Abstract
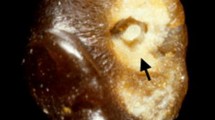
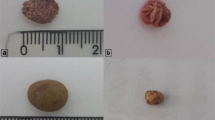
Experimental diet-induced dog gallstones contained mainly protein, mucous substances, bile salts, bilirubin, an insoluble pigment which formed an insoluble black residue after acid hydrolysis, and only traces of cholesterol. Added dietary cholesterol was necessary to pigmented gallstone production and led to hypercholesterolemia. In bile, the ratio of cholesterol to bile salts was increased, but phospholipids were increased and cholesterol insolubility was not found. Dry weight, osmolality, and concentration of sodium and potassium in bile were reduced, but were not considered sufficient to influence micelle formation or lipid-pigment solubility. Taurine was reduced in serum and bile and unconjugated bile acids appeared in gallbladder bile; the pKa of these acids is near the pH of bile in these animals and may have caused precipitation of bile acids, accounting for their presence in the stones. Bile cultures were sterile. Total bilirubin content was unaltered but the methods used did not exclude the presence of unconjugated bilirubin as a potential cause of pigment precipitation in aqueous bile. Increased numbers of secretory vesicles occurred in gallbladder epithelium and large amounts of mucus were in the epithelial crypts. These observations suggest that bile proteins or mucous substances are important to lithogenesis in this model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchier IAD, Freston JW: The etiology of gallstones. Lancet 1:340, 1968
Englert E Jr, Harman CG, Wales E Jr: Gallstones induced by normal foodstuffs in dogs. Nature 224:280, 1969
Oser BL: Hawk's Physiological Chemistry. New York, McGraw-Hill, 1965, p 1062
Mangold HK: Thin layer chromatography of lipids. J Am Oil Chem Soc 38:703, 1961
Boberg J: Separation of labelled plasma and tissue lipids by thin layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 14:325, 1966
Bartlett GR: Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem 234:466, 1959
Iwata T, Yamasaki K: Enzymatic determination and thinlayer chromatography of bile acids in blood. J Biochem (Tokyo) 56:424, 1964
Nakayama F, Michihiko O, Sakaguchi N, Miyake H: Thinlayer chromatography of bile lipids. Clin Chim Acta 10:544, 1964
Henry RJ: Clinical Chemistry-Principles and Technics. New York, Harper & Row, 1965, p 584
Spackman DH, Stein WF, Moore S: Automatic recording apparatus for use in chromatography of amino acids. Anal Chem 30:1190, 1958
Bouchier IAD, Cooperband SR, ElKodsi BM: Mucous substances and viscosity of normal and pathological human bile. Gastroenterology 49:343, 1965
Nakayama F: Quantittive microanalysis of gallstones. J Lab Clin Med 72:602, 1968
Maki T, Sato T, Suzuki N: Onin vitro synthesis of calcium bilirubinate. Tohoku J Exp Med 82:117, 1964
Blair JE, Lennette EH, Truant JP (Ed): Manual of Clinical Microbiology. Bethesda, Maryland, American Society for Microbiology, 1970
Hayflick L (Ed): The Mycoplasmatales and the L-Phase of Bacteria. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1969
Difco Manual. Detroit, Michigan, Difco Laboratories Inc., 1964, 9th Edition, p 238
Nakayama F: Composition of gallstone and bile: Species difference. J Lab Clin Med 73:623, 1969
Trotman BW, Soloway RD: Pigment vs cholesterol cholelithiasis: Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Am J Dig Dis 20:735, 1975
Trotman BW, Ostrow JD, Soloway RD: Pigment vs cholesterol cholelithiasis: Comparison of stone and bile composition. Am J Dig Dis 19:585, 1974
Small DM, Bourges M, Dervichian DG: Ternary and quaternary aqueous systems containing bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol. Nature 211:816, 1966
Admirand WH, Small DM: The physiochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. J Clin Invest 47:1043, 1968
Hofmann AF, Small DM: Detergent properties of bile salts: Correlation with physiological function. Ann Rev Med 18:333, 1967
O'Maille ERL, Richards TG, Short AH: The influence of conjugation of cholic acid on its uptake and secretion: Hepatic extraction of taurocholate and cholate in the dog. J Physiol 189:337, 1967
Palmer RH, Hruban A: Production of bile duct hyperplasia and gallstones by lithocholic acid. J Clin Invest 45:1255, 1966
Tabaqchali S, Hatzioannou J, Booth CC: Bile-salt deconjugation and steatorrhea in patients with the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet 2:12, 1968
Drasar BS: Cultivation of anaerobic intestinal bacteria. J Pathol Bacteriol 94:417, 1967
Freston JW, Bouchier IAD, Newman J: Biliary mucous substances in dihydrocholesterol-induced cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology 57:670, 1969
Meckel von Hemsbach H: (Edited with a foreword after the author's death by Dr. T. Bilroth) Mikrogeologie. Ueber die Concremente in thierischen Organismus, Berlin, Verlag von Georg Reimer, 1856
Womack NA, Zeppa R, Irvin GL III: The anatomy of gallstones. Ann Surg 157:670, 1963
Lonsdale K: Epitaxy as a growth factor in urinary calculi and gallstones. Nature 217:56, 1968
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265, 1951
Schultze HE, Heremans JF: Molecular Biology of Human Proteins, with Special Reference to Plasma Proteins. Vol. 1. Nature and Metabolism of Extracellular proteins. New York, American Elsevier, 1966, p 802
Bjogren H, Larsson K: On the pigment in biliary calculi. J Clin Lab Invest 15:569, 1963
Suzuki N: On black pigment of gallstones with special reference to comparison with bilirubin derivatives. Tohoku J Exp Med 85:396, 1965
Dam H, Prange I, Sondergaard E: Alimentary production of gallstones in hamsters. 20. Influence of dietary cholesterol on gallstone formation. Z. Ernaehrungswiss 9:43, 1968
Fitz-James P, Burton AC: Interfacial precipitation in human and “artificial” bile. Can J Res (Sec. E) 27:309, 1949
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With the Technical Assistance of P.N. Sine
Supported in part by Graduate Training Grant in Gastroenterology 5T01-AM5206 and Research Grant AM 08708 from the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Public Health Grant Service, Bethesda, Maryland, and in part by a Veterans Administration Research and Education Associateship Award, and by the Medical Research Service.
Dr. Freston is a Burroughs-Wellcom Scholar in Clinical Pharmacology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Englert, E., Harman, C.G., Freston, J.W. et al. Studies on the pathogenesis of diet-induced dog gallstones. Digest Dis Sci 22, 305–314 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01072187
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01072187