Abstract
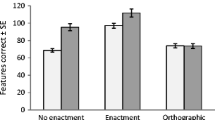
This report describes an experiment that emphasizes: (a) the influence of organizing factors in remembering and comprehending and (b) the development of those skills that are related to the ability to organize. The analysis of the data was based on a theory of comprehension that emphasized a pair of interrelated processes, one providing for the construction of a schema or plan and the other for the semantic integration of items into the evolving plan. As predicted, adults perform more accurately with the paragraphs vs. the scrambled paragraphs and with the word lists as compared to the scrambled word lists. Accuracy with unrelated words is generally greater than with related words, a finding that is consistent with a reconstructive theory of remembering. The pattern of results for the 5th grade Ss is quite different: they perform more accurately with the scrambled paragraphs than with the paragraphs and somewhat more accurately with scrambled word lists rather than with word lists. These results were interpreted as evidence for a problem of control for the 5th grade Ss. We have assumed that the ability to process certain forms of information depends upon the ability to select and maintain an appropriate focus of attention. The results for these younger Ss suggest that their ability to file information into a schema as a filing system is compromised by the need to change or modify the filing system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barclay, J. R. The role of comprehension in remembering sentences.Cognitive Psychology, 1973,4, 229–254.
Bower, G. Organizational factors in memory.Cognitive Psychology, 1970,1, 18–46.
Bower, G. H., Clark, M., Lesgold, A., & Winzenz, D. Hierarchical retrieval schemes in recall of categorized word lists.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 1969,8, 323–343.
Bower, G., Lesgold, A., & Tieman, D. Grouping operations in free recall.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 1969,8, 481–493.
Bransford, J. D., Barclay, J. R., & Franks, J. J. Sentence memory: A constructive versus interpretive approach.Cognitive Psychology, 1972,3, 192–209.
Bransford, J. D., & Johnson, M. K. Consideration of some problems of comprehension. In W. Chase (Ed.),Visual information processing. New York: Academic Press, 1973.
Brown, A. L.: Semantic integration in children's reconstruction of narrative sequences.Cognitive Psychology, 1976,8, 247–262.
Dooling, D. J. & Lachman, R. Effects of comprehension on retention of prose.Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1971,88, 216–222.
Ericsson, D. A., Chase, W. G., & Faloon, S. Acquisition of a memory skill.Science, 1980,208, 1181–1182.
Flavell, J. H. Developmental studies of mediated memory. In H. W. Reese & L. P. Lipsitt (Eds.),Advances in child development and behavior, Volume 5,. New York: Academic Press, 1970.
Flavell, J. H., & Wellman, H. M. Metamemory. In R. B. Kail, Jr. & J. W. Hagen (Eds.),Perspectives on the development of memory and cognition. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum, 1977.
Freedle, R. and Hale, G. Acquisition of new comprehension schemata for expository prose by transfer of a narrative schema. In R. Freedle (Ed.),New directions in discourse processing, Vol. II. Norwood, New Jersey: Ablex, 1979.
Hall, J. W. The effect of word categorizability on recall by preschoolers and young school children.Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 1976,8, 369–370.
Hall, J. W., & Madsen, S. K. Modifying children's processing of categorizable information for memory.Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 1978,5, 291–294.
Halliday, M. A. K., & Hasan, R.Cohesion in english. London: Longman, 1976.
Hunt, E., & Love, T. How good can memory be. In A. W. Melton & E. Martin (Eds.),Coding processes in human memory. Washington, D.C.: Winston, 1972.
Jacobs, R., & Rosenbaum, P.English transformational grammar. Waltham, Massachusetts: Blaisdell, 1968.
Johnson, M. K., Bransford, J. D., & Solomon, S. Memory for tacit implications of sentences.Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1973,98, 203–205.
Kail, R.The development of memory in children. San Francisco: Freeman, 1979.
Kintsch, W., & Van Dijk, T. Recalling and summarizing stories.Language, 1975,40, 98–116.
Krulee, G. K., Fairweather, P. G., & Bergquist, S. R. Organizing factors in the comprehension and recall of connected discourse.Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 1979,8, 141–163.
Kucera, H., & Francis, W. N.Computational analysis of present-day American English. Providence, Rhode Island: Brown University Press, 1967.
McNamee, G. D.The social origins of narrative skills. Ph.D. Thesis., Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois, 1980.
Meyer, B. J. F.The organization of prose and its effects on memory. New York: American Elsevier, 1975.
Miller, G. A., Galanter, E., & Pribram, K. H.Plans and the structure of Behavior. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston, 1960.
Moely, B. E. Organizational factors in the development of memory. In R. V. Kail, Jr. & J. W. Hagen (Eds.),Perspectives on the development of memory and cognition. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum, 1977.
Moely, B. E., Olson, F. A., Halwes, T. G. & Flavell, J. H. Production deficiencies in young children's clustered recall.Developmental Psychology, 1969,1, 26–34.
Paivio, A., Yuille, J. C., & Madigan, S. Concreteness, imagery, and meaningfulness values for 925 nouns.Journal of Experiment of Psychology, 1968,76, (1, Pt. 2).
Paris, S., & Lindauer, B. K. Constructive aspects of children's comprehension and memory. In R. V. Kail & J. W. Hagen (Eds.),Perspectives on the development of memory and cognition, Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum, 1975.
Paris, S., & Lindauer, B. K. The role of inference in children's comprehension and memory for sentences.Cognitive Psychology, 1976,8, 217–227.
Postman, L. A pragmatic view of organization theory. In E. Tulving & W. Donaldson (Eds.),Organization of memory. New York: Academic Press, 1972.
Rumelhart, D. E. The structure of stories. In D. C. Bobrow & A. M. Collins (Eds.),Representation and understanding: Studies in cognitive science. New York: Academic Press, 1975.
Rumelhart, D. E. Understanding and summarizing brief stories. In D. LaBerge & S. J. Samuels (Eds.),Basic studies in reading: Perception and comprehension Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum, 1977.
Rumelhart, D. E. Schemata: The building blocks of cognition. in R. J. Spiro, B. C. Bruce, & W. F. Brewer (Eds.),Theoretical Issues in Reading Comprehension. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum, 1980.
Scribner, S., & Cole, M. Effects of constrained recall training in children's performance in a verbal memory task.Child Development, 1972,43, 845–857.
Stein, N. L., & Glenn, C. G. An analysis of story comprehension in elementary school children. In R. Freedle (Ed.),New directions in discourse processing, Vol. II. Norwood, New Jersey: Ablex, 1979.
Stein, N. L., & Trabssso, T. What's in a story: Critical issues in comprehension and instruction. In R. Glaser (Ed.),Advances in the psychology of instruction, Vol. 2. Hillsdale, New Jersey, Erlbaum, 1981.
Thorndyke, P. W.Cognitive structures in human story comprehension and memory. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, 1975.
Underwood, B. J. Attributes of memory.Psychological Review, 1969,76, 559–573.
Underwood, B. J., Reichardt, C. S., & Malmi, R. A. Sources of facilitation in learning conceptually structured paired-associate lists.Journal of Experimental Psychology, Human Learning and Memory, 1975,104, 160–166.
Yates, F. A.The art of memory. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bailyn, R.V., Krulee, G.K. Organizing factors in remembering and comprehending: A developmental analysis. J Psycholinguist Res 12, 171–198 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067410
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067410