Abstract
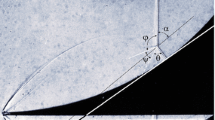
Experimental investigations [1] show that when allowance is made for the real properties of a gas it is possible to have a regime of regular reflection of a shock wave from the surface of a wedge in which the reflected shock wave is attached to the tip of the wedge. In the present paper, which uses perturbation theory in a form close to a modified small-parameter method [2], an approximate analytic solution is constructed to the problem of the interaction of a strong shock wave with the surface of a wedge for such a regime. In contrast to the problem considered by the same authors in an earlier paper [3], the half-angle at the tip of the wedge is not assumed to be small.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
T. V. Vazhenova and L. G. Gvozdeva, Time-Dependent Interactions of Shock Waves [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1977), p. 143.
A. L. Gonor and N. A. Ostapenko, “Hypersonic flow past wings with a Mach system of shock waves,” Izv, Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekh. Zhidk. Gaza, No. 3, 104 (1972).
V. I. Bogatko and G. A. Kolton, “Irregular reflection of a strong shock wave by a thin wedge,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekh. Zhidk. Gaza, No. 5, 55 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Mekhanika Zhidkosti i Gaza, No. 2, pp. 92–96, March–April, 1983.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogatko, V.I., Kolton, G.A. Regular reflection of a strong shock wave by the surface of a wedge. Fluid Dyn 18, 243–247 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01091112
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01091112