Summary
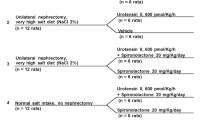
The effects of three experimental conditions on the concentration of plasma renin substrate were studied with special reference to plasma renin concentration in unilaterally nephrectomized rats.
After simultaneous bilateral nephrectomy the maximum increase in plasma renin substrate was 17 times higher than normal within 24 h, while in rats which were unilaterally nephrectomized 10 days previously, followed by the removal of the remaining kidney (two-step bilateral nephrectomy), the maximum increase in plasma renin substrate was markedly suppressed (6-fold of normal). The maximum increases in plasma renin substrate by estradiol treatment in normal and unilaterally nephrectomized rats were about the same, associated with similarly decreased plasma renin concentrations. The similar increase in plasma renin substrate was found after ureteral ligation in unilaterally nephrectomized rats and bilateral ligation of the ureters in normal rats. This was the case where the plasma renin concentrations changed differently after ureteral ligation. After two-step bilateral nephrectomy plus estradiol treatment the maximum increase in plasma renin substrate was found to be higher than that found after two-step bilateral nephrectomy, but was lower than that after simultaneous bilateral nephrectomy.
It is suggested that under the pathological conditions that stimulate renin substrate production, the plasma rein substrate concentration is less affected by circulating renin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bing, J., Jørgensen, J.: Relation between ceased urine excretion and postnephrectomy increase in renin substrate. Acta path. microbiol. scand.80, 21–30 (1972a)
Bing, J., Jørgensen, J.: Reduced post-binephrectomy increase in renin substrate in previously uniephrectomized rats. Acta path. microbiol. scand.80, 31–37 (1972b)
Bing, J., Poulsen, K.: Experimentally induced changes in plasma angiotensinogen and plasma renin. Acta path. microbiol. scand.77, 389–398 (1969)
Bing, J., Poulsen, K.: Cause of increased plasma angiotensinogen after nephrectomy. Acta path. microbiol. scand.78, 669–673 (1970)
Blaine, E. H., Davis, J. O., Baumber, J. S.: Plasma renin substrate changes in experimental uremia. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)136, 21–24 (1971)
Boucher, R., Ménard, J., Genest, J.: A micromethod for measurement of renin in the plasma and kidney of rats. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.45, 881–890 (1967)
Carretero, O., Gross, F.: Renin substrate in plasma under various experimental conditions in the rat. Amer. J. Physiol.213, 695–700 (1967a)
Carretero, O., Gross, F.: Evidence for humoral factors participating in the renin-substrate reaction. Circulat. Res.20–21 (Supp. II), 115–126 (1967b)
Dévényi, I., Dauda, G., Nemes, Z.: The role of the liver in angiotensinogen production. Acta physiol. Acad. Sci. hung.34, 43–46 (1968)
Freeman, R. H., Rostorfer, H. H.: Hepatic changes in renin substrate biosynthesis and alkaline phosphatase activity in the rat. Amer. J. Physiol.223, 364–370 (1972)
Gornall, A. J., Bardawill, C. S., Davis, M. M.: Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J. biol. Chem.177, 751–766 (1949)
Hasegawa, H., Nasjletti, A., Rice, K., Masson, G. C. M.: Role of pituitary and adrenals in the regulation of plasma angiotensinogen. Amer. J. Physiol.225, 1–6 (1973)
Hass, E., Lamfrom, H., Goldblatt, H.: A simple method for extraction and partial purification of renin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.48, 256–260 (1954)
Hirasawa, K., Yamamoto, H., Matsui, A., Shinozaki, K., Kobayashi, S., Yagi, Y., Morimoto, S., Takeda, R., Murakami, M.: The effect of mercuric chloride of bilateral ureteral ligation and of bilateral nephrectomy on plasma renin substrate concentration in rats. Jap. Circulat. J.32, 1591–1595 (1968)
Khayyall, M., MacGregor, J., Brown, J. J., Lever, A. F., Robertson, J. I. S.: Increase of plasma renin-substrate concentration after infusion of angiotensin in the rat. Clin. Sci.44, 87–90 (1973)
Kokubu, T., Hiwada, K., Nagasaka, Y., Yamamura, Y.: Effect of several proteinase inhibitors on renin reaction. Jap. Circulat. J.38, 955–958 (1974)
Kokubu, T., Hiwada, K., Yamamura, Y.: Effects of unilateral nephrectomy on plasma renin substrate and renin concentration in rats. Pflügers Arch.358, 303–310 (1975)
Kokubu, T., Hiwada, K., Yamamura, Y., Hayashi, K., Okumura, J., Hori, M., Kobayashi, S., Ueno, H.: Isolation and identification of a renin inhibitor from ox bile. Biochem. Pharmacol.21, 209–217 (1972)
Lazar, J., Hoobler, S. W.: Studies on the role of the adrenal in renin kinetics. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)138, 614–618 (1971)
Ménard, J., Breminer, J., Corvol, P.: Physicochemical properties of plasma renin substrate in normal, binephrectomized, and estrogen-treated rats. Amer. J. Physiol.226, 1434–1437 (1974)
Ménard, J., Catt, K. J.: Effects of estrogen treatment on plasma renin parameters in the rat. Endocrinology92, 1382–1388 (1973)
Ménard, J., Malmejac, A., Milliez, P.: Influence of diethylstilbesttrol on the renin-angiotensin system of male rats. Endocrinology86, 774–780 (1970)
Montague, D.: Kinetics of renin-angiotensinogen reaction in plasma of normal and nephrectomized rats. Amer. J. Physiol.215, 78–83 (1968)
Nasjletti, A., Masson, G. M. C.: Effects of corticosteroids on plasma angiotensinogen and renin activity. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 1396–1400 (1969)
Nasjletti, A., Masson, G. M. C.: Studies on angiotensinogen formation in a liver perfusion system. Circulat. Res.30–31 (Suppl. II), 187–198 (1972)
Nasjletti, A., Masson, G. M. C.: Stimulation of angiotensinogen formation by renin and angiotensin. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)142, 307–310 (1973)
Nasjletti, A., Matsunaga, M., Masson, G. M. C.: Effects of estrogens on plasma angiotensinogen and renin activity in nephrectomized rats. Endocrinology85, 967–970 (1969)
Page, I. H., McCubbin, J. W.: Renal hypertension, pp.20–27. Chicago: Year Book Med. Publ. Inc. 1968
Romero, J. C., Hoobler, S. W.: Changes in renin kinetics induced by nephrectomy. Amer. J. Physiol.223, 1076–1080 (1972)
Sen, S., Hirasawa, K., Smeby, R. R., Bumpus, F. M.: Measurement of plasma renin substrate using homologous and heterologus renin. Amer. J. Physiol.221, 1476–1480 (1971)
Sen, S., Smeby, R. R., Bumpus, F. M.: Isolation of a phospholipid renin inhibitor from kidney. Biochemistry6, 1572–1581 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by a grant No. 048212 from the Japanese Ministry of Education
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiwada, K., Tanaka, H. & Kokubu, T. The influence of nephrectomy, ureteral ligation, and of estradiol on plasma renin substrate in unilaterally nephrectomized rats. Pflugers Arch. 365, 177–182 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067016
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067016