Abstract
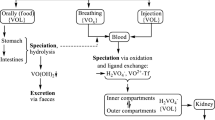
The possible use of vanadium compounds in the treatment of diabetic patients is now being evaluated. However, previously to establish the optimal maximum dose for diabetes therapy, it should be taken into account that vanadium is a highly toxic element to man and animals. The toxic effects of vanadium are here reviewed. The tissue vanadium accumulation, which would mean an additional risk of toxicity following prolonged vanadium administration is also discussed. Recently, it has been shown that coadministration of vanadate and TIRON, an effective chelator in the treatment of vanadium intoxication, reduced the tissue accumulation of this element, decreasing the possibility of toxic side effects derived from chronic vanadium administration without diminishing the hypoglycemic effect of vanadium. However, previously to assess the effectiveness of this treatment in diabetic patients, a critical reevaluation of the antidiabetic action of vanadium and its potential toxicity is clearly needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shechter Y: Insulin mimetic effects of vanadate. Possible implications for future treatment of diabetes. Diabetes 39: 1–5, 1990
Brichard SM, Lederer J, Henquin JC: The insulin-like properties of vanadium: a curiosity or a perspective for the treatment of diabetes?. Diabet Metab 17: 435–440, 1991
Shechter Y, Shisheva A: Vanadium salts and the future treatment of diabetes. Endeavour 17: 27–31, 1993
Fantus IG, Deragon G, Posner BI: Insulin-mimetic effects of vanadate and pervanadate: potential therapeutic use in diabetes mellitus. Med Sci 7: 255–258, 1991
Cros GH, Mongold JJ, Serrano JJ, Ramanadham S, McNeill JH: Effects of vanadyl derivatives on animal models of diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 109: 163–166, 1992
Roschin AV, Ordzhonikidze EK, Shalganova IV: Vanadium: toxicity, metabolism, carrier state. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol 24: 377–383, 1980
Kawai T, Seiji K, Watanabe T, Ikeda M: Urinary vanadium as a biological indicator of exposure to vanadium. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 61: 283–287, 1989
Faulkner-Hudson TG: Vanadium Toxicity and Biological Significance. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1964
Llobet JM, Domingo JL: Acute toxicity of vanadium compounds in rats and mice. Toxicol Lett 23: 227–231, 1984
Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Tomas JM, Corbella J: Short-term toxicity studies of vanadium in rats. J Appl Toxicol 5: 418–421, 1985
Zaporowska H, Wasilewski W: Some selected peripheral blood and haemopoietic system indices in Wistar rats with chronic vanadium intoxication. Comp Biochem Physiol 93C: 175–180, 1989
Zaporowska H, Wasilewski W: Hematological effects of vanadium on living organisms. Comp Biochem Physiol 102C: 223–231, 1992
Zaporowska H, Wasilewski W, Slotwinska M: Effect of chronic vanadium administration in drinking water to rats. Biometals 6:3–10, 1993
Al-Bayati MA, Giri SN, Raabe OG: Time and dose-response study of the effects of vanadate in rats: changes in blood cells, serum enzymes, protein, cholesterol, glucose, calcium, and inorganic phosphate. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 10: 206–213, 1990.
Llobet JM, Colomina MT, Sirvent JJ, Domingo JL, Corbella J: Reproductive toxicity evaluation of vanadium in male mice. Toxicology 80: 199–206, 1993
Domingo JL, Paternain JL, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Effects of vanadium on reproduction, gestation, parturition and lactation in rats upon oral administration. Life Sci 39: 819–824, 1986
Paternain JL, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Embryotoxic and teratogenic effects of sodium metavanadate administered to rats during organogenesis. Rev Esp Fisiol 43: 223–228, 1987
Sanchez DJ, Ortega A, Domingo JL, Corbella J: Developmental toxicity evaluation of orthovanadate in the mouse. Biol Trace Elem Res 30: 219–226, 1991
Gomez M, Sanchez DJ, Domingo JL, Corbella J: Embryotoxic and teratogenic effects of intraperitoneally administered metavanadate in mice. J Toxicol Environ Health 37: 47–56, 1992
Domingo JL, Bosque MA, Luna M, Corbella J: Prevention by Tiron (sodium 4,5-dihydroxybenzene-1,3-disulfonate) of vanadate-induced developmental toxicity in mice. Teratology 48: 133–138, 1993
Paternain JL, Domingo JL, Gomez M, Ortega A, Corbella J: Developmental toxicity of vanadium in mice after oral administration. J Appl Toxicol 10: 181–186, 1990
Parker RDR, Sharma RP: Accumulation and depletion of vanadium in selected tissues of rats treated with vanadyl sulfate and sodium orthovanadate. J Environ Pathol Toxicol 2: 235–245, 1978
Al-Bayati MA, Giri SN, Raabe OG, Rosenblatt LS, Shifrine M: Time and dose-response study of the effects of vanadate on rats: morphological and biochemical changes in organs. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 9:435–455, 1989
