ann N Y Acad Sci 201: 234–242
van Geet C, Hauglustaine D, Verresen L, Vanrusselt M, Vermylen J (1989) Hemostatic effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in chronic haemodialysis patients. Thromb Haemost 61: 117–121
Fernandez F, Goudable C, Sie P, Ton-That H, Durand D, Sue JM, Boneu B (1985) Low haematocrit and prolonged bleeding time in uremic patients: effect of red cell transfusions. Br J Haematol 59: 139–148
Bloom A, Greaves M, Preston FE, Brown B (1986) Evidence against a platelet cyclooxygenase defect in uremic subjects on chronic haemodialysis. Br J Haematol 62: 143–149
Hill J, Levin J (1989) Regulators of thrombopoiesis: their biochemistry and physiology. Blood Cells 15: 141–166
Thompson CB, Jakubowski JA (1988) The pathophysiology and clinical relevance of platelet heterogeneity. Blood 72: 1–8
Ishibashi T, Koziol JA, Burstein SA (1987) Human recombinant erythropoietin promotes differentiation of murine megakryocytes in vitro. J Clin Invest 79: 286–289
Bommer J, Muller-Buhl E, Ritz E, Eifert J (1987) Recombinant human erythropoietin in anaemic patients in haemodialysis. Lancet I: 392
Thompson CB, Jakubowski JA, Quin PG, Deykin D, Valeri CR (1984) Platelet size and age determine platelet function independently. Blood 63: 1372–1375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabris, F., Cordiano, I., Randi, M.L. et al. Effect of human recombinant erythropoietin on bleeding time, platelet number and function in children with end-stage renal disease maintained by haemodialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 5, 225–228 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01095958
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01095958