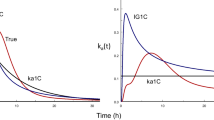
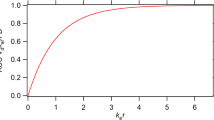
Abstract
The theoretical accuracy of concurrent administration of labeled intravenous tracer and oral doses to estimate the bioavailability of drugs exhibiting Michaelis-Menten kinetics was determined by computer simulation. The simulation model consisted of sampling and hepatic compartments with elimination occurring by hepatic metabolism according to the venous equilibration model. The relationships between error in bioavailability estimation and dose, metabolic activity (Vmax),first-order absorption rate constant (k a), and volume of distribution (V) and the fraction of the dose absorbed were examined. Error was hypothesized to be relatively low when conditions result in a relatively constant value of clearance after oral dosing or when the concentration-time curves after intravenous and oral dosing are similar. The results were consistent with these hypotheses and, under most conditions, error was less than 15%. The effects, on error, of altering the intravenous tracer dose input and having a lag time in absorption of drug from the oral dose were also determined. In general, accuracy was improved by delaying administration of the iv tracer for a time equal to 50% of the oral dose peak time or by administering the tracer dose by constant-rate infusion from the time of oral dosing to the peak time. Lag time in absorption of the oral dose was shown to often result in overestimates in bioavailability of greater than 50%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. M. Rubin and T. N. Tozer. Theoretical considerations in the calculation of bioavailability of drugs exhibiting Michaelis-Menten elimination kinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 12:437–450 (1984).
L. Martis and R. Levy. Bioavailability calculations for drugs showing simultaneous first-order and capacity-limited elimination kinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:283–294 (1973).
W. J. Jusko, J. R. Koup, and G. Alván. Nonlinear assessment of phenytoin bioavailability.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 4:327–336 (1976).
M. M. Eichelbaum, G. E. von Unruh, and A. Somogyi. Application of stable labelled drugs in clinical pharmacokinetic investigations.Clin. Pharmacokin. 7:490–507 (1982).
M. Eichelbaum, M. Albrecht, G. Kliems, K. Schäfer, and A. Somogyi. influence of meso-caval shunt surgery on verapamil kinetics, bioavailability and response.Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 10:527–530 (1980).
A. Somogyi, M. Albrecht, G. Kleims, K. Schäfer, and M. Eichelbaum. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and ECG response of verapamil in patients with liver cirrhosis.Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 12:51–60 (1981).
J. M. Strong, J. S. Dutcher, W.-K. Lee, and A. J. Atkinson. Absolute bioavailability in man of N-acetylprocainamide determined by a novel stable isotope method.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:613–622 (1975).
Y. Kasuya, K. Mamada, S. Baba, and M. Matsukura. Stable-isotope methodology for the bioavailability study of phenytoin during multiple-dosing regimens.J. Pharm. Sci. 74:503–507 (1985).
J. A. Waschek, G. M. Rubin, T. N. Tozer, R. M. Fielding, W. R. Couet, D. J. Effeney, and S. M. Pond. Dose-dependent bioavailabilty and metabolism of salicylamide in dogs.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 230:89–93 (1984).
D. M. Kornhauser, A. J. J. Wood, R. E. Vestal, G. R. Wilkinson, R. A. Branch, and D. G. Shand. Biological determinants of propranolol disposition in man.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 23:165–174 (1978).
J. A. Clements, R. C. Heading, W. S. Nimmo, and L. F. Prescott. Kinetics of acetaminophen absorption and gastric emptying in man.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 24: 420–431 (1978).
T. R. Browne, A. van Langenhove, C. E. Costello, K. Biemann, and D. J. Greenblatt. Kinetic equivalence of stable-isotope-labeled and unlabeled phenytoin.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 29:511–515 (1981).
K. Mamada, Y. Kasuya, and S. Baba. Pharmacokinetic equivalence of deuterium-labeled and unlabeled phenytoin.Drug Metab. Dispos. 14:509–511 (1986).
D. J. Jenden and A. K. Cho. Selected ion monitoring in pharmacology.Biochem. Pharmacol. 28:705–713 (1979).
H. Schmid, A. Prox, H. Zipp, and F. W. Koss. Use of stable isotopes to prove the saturable first-pass effect of methoxsalen.Biomed. Mass Spec. 7:560–564 (1980).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a “well-stirred” model and a “parallel-tube” model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:625–653 (1977).
P. K. Wilkinson, A. J. Sedman, E. Sakamar, R. H. Earhart, D. J. Weidler, and J. G. Wagner. Blood ethanol concentrations during and following constant-rate intravenous infusion of alcohol.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:213–223 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by grants GM 26556 and GM 07175 from the Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubin, G.M., Waschek, J.A., Pond, S.M. et al. Concurrent intravenous administration of a labeled tracer to determine the oral bioavailability of a drug exhibiting Michaelis-Menten metabolism. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 15, 615–631 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01068416
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01068416