Abstract
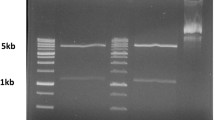
In SDS-PAGE the immune complexes (IC) of kala-azar patient sera showed intense bands at 55 kDa and 20 kDa corresponding to heavy and light chains of immunoglobulins. In immunoblot experiment, kala-azar and normal IC after treatment with patient sera showed multiple bands of which the band at 55 kDa was most prominent in kala-azar IC. It is known that in kala-azar sera antihuman IgG is present, so the heavy band at 55 kDa region may be due to higher amount of IgG and/or other antigen(s) present at that region. Immunoblot experiments of kala-azar IC with anti gp63 also developed a major band at 55 kDa. It suggests that the antigen (55 kDa) and gp63 have common antigenic epitope (s). Normal IC did not react with anti gp63 indicating absence of this antigen in normal IC. Antigenic similarity between the IC antigen (55 kDa) and gp63 indicated that the former antigen may have been processed from gp63. In summary, identification of a parasite antigen (55 kDa) in IC of kala-azar patients sera may be useful in developing a serodiagnostic assay for visceral leishmaniasis. (Mol Cell Biochem130: 11–17, 1994)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IC:
-
Immune Complexes
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene Glycol (Mol wt 8000)
- PBS:
-
Phosphate Buffer Saline
- VL:
-
Visceral Leishmaniasis
- AVL:
-
American Visceral Leishmaniasis
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- TBS:
-
Tris Buffer Saline
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
- gp63:
-
A leishmanial surface glycoprotein of molecular mass 63,000
- TEMED:
-
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine
References
Evans T, Reis FE, Allencer JE, Naidu TG, Loceroa JA, McAuliffe JF, Pearson RD: American visceral leishmaniasis (kala-azar). West J Med 124: 777–781, 1985
Argov S, Jaffe CL, Krupp M, Slor H, Shoenfield Y: Auto-antibody production by patients infected with Leishmania. Clin Exp Immunol 76: 190–197, 1989
Hauba V, Allison AC: M-antiglobulins (Rheumatoid factor like globulins) and other γ-glubulins in relationship with tropical parasitic infections. Lancet I: 848–852, 1966
Carvalho EM, Andrews BS, Martinelli R, Dutra M, Rocha H: Circulating immune complexes and rheumatoid factor in visceral leishmaniasis and scistosomiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 32: 61–68, 1983
Pearson RD, Allencar JE, Romito R, Naidu TG, Young AC, Davis JS IV: Circulating immune complexes and rheumatoid factor in visceral leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis 147: 1102, 1983
Howard MK, Gull K, Miles MA: Antibodies to tubulin in patients with parasitic infections. Clin Exp Immunol 68: 78–85, 1987
Pateraki E, Partocala R, Labrousse H, Guesdon JL: Antiactin and anti-tubulin antibodies in canine visceral leishmaniasis. Infect Immun 42: 496–500, 1983
Galvao-castro B, Sa-Ferreira JA, Marzochi I, Marzochi MC, Countinho SG, Lambert PH: Polyclonal B-cell activation, circulating immune complexes and autoimmunity in human visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol 56: 58–66, 1984
Houba V: Immunological investigation of tropical and parasitic diseases. In: Nairn RC (ed) Practical Methods in Clinical Immunology Series, Vol 2, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London and New York, 1980, pp 1–5
Kohanteb J, Ardehali SM, Rezai HR: Detection ofLeishmania donovani soluble antigen and antibody in the urine of visceral leishmaniasis patients. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hyg 81: 578–580, 1987
Sanyal T, Ghosh DK, Sarkar D: Identification of immune complex antigens in sera of Indian kala-azar patients. Ind J Exp Biol 29: 411–415, 1991
Chia D, Burnett EV, Yamagata J, Knotson D, Restivo C, Frust D: Quantitiation and characterization of soluble immune complexes precipitated from sera by polyethylene glycol (PEG). Clin Exp Immunol 37: 399–407, 1979
Laemml UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685, 1970
Fairbanks G, Sleck TL, Wallach DFH: Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythocyte membrane. Biochemistry 10: 2606–2617, 1971
Burnett WN: ‘Western Blotting’ Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose and radioactive protein A. Anal Biochem 112: 195–203, 1981
Michael GM: Preparation of Fab fragments from IgGs of different animal species. Methods Enzymol 70: 142–150, 1980
Schubart UK, Fields KL: Identification of a calcium regulated insulinoma cell phosphoprotein as an islet cell keratin. J Cell Biol 98: 1001–1009
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275, 1951
Valentin FB, Rabilloud R, Rousset B: Evidence for anti-tubulin autoantibodies in the form of immune complexes in human sera. Clin Exp Immunol 71: 261–268, 1988
Fong D, Chang K-P: Tubulin biosynthesis in the developmental cycle of a parasitic protozoan,Leishmania mexicana: Changes during differentiation of motile and nonmotile stages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 7624–7628, 1981
Sanyal T: Studies onLeishmania donovani antigens with special reference to surface and immune complex antigens. Ph D Thesis, Jadavpur University, Calcutta, India, 1993
Kink JA, Chang K-P: N-glycosylation as a biochemical basis for virulence inLeishmania mexicana amazonensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 27: 181–190, 1988
Reed SG, Carvalho EM, Sherbert CH, Sampio DP, Russo DN, Bacelor O, Pihl DH, Scott JM, Barrel A, Grabstein KH, Johnson WD Jr:In vitro responses toLeishmania antigens by lymphocytes from patients with leishmaniasis or Chagas' disease. J Clin Invest 85: 690–696, 1990
Russel DG, Alexander J: Effective immunization against cutaneous leishmaniasis with defined membrane antigens reconstituted into liposomes. J Immunol 140: 1274–1279, 1988
Russo DM, Burns JM Jr, Carvalho EM, Armitage RJ, Grabstein KH, Button LL, McMaster WR, Reed SG: Human T-cell responses to gp63, a surface antigen of Leishmania. J Immunol 147: 3575–3580, 1991
Reed SG, Badaro R, Lloyd RMC: Identification of specffic and cross-reactive antigens ofLeishmania donovani chagasi by human infection sera. J Immunol 138: 1596–1601, 1987
Colomer-Gould V, Quintao LG, Keithly J, Nogueira N: A common major surface antigen on amastigotes and promastigotes ofLeishmania species. J Exp Med 162: 902–916, 1985
Medina-Acosta E, Karess RE, Schwartz H, Russell DG. The promastigote surface protease (gp63) ofLeishmania is expressed but differentially processed and localized in the amastigote stage. Mol Biochem Parasitol 37: 263–274, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanyal, T., Ghosh, D.K. & Sarkar, D. Immunoblotting identifies and antigen recognized by anti gp63 in the immune complexes of Indian kala-azar patient sera. Mol Cell Biochem 130, 11–17 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01084263
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01084263