Abstract
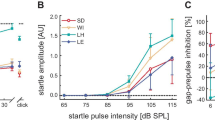
Albino (c/c) and nonalbino (+/c and +/+) congenic C57BL/6J mice were examined for the effects of acoustic prestimulation (priming) on audiogenic seizures. While no genotypic-specific effects were noticed 1 day after priming, major effects were observed in separate groups of mice tested 5 days after priming. The c/c mice were most susceptible to audiogenic seizures, and no differences were observed between +/c and +/+ mice. While cross-fostering did not change this relationship, it provided protection for mice of all three genotypes. The interpretation that melanin offers protection from acoustic trauma is considered inconclusive because of the interaction of innate- and priming-induced audiogenic seizures in the +/c and c/c mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boggan, W. O., Freedman, D. X., Lovell, R. A., and Schlesinger, K. (1971). Studies in audiogenic seizure susceptibility.Psychopharmacologia 20:48–56.
Bonaccorsi, P. (1963). Comportamento delle barriere emolabirintica, liquorale ed oftalmica nell' albinismo.Ann. Laringol. Otol. Rinol. Faringol. 62:432–456.
Chen, C.-S., Gates, G. R., and Bock, G. R. (1973). Effect of priming and tympanic membrane destruction on development of audiogenic seizure susceptibility in BALB/c mice.Exp. Neurol. 39:277–284.
Cherubino, M. (1968). I melanaciti dell' orecchio interno. In Crifo (1973).
Crifo, S. (1973). Shiver-audiometry in the conditioned guinea-pig (simplified Anderson-Wedenberg test).Acta Oto-Laryngol. 75:38–44.
DeFries, J. C., Hegmann, J. P., and Weir, M. W. (1966). Open-field behavior in mice: Evidence for a major gene effect mediated by the visual system.Science 154:1577–1579.
Galioto, G. B., and Bonaccorsi, P. (1965). Il fattore constituzionale del trauma acuatico individuato sperimentalmente nella diversa concentrazione di melania nella strai vaacolare. In Crifo (1973).
Gutherz, K., and Thiessen, D. D. (1966). Albinism and audiogenic seizures in the mouse.Psychon. Sci. 6:97–98.
Henry, K. R. (1967). Audiogenic seizure susceptibility induced in C57BL/6J mice by prior auditory exposure.Science 158:938–940.
Henry, K. R., and Bowman, R. E. (1968). The dilute locus, pyridoxine deficiency, and audiogenic seizures in mice.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 128:635–638.
Henry, K. R., and Bowman, R. E. (1970). Behavior-genetic analysis of the ontogeny of acoustically primed audiogenic seizures in mice.J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 70:235–241.
Henry, K. R., and Haythorn, M. M. (1974). Similarities in auditory processing associated with auditory deprivation in the DBA/2J and the acoustically primed C57BL/6J mouse.J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol., in press.
Henry, K. R., and Haythorn, M. M. (1975). Albinism and auditory function in the laboratory mouse. I. Effects of single-gene substitutions on auditory physiology, audiogenic seizures, and developmental processes.Behav. Genet. 5:137–149.
Karsai, L. K., Bergman, M., and Bin Choo, Y. (1972). Hearing in ethnically different longshoremen.Arch. Otolargyngol. 96:499–504.
McClearn, G. E. (1960). Strain differences in activity of mice: Influence of illumination.J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 53:142–143.
McGinn, M. D., Willott, J. F., and Henry, K. R. (1974). Effects of conductive hearing loss on auditory evoked potentials and audiogenic seizures in mice.Nature New Biol. 244:255–256.
Savin, C. (1965). The blood vessels and pigmentary cells of the inner ear.Ann. Otol. 74:611–622.
Sze, P. Y. (1970). Neurochemical factors in auditory stimulation and development of susceptibility to audiogenic seizures. In Welch, B. L., and Welch, A. S. (eds.),Physiological Effects of Noise, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 259–270.
Thiessen, D. D., Owen, K., and Whitsett, M. (1970). Chromosome mapping of behavioral activities. In Lindzey, G., and Thiessen, D. D. (eds.),Contributions to Behavior-Genetic Analysis: The Mouse as a Prototype, Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York.
Willott, J. F., and Henry, K. R. (1974). Auditory evoked potentials: Developmental changes of threshold and amplitude following early acoustic trauma.J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 86:1–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NSF Grant GB31921 and PHS Grant NS11565-01 to the second author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haythorn, M.M., Henry, K.R. Albinism and auditory function in the laboratory mouse. II. Effects of acoustic priming and cross-fostering. Behav Genet 5, 321–329 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01073202
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01073202