Summary
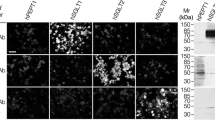
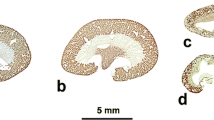
Histochemical and immunohistochemical staining techniques have been used to investigate the localization of hexokinase isoenzymes within rat kidney tissue. Hexokinase type I was shown to be the major isoenzyme present. It was located mainly in the thin and thick limbs of loops of Henle, in distal tubules and in the transitional or dark cells in the initial portions of collecting ducts. The smooth muscle cells of arteries and arterioles, peripheral nerves and the transitional epithelial cells lining the renal pyramid also contained large amounts of the isoenzyme while smaller quantities were present in glomeruli and in collecting tubules near the papillary tip. The distribution pattern obtained in tubular epithelia agrees well with that demonstrated in earlier microdissection studies. It is also consistent with the suggestion that glycolysis provides the majority of the energy fuelling the sodium transport mechanisms which form such an essential feature of the countercurrent urine concentration system present within the renal medulla.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. B., Brocklebank, J. L. &Walker, D. G. (1980) Apparent ‘glucokinase’ activity in non-hepatic tissues due toN-acetyl-d-glucosamine kinase.Biochim. biophys. Acta 614, 357–66.
Allen, M. B. &Walker, D. G. (1980) The isolation and preliminary characterization ofN-acetyl-d-glucosamine kinase from rat kidney and liver.Biochem. J. 185, 565–75.
Ballatori, N. &Cohen, J. J. (1981) Intracellular distribution of hexokinase in the tissue zones of rat kidney.Biochim. biophys. Acta. 657, 448–56.
Boorsma, D. M. &Streefkerk, J. G. (1979) Periodate or glutaraldehyde for preparing peroxidase conjugates?J. Immunol. Methods 30, 245–55.
Brannan, T. S., Corder, C. N. &Rizk, M. (1975) Histochemical measurements of rat kidney hexokinase.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 148, 714–9.
Briggs, F. N., Chernick, S. &Chaikoff, I. L. (1949) The metabolism of arterial tissue. 1. Respiration of rat thoracic aorta.J. biol. Chem. 179, 103–11.
Brown, G. G. (1978)An Introduction to Histotechnology, p. 344. New York, London: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Cohen, J. J. (1979) Is the function of the renal papilla coupled exclusively to an anaerobic pattern of metabolism?Am. J. Physiol. 236, F423-F433.
Colowick, S. P. (1973) The hexokinases. InThe Enzymes (edited byBoyer, P. D.), Vol. 9, Part B, 3rd edn. pp. 1–48. New York: Academic Press.
Copenhaver, W. M. Kelly, D. E. &Wood, R. L. (1978)Bailey's Textbook of Histology, 7th edn. Baltimore: Waverley Press.
Grossbard, L. &Schimke, R. T. (1966) Multiple hexokinases of rat tissues. Puritication and comparison of soluble forms.J. biol. Chem. 241, 3546–60.
Guder, W. G. &Schmidt, U. (1976) Substrate and oxygen dependence of renal metabolism.Kidney. Int. 10, S32-S38.
Gyorgy, P., Keller, W. &Brehme, T. (1928) Nierenstoff wechsel und Nierentwicklung.Biochem. Z. 200, 356–66.
Kao-Jen, J. &Wilson, J. E. (1980) Localisation of hexokinase in neural tissue. Electron microscopic studies of rat cerebellar cortex.J. Neurochemistry 35, 667–78.
Katzen, H. M. &Schimke, R. T. (1965) Multiple forms of hexokinase in the rat: tissue distribution, age dependency and properties.Proc. Soc. Natn. Acad. Sci. USA 54, 1218–25.
Katzen, H. M., Soderman, D. D. &Cirillo, V. J. (1968) Tissue distribution and physiological significance of multiple forms of hexokinase.Ann. NY Acad. Sci 151, 351–8.
Kirk, J. E., Effersoe, P. G. &Chiang, S. P. (1954) The rate of respiration and glycolysis by human and dog aortic tissue.J. Gerontol. 9, 10–35.
Kosan, R. L. &Burton, A. (1966) Oxygen consumption of arterial smooth muscle as a function of active tone and passive stretch.Circ. Res. 27, 79–88.
Lawrence, G. M. & Trayer, I. P. (1984) The use of immunological methods to investigate evolutionary relationships between hexokinase isoenzymes.Biochem. Soc. Trans. (in press).
Lawrence, G. M., Walker, D. G. &Trayer, I. P. (1983) Antigenic cross-reactivities between mammalian hexokinases.Biochim. biophys. Acta 743, 219–25.
Lee, J. B. &Vater, H. M. (1969) Effect of oxygen on glucose metabolism in rabbit kidney cortex and medulla.Am. J. Physiol. 217, 1464–71.
Lee, J. B., Vance, V. K. &Cahill, G. F. (1962) Metabolism of C14-labelled substrates by rabbit kidney cortex and medulla.Am. J. Physiol. 203, 27–36.
Lowry, O. H., Passonneau, J. V., Hasselberger, F. X. &Schulz, D. W. (1964) Effect of ischemia on known substrates and co-factors of the glycolytic pathway in brain.J. Biol. Chem. 239, 18–30.
Lundholme, L., Andersson, R. G. G., Arnqvist, H. J. &Mohme-Lundholm, E. (1977) Glycolysis and glycogenolysis in smooth muscle. InThe Biochemistry of Smooth Muscle (edited byStephens, N. L.), pp. 159–207. Baltimore, London, Tokyo: University Park Press.
Sacktor, B., Wilson, J. E. &Tiekert, C. G. (1966) Regulation of glycolysis in brain,in situ, during convulsions.J. biol. Chem. 241, 5071–5.
Schmidt, U., Marosvari, I. &Dubach, U. C. (1975) Renal metabolism of glucose: anatomical sites of hexokinase activity in rat nephron.FEBS Lett. 53, 26–8.
Vandewalle, A., Wirthensohn, G., Heidrich, H.-G. &Guder, W. G. (1981) Distribution of hexokinase and phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase along the rabbit nephron.Am. J. Physiol. 240, F492-F500.
Waldman, R. H. &Burch, H. B. (1963) A rapid method for the study of enzyme distribution in rat kidney.Am. J. Physiol. 204, 749–52.
Widemann, M. J. &Krebs, H. A. (1969) The fuel of respiration of rat kidney cortex.Biochem. J. 112, 149–66.
Weinstein, S. W. &Szyjewicz, J. (1974) Individual nephron function and renal oxygen consumption in the rat.Am. J. Physiol. 227, 171–7.
Wilkin, G. P. &Wilson, J. E. (1977) Localisation of hexokinase in neural tissue: light microscopic studies with immunofluoroescence and histochemical procedures.J. Neurochemistry 29, 1039–51.
Wilson, J. E. (1980) Brain hexokinase: the prototype ambiquitous enzyme. InCurrent Topics in Cellular Regulation, Vol. 16 (edited byHorecker, B. L. andStadtman, E. R.), pp. 1–54. New York: Academic Press.
Wilson, M. B. &Nakane, P. K. (1978) InImmunofluorescence and Related Staining Techniques (edited byKnapp, W., Holubar, K. andWick, G.), p. 215. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North Holland Biochemical Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawrence, G.M., Trayer, I.P. Histochemical and immunohistochemical localization of hexokinase isoenzymes in rat kidney. Histochem J 16, 697–708 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01095276
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01095276