Abstract
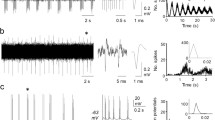
Responses of motoneurons and interneurons of the cervical enlargement of the cat spinal cord were studied by a microelectrode technique during selective stimulation of propriospinal fibers of the dorsolateral tract of the lateral white column. The long descending and ascending pathways were blocked by preliminary (10–16 days earlier) hemisection of the spinal cord cranially and caudally to the segments studied. Stimulation of the dorsolateral tract at a distance of 15–25 mm from the site of recording evoked complex postsynaptic potentials consisting of several successive waves in the motoneurons. The character of the PSPs was not clearly linked with the function of the motoneurons. By their latent periods the components of the PSPs could be placed in three groups. The "primary" components were reproduced in response to stimulation at 50–100/sec whereas the "secondary" and "tertiary" components were weakened or blocked. It is postulated that the "primary" components are evoked through monosynaptic connections between propriospinal fibers of the dorsolateral tract and motoneurons of the forelimb muscles, while the late components are evoked through polysynaptic pathways, including segmental interneurons. Many of these interneurons, located in the ventral horn and intermediate zone, were strongly excited during stimulation of the dorsolateral tract.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
K. V. Baev, "Convergence of corticospinal and rubrospinal influences on motoneurons of the cervical division of the spinal cord," Neirofiziologiya,3, 599 (1971).
K. V. Baev, D. A. Vasilenko, and L. I. Manzhelo, "Functional properties of propriospinal pathways of the dorsolateral tract of the cat spinal cord," Neirofiziologiya,5, 54 (1973).
D. A. Vasilenko, "Propriospinal pathways of the lateral funiculus and their possible role in the transmission of pyramidal influences," in: Mechanisms of Descending Control of Spinal Cord Activity [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1971), pp. 39–44.
D. A. Vasilenko, A. G. Zadorozhnyi, and P. G. Kostyuk, "Synaptic processes in spinal neurons activated monosynaptically by the pyramidal tract," Byull. Éksperim. Biol. i Med., No. 11, 20 (1967).
D. A. Vasilenko, A. I. Kostyukov, and A. I. Pilyavskii, "Corticofugal and rubrofugal activation of interneurons forming the propriospinal pathways of the dorsolateral tract of the cat spinal cord," Neirofiziologiya,4, 489 (1972).
P. G. Kostyuk, D. A. Vasilenko, and A. G. Zadorozhnyi, "Responses of motoneurons of the lumbar division of the spinal cord evoked by activity of propriospinal pathways," Neirofiziologiya,1, 5 (1969).
P. G. Kostyuk, V. A. Maiskii, and L. A. Savos'kina, "Synaptic connections of propriospinal neurons in the lumbar division of the spinal cord," Neirofiziologiya,3, 401 (1971).
R. Corazza, E. Fadiga, and P. L. Parmeggiani, "Patterns of pyramidal activation of cats' motoneurons," Arch. Ital. Biol.,101, 337 (1963).
P. G. Kostyuk and V. A. Maisky, "Propriospinal projections in the lumbar spinal cord of the cat," Brain Res.,39, 530 (1972).
P. G. Kostyuk, D. A. Vasilenko, and E. Lang, "Propriospinal pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus and their effects on lumbo-sacral motoneuronal pools," Brain Res.,28, 233 (1971).
A. Rustioni, H. G. J. M. Kuypers, and G. Holstege, "Propriospinal projections from the ventral and lateral funiculi to the motoneurons in the lumbo-sacral cord of the cat," Brain Res.,34, 255 (1971).
M. E. Scheibel and A. B. Scheibel, "Terminal axonal patterns in cat spinal cord. I. The lateral corticospinal tract," Brain Res.,2, 333 (1966).
R. F. Schmidt and W. D. Willis, "Intracellular recording from motoneurons of the cervical spinal cord of the cat," J. Neurophysiol.,26, 28 (1963).
P. Sterling and H. G. J. M. Kuypers, "Anatomical organization of the brachial spinal cord of the cat. III. The propriospinal connections," Brain Res.,7, 419 (1968).
J. Szentagothai, "Propriospinal pathways and their synapses," in: Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 11, Elsevier, Amsterdam (1964), pp. 155–177.
R. C. Thomas and V. J. Wilson, "Recurrent interaction between motoneurons of known location in the cervical cord of the cat," J. Neurophysiol.,30, 661 (1967).
Additional information
A. A. Bogomolets' Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR, Kiev. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 61–69, January–February, 1973.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baev, K.V., Vasilenko, D.A. & Kostyuk, P.G. Synaptic processes in neurons of the cervical enlargement of the cat spinal cord during stimulation of propriospinal pathways of the dorsolateral tract. Neurophysiology 5, 50–56 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065212
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065212