Abstract
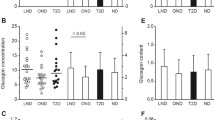
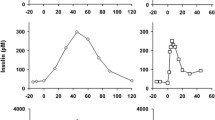
The secretory capacity of the B-cells in 40 patients with chronic or chronic relapsing pancreatitis was examined by means of the oral glucose tolerance test (100 g of glucose, orally) and combined stimulation (100 g of glucose, orally, 1 mg of glucagon, and 0.5 g of tolbutamide intravenously. Under both the test conditions, the immunologically measurable insulin was significantly reduced compared to that of controls. The maximal insulin differences and the insulinogenic index (35-minute value) of the combined stimulation method were most satisfactory for the diagnosis of the secretory B-cell insufficiency. In addition to these parameters, the constancy of insulin levels in the period between 35 and 60 minutes indicated a dysfunction of the endocrine pancreas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creutzfeld W, Fehr H, Schmidt H: Verlaufsbeo-bachtungen und diagnostische Verfahren bei der chronisch rezidivierenden und chronischen Pankreatitis. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 100:1180–1189, 1970
Grabner W, Bergner D, Scharrer H, Sommer B, Berg G: Untersuchungen zur B-Zellenstimulation der Bauchspeicheldrüse bei Stoffwechselgesunden. Klin Wochenschr 49:763–767, 1971
Grabner W, Bergner D, Scharrer H, Sommer B, Berg G: B-Zellenstimulation bei chronischer und chronisch-rezidivierender Pankreatitis. Klin Wochenschr 49:765–767, 1971
Ryan WG, Nibbe AF, Schwartz ThB: Betacytotrophic effects of glucose, glucagon and tolbutamid in man. Lancet 1:1255–1256, 1967
Yalow RS, Berson SA: Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest 39:1157–1175, 1960.
Niemann E: Arbeitsanleitung zum Radio-immunbesteck der Farbwerke Hoechst AG, 1970
Schmidt FH: Enzymatische Methoden zur Bestimmung von Blut- und Harnzucker unter Berücksichtigung von Vergleichsuntersuchungen mit klassischen Methoden. Internist 4:554, 1963
Sachs L: Statistiche Auswertungsmethoden. Berlin, Springer-Verlag, 1969
Prellwitz W: Klinisch-Chemische Diagnostik. Stuttgart, George Thieme Verlag, 1972, p 77
Seltzer HS, Allen EW, Herron AL, Brennan MT: Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 46:323–335, 1967
Joffe BI, Bank S: Insulin reserve in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Lancet 2:890–891, 1968
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grabner, W., Phillip, J. & Strigl, P. The diagnostic value of oral glucose tolerance test and combined B-cell stimulation in chronic pancreatitis. Digest Dis Sci 18, 1055–1060 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01076521
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01076521