Abstract
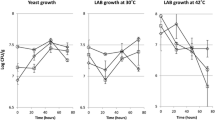
Natural as well as single, mixed and sequential pure cutlure (S. diastaticus, S. cerevisiae, L. brevis andL. fermentum) fermentations of pearl millet flour for 72h lowered pH and raised titratable acidity. The fermentation either decreased or did not change the protein content of pearl millet flour. Natural fermentation increased whereas pure culture fermentation decreased the fat content. Ash content did not change. Natural fermentation at 20°C and 25°C increased whereas at 30°C it decreased the thiamine content of the pearl millet flour. Yeast fermentation raised the level of thiamine two- to three-fold, while lactobacilli fermentation lowered it significantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliya S, Geervani P (1981) An assessment of the protein quality and vit B contents of commonly used fermented products of legumes and millets. J Sci Food Agric 32:837–842
Amerine MA, Berg HW, Cruess WV (1967) The technology of wine making. West Port, Connecticut: The AVI Publishing Company Inc.
AOAC (1980) Official methods of analysis. Washington DC: Association of Analytical Chemists
Banigo EOI, Muller MG (1972) Manufacture ofogi (A Nigerian fermented cereal porridge): comparative evaluation of corn, sorghum and millet. Can Inst Food Sci Technol J 5:217–221
Baseler ME, Fields ML (1984) Use ofCandida tropicalis ATCC 9968 to adjust the pH of a natural lactic acid fermentation of corn meal. J Food Sci 49:1198–1199
Boralkar M, Reddy NS (1985) Effect of roasting, germination and fermentation on the digestibility of starch and protein present in soybean. Nutr Reports International 3:833–836
Chauhan BM, Suneja N, Bhat CM (1986) Nutritional value and fatty acid composition of some high yielding varieties of bajra. Bull Grain Technol 21:441–442
Daniels DGH, Fisher N (1981) Hydrolysis of phytate of wheat flour during bread making. Brit J Nutr 46:1–6
Dhankher N (1985) Studies on the nutritional value ofrabadi — a fermented bajra product. M.Sc thesis Haryana Agricultural University Hisar (India)
Dhankher N, Chauhan BM (1987) Effect of temperature and period of fermentation on the protein and starch digestibility (in vitro) ofrabadi — a pearl millet fermented food. J Food Sci 52:489–490
Dhankher N, Chauhan BM (1987) Effect of temperature and fermentation time on phytic acid and polyphenol content ofrabadi — a fermented pearl millet food. J Food Sci 52:828–829
Dhankher N, Chauhan BM (1987) Preparation, acceptability and B vitamin content ofrabadi — a fermented pearl millet food. Int J Food Sci Technol 22:173–176
Eka OU (1980) Effect of fermentation on the nutrient status of locust beans. Food Chem 5:303–308
Ezeala DO (1984) Changes in nutrition quality of fermented cassava tuber meal. J Agric Food Chem 32:467–469
Khetarpaul N (1988) Improvement of nutritional value of pearl millet by fermentation and utilisation of the fermented product. Ph.D. thesis Haryana Agricultural University Hisar India
Knuckles BE, Kuzmicky DD, Betschart AA (1985) Effect of phytate and partially hydrolyzed phytate on in vitro protein digestibility. J Food Sci 50:1080–1082
Lee BY, Man PJ, Kim YB, Fields ML, Tongnvel PK (1980) Studies on the effects of fermentation on the nutritive value of Korean rice. Research reports of the office of Rural Development S Korea 22:36–42
Mahajan S (1986) Studies on improvement of nutritional value of bajra through fermentation. M.SC thesis Haryana Agricultural University Hisar India
Mahajan S, Chauhan BM (1987) Phytic acid and extractable phosphorus of pearl millet flour as affected by natural lactic acid fermentation. J Sci food Agric 41:381–382
Nanson NJ, Fields ML (1984) Influence of temperature of fermentation on the nutritive value of lactic acid fermented corn meal. J Food Sci 49:958–959
Nolan KB, Duffin PA (1987) Effect of phytate on mineral bioavailability. In vitro studies on Mg2+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Zn2+ in the presence of phytate. J Sci Food Agric 40:79–83
Pandey NK, Bhaskaran S (1987) Biotechnological approaches for augmenting supply of edible oils. Proceeding of the Nutrition Society of India 33:19–32
Panse YG, Sukhatme PV (1961) Statistical Methods of Agricultural Workers, 2nd edn. New Delhi: Indian Council of Agricultural Research
Paul P (1979) Study on fermentation of grain sorghum to improve its amino acid and vitamin content. M.Sc thesis, University of Missouri, Columbia
Paul M Au, Fields ML (1981) Nutritional quality of fermented sorghum. J Food Sci 46:652–654
Rao RV, Basu KP (1952) Effect ofdahi fermentation on the thiamine, riboflavin and nicotinic acid contents of milk. Indian J Dairy Sci 5:1–8
Serraino MR, Thompson LU, Sovoie L, Parent G (1985) Effect of phytic acid on the in vitro rate of digestibility of rapeseed protein and amino acids. J Food Sci 50:1689–1692
Sullins LW, Ronney RD (1977) In: Proceedings of a Symposium on ‘Sorghum and Millets for Human Food’ London: Tropical Products Institute, pp. 91
Sutardi, Buckle KA (1985) Reduction in phytic acid levels in soybeans duringtempeh production, storage and frying. J Food Sci 50:260–261
Tongnual P, Fields ML (1979) Fermentation and relative nutritive value of rice meal and chips. J Food Sci 44:1784–1785
Venkatasubbaiah P, Dwarkanath CT, Sreenivasa Murthy V (1984) Microbiological and physico-chemical changes inidli batter during fermentation. J Food Sci Technol 21:59–62
Yoon JH, Thompson LU, Jenkins DJA (1983) The effect of phytic acids on in vitro rate of starch digestibility and blood glucose response. Am J Clin Nutr 38:835–842
Zamora AF, Fields ML (1979) Nutritive quality of fermented cowpea and chickpeas. J Food Sci 44:234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khetarpaul, N., Chauhan, B.M. Effect of fermentation on protein, fat, minerals and thiamine content of pearl millet. Plant Food Hum Nutr 39, 169–177 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01091897
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01091897