Al-Bayati MA, Culberston MR, Schreider JP, Rosenblatt LS, Raabe OG: The lymphotoxic action of vanadate. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 11: 19–27, 1992
Kowalska M: The effect of vanadium on lung collagen content and composition in two succesive generations of rats. Toxicol Lett 41: 203–208, 1988
Kowalska M: Changes in rat lung collagen after life-time treatment with vanadium. Toxicol Lett 47: 185–190, 1989
Cohen MD, Wei CI, Tan H, Kao KJ: Effect of ammonium metavanadate on the murine immune response. J Toxicol Environ Health 19: 279–298, 1986
Donaldson J, LaBella F: Pro-oxidant properties of vanadate in vitro on catecholamines and on lipid peroxidation by mouse and rat tissues. J Toxicol Environ Health 12: 119–126, 1983
Bruech M, Quintanilla ME, Legrum W, Koch J, Netter KJ, Furhmann GF: Effects of vanadate on intracellular reduction equivalents in mouse liver and the fate of vanadium in plasma, erythrocites and liver. Toxicology 31: 283–295, 1984
Taqui Khan MM, Martell AE: Kinetics of metal ion and metal chelate catalyzed oxidation of ascorbic acid. III. Vanadyl ion catalyzed oxidation. J Am Chem Soc 90: 6011–6017, 1968
Sasi MM, Haider SS, El-Fakhri M, Ghwarsha KM: Microchromatographic analysis of lipids, protein, and occurrence of lipid peroxidation in various brain areas of vanadium exposed rats: A possible mechanism of vanadium neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 14: 57–64, 1993
Younes M, Strubelt O: Vanadate-induced toxicity towards isolated perfused rat livers: the role of lipid peroxidation. Toxicology 66: 63–74, 1991
Younes M, Kayser E, Strubelt O: Effect of antioxidants on vanadate-induced toxicity towards isolated perfused rat livers. Toxicology 70: 141–149, 1991
Heyliger CE, Tahiliani AG, McNeill JH: Effect of vanadate on elevated blood glucose and depressed cardiac performance of diabetic rats. Science 277: 1474–1477, 1985
Marfaing-Jallat P, Penicaud L: Effect of vanadium on regional brain glucose utilization in rats. Physiol Behav 54: 407–409, 1993
Paulson DJ, Kopp SJ, Tow JP, Peace DG: Effects of vanadate on in vivo myocardial reactivity to norepinephrine in diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240: 529–534, 1987
Domingo JL, Gomez M, Llobet JM, Corbella J, Keen CL: Oral vanadium administration to streptozotocin-diabetic rats has marked negative side-effects which are independent of the form of vanadium used. Toxicology 66: 279–287, 1991
Jandhyala BS, Hom GJ: Physiological and pharmacological properties of vanadium. Life Sci 33: 1325–1340, 1983
Cantley LC, Josephson L, Warner M, Yanagisawa C, Lechene C, Guidotti G: Vanadate is a potent (NaK)ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem 252: 7421–7423, 1977
Nechay BR: Mechanisms of action of vanadium. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 24: 501–524, 1984
Nechay BR, Sauners JP: Inhibition by vanadium of sodium and potassium dependent adenosinetriphosphatase derived from animal and human tissues. J Environ Pathol Toxicol 2: 247–262, 1978
Domingo JL, Gomez M, Llobet JM, Corbella J, Keen CL: Improvement of glucose homeostasis by oral vanadyl or vanadate treatment in diabetic rats is accompanied by negative side effects. Pharmacol Toxicol 68: 249–253, 1991
Pederson RA, Ramanadham S, Buchan AMJ, McNeill JH: Long-term effects of vanadyl treatment on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Diabetes 38: 1390–1395, 1989
Meyerovitch J, Farfel Z, Sack J, Shechter Y: Oral administration of vanadate normalizes blood glucose levels in streptozotocin-treated rats. J Biol Chem 262: 6658–6662, 1987
Bendayan M, Gingras D: Effect of vanadate administration on blood glucose and insulin levels as well as on the exocrine pancreatic function in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 32: 561–567, 1989
Sekar N, Kanthasamy A, William S, Subramanian S, Govindasamy S: Insulinic actions of vanadate in diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res 22: 207–217, 1990
Becker DJ, Ongemba LN, Henquin JC: Comparison of the effects of various vanadium salts on glucose homeostasis in streptozotocindiabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 260: 169–175, 1994
Dai S, Thompson KH, McNeill JH: One-year treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with vanadyl sulphate. Pharmacol Toxicol 74: 101–109, 1994
Mongold JJ, Cros GH, Vian L, Tep A, Ramanadham S, Siou G, Diaz J, McNeill JH, Serrano JJ: Toxicological aspects of vanadyl sulphate on diabetic rats: effect of vanadium levels and pancreatic β-cell morphology. Pharmacol Toxicol 67: 192–198, 1990
Okpere BE, Williams G, Bloom SR: Failure of oral metavanadate to correct streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats (Abstract). Diabetic Med 5 (S2): 8, 1988
Cam NC, Pederson RA, Brownsey RW, McNeill JH: Long-term effectiveness of oral vanadyl sulphate in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 36: 218–224, 1993
