Abstract
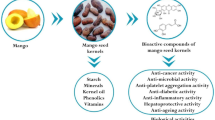
The chemical and toxicological composition of ten wild legumes collected in Yucatan, Mexico was determined. For each species the whole fruit, (seed and pod), were studied as well as the seed and pod separately. A higher protein content was found in the seeds ofA. lebbeck andP. saman (37.07 and 37.60% respectively). In the seeds ofL. longystilus, C. yucatanensis andP. keyense a high concentration of fat was found, especially in the first with 31.34%. A high quantity of fiber was found in the pods. In general, the samples were rich in lysine (especially seeds) and scant in sulfur amino acids and tryptophan. All the samples showed high concentration of potassium and calcium. Some of them exhibited significant concentrations of iron. The pods ofP. saman and P. keyense showed a high content of lectins. In the seeds ofC. yucatanensis and in the pod ofP. keyense high concentrations of trypsin inhibitors were found 60 and 406.7 TUI/mg sample respectively. The presence of saponins, was detected in seven samples, of which the seed ofP. keyense had the highest concentration. Alkaloids were found only in the whole fruit and pod ofP. saman and cyanogenic glucosides were present inA. pennatula. In general terms, the whole legume showed better digestibility than the pods alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sousa M, Delgado A (1993) Mexican leguminosae: Phytogeography, endemism and origins. In Ramamoorthy TP, Bye R, Lot A, Fa J (eds), Biological diversity of Mexico: Origin and distribution. New York/Oxford: Oxford University, pp. 459–511.
Sosa V, Flores JS, Rico-Gray V, Lira R, Ortiz JJ (1985) Etnoflora Yucatanense. Flora y Sinominia Maya. INIREB. Dante ed. Mérida, Yuc.
AOAC (1990) Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 15th. ed. Arlington, Vol. I and II.
Lucas B, Sotelo A (1992) Amino acid determination in pure protein, foods and feeds using two differents acid hydrolysis methods. Anal Biochem 123: 349–356.
Lucas B, Sotelo A (1980) Effect of two differents alkalis temperature, and hydrolysis times on tryptophan determination of pure proteins and foods. Anal Biochem 109: 192–197.
Rama Dao MV, Krishnan CK (1974) Colorimetric estimation of tryptophan content of pulses. J Food Sci Techn 11: 213–216.
Perkin-Elmer 303-0152. (1976) Analytical methods for atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Norwalk, CT.
Kakade ML (1974) Determination of trypsin inhibitor activity of soybean products. Cereal Chem 51: 376–382.
Jaffé WG, Levy A, González DI (1974) Isolation and partial characterization of beans phytohemagglutinins. Phytochemistry 13: 2685–2893.
Abisch E, Reichstein T (1960) Alkaloid-screening (Micro method). Helv Chim. Acta 43: 1844–1861.
Lucas B, Sotelo A (1984) A simplified test for the quantification of cyanogenic glucosides in wild and cultivated seed. Nutr Rep Int 29: 711–719.
Tilley JM, Terry RA (1963) A two stage technique for the in vitro digestion of forage crops. J Br Grass Soc 28: 104–111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sotelo, A., Contreras, E. & Flores, S. Nutritional value and content of antinutritional compounds and toxics in ten wild legumes of Yucatan Peninsula. Plant Food Hum Nutr 47, 115–123 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01089260
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01089260