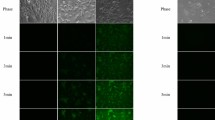
Summary
The present study describes for the first time the use of the fluorescent dye sulfonefluorescein for intravital microscopy and microphotometry on the renal surface of rats. With help of this dye tubular secretion can be observed in mammalian kidney in vivo. Tubular secretion can further be quantified with microphotometrical measurements. The molecular structure of sulfonefluorescein is closely related to phenol red, which is known for its tubular secretion. Clearance experiments also show a secretion of sulfonefluorescein. The secretion can be inhibited by probenecid. Ureter ligation causes a strong increase in tubular concentration of the dye. After a temporary ischemia dye accumulation in tubular lumen is greatly reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deetjen, P.: Nierenphysiologie. In: Physiologie des Menschen, Bd. 7, hrsg. von O. H. Gauer, K. Kramer, R. Jung, 2. Aufl. München-Berlin-Wien: Urban & Schwarzenberg 1973
Eisenbach, G. M., Kitzlinger, B., Steinhausen, M.: Renal blood flow after temporary ischemia of rat kidneys. Pflügers Arch.347, 223–234 (1974)
Eisenbach, G. M., Steinhausen, M.: Micropuncture studies after temporary ischemia of rat kidneys. Pflügers Arch.343, 11–25 (1973)
Fuehr, J., Kaczmaeczyk, J., Krüttgen, C. D.: Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgeseunden und Diabetikern. Klin. Wschr.33, 729–730 (1955)
Giebisch, G., Klose, R. M., Windhager, E. E.: Micropuncture study of hypertonic sodium chloride loading in the rat. Amer. J. Physiol.206, 687–693 (1964)
Kinter, W. B.: Chlorphenol red influx and efflux: Microspectrophotometry of flounder kidney tubules. Amer. J. Physiol.211, 1152–1164 (1966)
Malvin, R. L., Wilde, W. S., Sullivan, L. P.: Localization of nephron transport by stop flow analysis. Amer. J. Physiol.194, 135–142 (1958)
Popa, G., Parekh, N., Steinhausen, M.: Renal test dyes II. Renal handling of dyes suitable for renal passage time measurements. Pflügers Arch.350, 273–280 (1974)
Remsen, J., Linn, A. F.: Investigations on the sulphon-phthaleins. I. Sulphon-fluorescein and related compounds. Amer. Chem. J.11, 73–80 (1889)
Steinhausen, M.: Corticales Gefäß- und Tubulussystem der Rattenniere. Wiss. Film beim Institut f. d. Wiss. Film, Göttingen (1975)
Steinhausen, M., Eisenbach, G. M., Galaske, R.: A counter current system of the surface of the renal cortex of rats. Pflügers Arch.318, 244–258 (1970)
Ullrich, K. J., Rumrich, G., Baumann, K.: Renal proximal tubular buffer-(Glycodiazine) transport. Inhomogeneity of local transport rate, dependence on sodium, effect of inhibitors and chronic adaptation. Pflügers Arch.357, 149–163 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 90)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinhausen, M., Müller, P. & Parekh, N. Renal test dyes IV. Pflugers Arch. 364, 83–89 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062916
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062916