Abstract
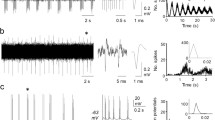
Experiments on anesthetized and immobilized cats showed that repeated antidromic discharges can be evoked in 32.5% of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lateral horns in segments T3, T8–9, and L2 of the spinal cord, with intervals of 16 msec or more between them, which is much greater than the refractory period of these neurons. This feature was shown not to be connected with the properties of axons of that group of neurons and, in particular, with their after-subnormality. After orthodromic discharges in neurons of this group, for a much longer period of time than could be accounted for by possible collision, no antidromic discharges likewise were evoked. As a result of antidromic activation of some of these neurons in one segment, definite inhibition of the orthodromic response of other neurons of the same segment appeared, etiher by a reflex mechanism or through stimulation of descending pathways. The results point definitely to the existence of a mechanism of recurrent inhibition in some sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lateral horns.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. P. Lebedev, "Properties of axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lower thoracic region of the spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,57, 1647 (1971).
V. P. Lebedev, V. I. Petrov, and A. D. Basova, "Distinguishing features of individual sympathetic preganglionic neurons and their axons in the upper thoracic region of the spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,62, 1433 (1976).
V. P. Lebedev and V. A. Skobelev, "Postsynaptic components of the early somatosympathetic reflex response in lumbar white rami communicantes," Neirofiziologiya,7, 194 (1975).
V. P. Lebedev, V. A. Skobelev, and T. A. Bushmarina, "Properties of axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the cat lumbar spinal cord," Neirofiziologiya,6, 143 (1974).
V. P. Lebedev, K. A. Smirnov, and N. N. Rozanov, "Early somatosympathetic reflex responses in the upper thoracic white rami communicantes during stimulation of segmental nerves," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,62, 1139 (1976).
K. A. Smirnov, V. P. Lebedev, and N. N. Rozanov, "Responses in the upper thoracic white rami communicantes to stimulation of the dorsolateral funiculi of the spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,62, 1130 (1976).
J. C. Eccles, The Inhibitory Pathways of the Central Nervous System, Liverpool University Press, Liverpool (1969), 160 pp.
J. C. Eccles, P. Fatt, and K. Koketsu, "Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motoraxon collaterals to motoneurones," J. Physiol. (London),126, 524 (1954).
W. C. De Groat and R. W. Ryall, "Recurrent inhibition in sacral parasympathetic pathways to the bladder," J. Physiol. (London),196, 579 (1968).
A. Fernandez de Molina, M. Kuno, and E. R. Perl, "Antidromically evoked responses of sympathetic preganglionic neurons," J. Physiol. (London),180, 321 (1965).
J. O. Foley and F. S. Du Bois, "A quantitative and experimental study of the cervical sympathetic trunk," J. Comp. Neurol.,82, 77 (1930).
F. Kirchner, D. Kirchner, and C. Polosa, "Spinal organization of sympathetic inhibition by spinal afferent volleys," Brain Res.,87, 161 (1975).
C. Polosa, "Silent period of sympathetic preganglionic neurons," Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.,45, 1033 (1967).
B. Renshaw, "Influence of discharge of motoneurones upon excitation of neighboring motoneurones," J. Neurophysiol.,4, 167 (1941).
M. Rethelyi, "Cell and neuropil architecture of the intermediolateral (sympathetic) nucleus of the spinal cord," Brain Res.,46, 203 (1972).
Additional information
I. P. Pavlov Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Leningrad. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 382–389, July–August, 1977.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedev, V.P., Petrov, V.I. & Skobelev, V.A. Recurrent inhibition of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lateral horns of the spinal cord. Neurophysiology 9, 294–300 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063694
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063694