Abstract
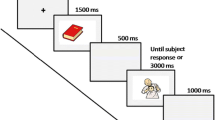
The notion that bilinguals possess a language-switching mechanism was examined. Subjects made comparative judgments about concrete concept pairs (e.g., cow-panther) and abstract concept pairs (e.g., joy-sorrow), which were presented either unilingually or in mixed language. There was no significant difference in latencies for unilingual and mixed language concept pairs, whether the pairs were concrete or abstract. The results substantiate neither the general switch hypothesis nor the notion that between-language and within-language associative networks have different transition probabilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blank, A. (1980). Measuring lexical access during sentence processing.Perception and Psychophysics, 28, 1–8.
Caramazza, A., & Brones, I. (1980). Semantic classification by bilinguals.Canadian Journal of Psychology, 34, 77–81.
Chan, M., Chau, H., & Hoosain, R. (1983). Input/output switch in bilingual code switching.Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 12, 407–415.
Dalrymple-Alford, E.C. (1968). Interlingual interference in a color-naming task.Psychonomic Science, 10, 215–216.
Dalrymple-Alford, E.C. (1985). Language switching during bilingual reading.British Journal of Psychology, 76, 111–122.
Dalrymple-Alford, E.C., & Aamiry, A. (1967). Speed of responding to mixed language signals.Psychonomic Science, 9, 535–536.
Desrochers, A., & Petrusic, W. (1983). Comprehension effects in comparative judgments. In J. Yuille (Ed.),Imagery, memory and cognition. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Fishman, J., & Cooper, R. (1969). Alternative measures of bilingualism.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 8, 276–282.
Harbluk, J., & Paivio, A. (1985, June).Bilingual memory organization. Poster presented at the meeting of the Canadian Psychological Association, Halifax, Canada.
Kirk, R. (1968).Experimental design: Procedures for the behavioral sciences. Belmont, California: Wadsworth.
Kolers, P. (1966). Reading and talking bilingually.American Journal of Psychology, 79, 357–376.
Kucera, H., & Francis, W. (1967).Computational analysis of present day American English. Providence, Rhode Island: Brown University Press.
Lambert, W., Havelka, J., & Crosby, C. (1958). The influence of language acquisition contexts on bilingualism.Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 56, 239–244.
Macnamara, J., & Kushnir, S. (1971). Linguistic independence of bilinguals: The input switch.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 10, 480–487.
Meyer, D., & Ruddy, M. (1974, April).Bilingual word recognition: Organization and retrieval of alternate lexical codes. Paper presented at the meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Philadelphia.
Paivio, A. (1971).Imagery and the verbal processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Paivio, A., & Desrochers, A. (1980). A dual-coding approach to bilingual memory.Canadian Journal of Psychology, 34, 388–399.
Paradis, M. (1977). Bilingualism and aphasia. In H. Whitaker & H. Whitaker (Eds.),Studies in neurolinguistics (Vol. 3). New York: Academic Press.
Paradis, M. (1980). The language switch in bilinguals: Psycholinguistic and neurological perspectives. In P. Nelde (Ed.),Languages in contact and conflict. Wiesbaden: Franz Steiner Verlag.
Seidenberg, M., Waters, G., Sanders, M., & Langer, P. (1984). Pre- and postlexical loci of contextual effects on word recognition.Memory and Cognition, 12, 315–328.
Soares, C., & Grosjean, F. (1984). Bilinguals in a monolingual and a bilingual speech mode: The effect on lexical access.Memory and Cognition, 12, 380–386.
Vander Beke, G. (1929).French word book. New York: Macmillan.
Vinay, J. (1962).Dictionnaire Canadien. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart.
Wakefield, J., Jr., Bradely, P., Yom, B., & Doughtie, E. (1975). Language switching and constituent structure.Language and Speech, 18, 14–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was based in part on the author's master's thesis, submitted to the University of Guelph.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popiel, S.J. Bilingual comparative judgments: Evidence against the switch hypothesis. J Psycholinguist Res 16, 563–576 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067085
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067085