McNeill JH, Yuen VG, Hoveyda HR, Orvig C: Bis(maltolato)-oxovanadium(IV) is a potent insulin mimic. J Med Chem 35: 1489–1491, 1992
Yuen VG, Orvig C, McNeill JH: Glucose-lowering effects of a new organic vanadium complex, bis(maltolato)oxovanadium(IV). Can J Physiol Pharmacol 71: 263–269, 1993
Oster MH, Llobet JM, Domingo JL, German JB, Keen CL: Vanadium treatment of diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats results in tissue vanadium accumulation and pro-oxidant effects. Toxicology 83: 115–130, 1993
Elfant M, Keen CL: Sodium vanadate toxicity in adult and developing rats. Role of peroxidative damage. Biol Trace Elem Res 14: 193–208, 1987
Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Tomas JM, Corbella J: Influence of chelating agents on the toxicity, distribution and excretion of vanadium in mice. J Appl Toxicol 6: 337–341, 1986
Zaporowska H: Effect of vanadium on L-ascorbic acid concentration in rat tissues. Gen Pharmac 25: 467–470, 1994
Thompson KH, McNeill JH: Effect of vanadyl sulfate feeding on susceptibility to peroxidative change in diabetic rats. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 80: 187–200, 1993
Domingo JL, Ortega A, Llobet JM, Keen CL: No improvement of glucose homeostasis in diabetic rats by vanadate treatment when given by gavage. Trace Elem Med 8: 181–186, 1991
Domingo JL, Sanchez DJ, Gomez M, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Administration of vanadyl sulfate by gavage does not normalize blood glucose levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 75: 369–372, 1992
Pugazhenthi S, Khandelwal RL: Insulinlike effects of vanadate on hepatic glycogen metabolism in nondiabetic and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 39: 821–827, 1990
Ramanadham S, Mongold JJ, Brownsey RW, Cros GH, McNeill JH: Oral vanadyl sulfate in treatment of diabetes mellitus in rats. Am J Physiol 257: H904-H911, 1989
Ramanadham S, Brownsey RW, Cros GH, Mongold JJ, McNeill JH: Sustained prevention of myocardial and metabolic abnormalities in diabetic rats following withdrawal from oral vanadyl treatment. Metabolism 38: 1022–1028, 1989
Brichard SM, Okitolonda W, Henquin JC: Long term improvement of glucose homeostasis by vanadate treatment in diabetic rats. Endocrinology 123: 2048–2053, 1988
Gil J, Miralpeix M, Carreras J, Bartrons R: Insulin-like effects of vanadate on glucokinase activity and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels in the liver of diabetic rats. J Biol Chem 263: 1868–1871, 1988
Blondel O, Bailbe D, Portha B: In vivo insulin resistance in streptozotocin-diabetic rats — evidence for reversal following oral vanadate treatment. Diabetologia 32: 185–190, 1989
Thompson KH, Leichter J, McNeill JH: Studies of vanadyl sulfate as a glucose-lowering agent in STZ-diabetic rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197: 1549–1554, 1993
Domingo JL, Gomez M, Sanchez DJ, Llobet JM, Keen CL: Tiron administration minimizes the toxicity of vanadate but not its insulin mimetic properties in diabetic rats. Life Sci 50: 1311–1317, 1992
Domingo JL, Gomez M, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Chelating agents in the treatment of acute vanadyl sulphate intoxication in mice. Toxicology 62: 203–211, 1990
Gomez M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Evaluation of the efficacy of various chelating agents on urinary excretion and tissue distribution of vanadium in rats. Toxicol Lett 57: 227–234, 1991
Gomez M, Domingo JL, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Effectiveness of some chelating agents on distribution and excretion of vanadium in rats after prolonged oral administration. J Appl Toxicol 11: 195–198, 1991
Domingo JL, Sanchez DJ, Gomez M, Llobet JM, Corbella J: Oral vanadate and Tiron in treatment of diabetes mellitus in rats improvement of glucose homeostasis and negative side-effects. Vet Hum Toxicol 35: 495–500, 1993
Malabu UH, Dryden S, McCarthy HD, Kilpatrick A, Williams G: Effects of chronic vanadate administration in the STZ-induced diabetic rat. The antihyperglycemic action of vandate is attributable entirely to its suppression of feeding. Diabetes 43: 9–15, 1994
Domingo JL, Gomez M, Sanchez DJ, Llobet JM, Corbella J, Keen CL: Normalization of hyperglycemia by vanadate or vanadyl treatment in diabetic rats: pharmacological and toxicological aspects. Trace Elem Electr 11: 16–22, 1994
Sanchez DJ, Gomez M, Llobet JM, Domingo JL, Corbella J: Is the streptozotocin-treated rat a suitable model to assess the therapeutic potential of vanadium in diabetes treatment?. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 72 (S3): 20, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domingo, J.L., Gomez, M., Sanchez, D.J. et al. Toxicology of vanadium compounds in diabetic rats: The action of chelating agents on vanadium accumulation. Mol Cell Biochem 153, 233–240 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01075942
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01075942