Abstract
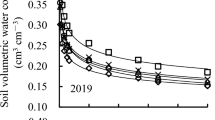
Maize was grown at four rates of N (28, 112, 252 and 448 mg pot−1) and basal P and K dressings at three soil water tensions on three soils of contrasting texture for 40 days in a greenhouse during July/August 1978. Water tensions were maintained as nearly as possible at 0.001, 0.01 and 0.08 MPa.
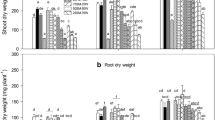
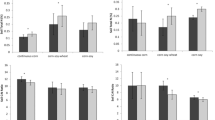
Dry matter yield increased with increase in N rate and decrease in soil water tension. N concentration in the tissue increased with both N rate and increase in soil water tension. Soil water tension had no effect on N uptake, but N uptake increased with increase in N rate. The effect of the interaction of soil water tension and N application rate on dry matter yield was significant. While there was no significant response to moisture tension with the lowest N rate, there was progressively and significantly more response to moisture tension at the higher N application rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batey TE, Cresser MS and Willet LR (1974) Sulphuric-perchloric acid digestion of plant material for nitrogen determination. Anal Chim Acta 69: 484–487
Eck HV and Fanning C (1961) Placement of fertilizers in relation to soil moisture supply. Agron J 53: 335–338
Glentworth R (1963) The soils of the country round Aberdeen, Inveruvie and Fraservurgh. Mem Soil Surv Great Britain, Scotland, pp. 85–190. HMSO
Hanway JJ and Dumenil L (1965) Corn leaf analysis — key to correct interpretation. Plant Food Review 11: 5–8
Jones JB and Eck HV (1973) Plant analysis as an aid in fertilizing corn and grain sorghum. In: Walsh LM and Beaton JD (eds). Soil testing and plant analysis, Madison, Wisc: Soil Science Soc of America, pp. 349–364
Mederski HJ and Wilson JH (1960) Relation of soil moisture to ion absorption by corn plants. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 24: 149–152
Melsted, SW, Motto HL and Pack TR (1969) Critical plant nutrient composition values useful in interpreting plant analysis data. Agron J 61: 17–20
Nnoham OI (1979) Effect of nitrogen levels and soil moisture tensions on growth and nutrient composition of maize (Zea mays L.). MSc Thesis, University of Aberdeen
Peterson HS and Ballard JC (1953) Effect of fertilizer and moisture on the growth and yield of sweet corn. Utah Agric Exp Sta Bull 360
Reitemeier RF (1946) Effect of moisture content on the dissolved and exchangeable ions of soils of arid regions. Soil Sci 61: 195–214
Richards LA (1965) Physical condition of water in soil. In: Black CA (ed.). Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Agronomy 9, Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy, pp. 128–152
Richards LA and Blood HH (1934) Some improvement in auto irrigator apparatus. J Agric Res 49: 115–121
Richards LA and Wadleigh CH (1952) Soil water and plant growth. In: Shaw Byron T (ed.). Soil physical conditions and plant growth. Agron 2, Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy, pp. 253–301
Shimshi D (1969) Interaction between irrigation and plant nutrition. Proc 7th Colloq Inter Potash Inst, Berne, pp. 111–120
Tinsley J (1970) Manual of experiments for students of Soil Science, University of Aberdeen
Veihmeyer FJ and Hendrickson AH (1950) Soil moisture in relation to plant growth. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 1: 285
Viets FG Jr. (1972) Water deficits and nutrient availability. In: Kozlowski TT (ed.). Water deficits and plant growth Vol 3. Academic Press, New York
Webster R (1965) The measurement of soil water tension in the field. The New Phytol 65: 2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nnoham, O.I., Odurukwe, S.O. Effects of N fertilizer rate, soil water tension and soil texture on growth and N uptake by maize (Zea mays L.). Fertilizer Research 13, 241–254 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01066447
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01066447