Abstract
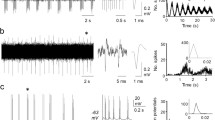
Antidromic discharges and spontaneous activity of single sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the lateral horns of the second lumbar segment of the spinal cord were recorded extracellularly in cats anesthetized with a mixture of chloralose and pentobarbital. A new technique used to identify antidromic discharges of sympathetic preganglionic neurons is described and the characteristics of discharges and sites where they were recorded are investigated. Changes in the frequency of spontaneous discharges of most neurons were shown to be connected with different types of fluctuation of the arterial pressure. Absence of functional specialization of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons is postulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
P. G. Kostyuk, Microelectrode Techniques [in Russian], Izd. Akad.Nauk Ukr.SSR, Kiev (1960).
V. P. Lebedev, "Orientation of the microelectrode axis during investigation of single units of certain lamellar and nuclear structures of the spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,57, 908 (1971).
V. P. Lebedev, "Properties of axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lower thoracic part of the spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,57, 1647 (1971).
V. P. Lebedev, "Some features distinguishing the responses of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lateral horns of the spinal cord to antidromic and orthodromic stimulation," in: Interneuronal Transmission in the Autonomic Nervous System [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1972), pp. 76–89.
V. P. Lebedev and G. P. Mikhailova, "Stereotaxic investigation of the lateral horn of the cat spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,57, 677 (1971).
V. P. Lebedev and B. Ya. Pyatigorskii, "Focal potentials of neurons of Clarke's columns," Neirofiziologiya,2, 528 (1970).
V. P. Lebedev, V. A. Skobelev, and T. A. Bushmarina, "Properties of axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lumbar spinal cord," Neirofiziologiya,6, 143 (1974).
V. P. Lebedev and K. A. Smirnov, "An apparatus for sampling the expired air during artificial respiration," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,58, 469 (1972).
L. Ya. Pines, A Short Course of Lectures on the Autonomic Centers [in Russian], Medgiz, Leningrad (1940).
V. I. Skok, The Physiology of the Autonomic Ganglia [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1970).
J. S. Coombs, D. R. Curtis, and J. C. Eccles, "The interpretation of spike potentials of motoneurons," J. Physiol. (London),139, 198 (1957).
I. M. Coote and C. B. B. Downman, "Central pathways of some autonomic reflex discharges," J. Physiol. (London),183, 714 (1966).
J. F. Cummings, "Thoracolumbar preganglionic neurons and adrenal innervation in the dog," Acta Anat.,73, 27 (1969).
J. C. Eccles, R. M. Eccles, A. Iggo, and A. Lundberg, "Electrophysiological studies on gammamotoneurons," Acta Physiol. Scand.,50, 32 (1960).
E. V. Evarts, "Relation of discharge frequency to conduction velocity in pyramidal tract neurons," J. Neurophysiol.,28, 216 (1965).
A. Fernandez de Molina, M. Kuno, and E. R. Perl, "Antidromically evoked responses from sympathetic preganglionic neurons," J. Physiol. (London),180, 321 (1965).
W. C. de Groat and R. W. Ryall, "The identification and characteristics of sacral parasympathetic preganglionic neurons," J. Physiol. (London),196, 563 (1968).
E. Henneman, G. Somjen, and D. Carpenter, "Functional significance of cell size in spinal motoneurons," J. Neurophysiol.,28, 560 (1965).
J. L. Henry and F. R. Calaresu, "Topography and numerical distributión of neurons of the thoracolumbar intermediolateral nucleus in the cat," J. Com. Neurol.,144, 205 (1972).
T. Hongo and R. W. Ryall, "Electrophysiological and microelectrophoretic studies on sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the spinal cord," Acta Physiol. Scand.,68, 96 (1966).
G. Horeyseck, W. Jänig, F. Kirchner, and V. Thämer, "Activation of muscle vasodilator neurons by hypothalamic stimulation," Brain Res.,48, 394 (1972).
C. C. Hunt and M. Kuno, "Properties of spinal interneurons," J. Physiol. (London),147, 346 (1959).
W. Jänig and R. F. Schmidt, "Single unit responses in the cervical sympathetic trunk upon somatic nerve stimulation," Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol.,317, 199 (1970).
H. P. Koepchen, P. Langhorst, H. Seller, J. Polster, and P. H. Wagner, "Neuronals Aktivität im unteren Hirnstamm mit Beziehung zum Kreislauf," Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol.,294, 40 (1967).
A. Mannard and C. Polosa, "Analysis of background firing of single sympathetic preganglionic neurons of cat cervical nerve," J. Neurophysiol.,36, 398 (1973).
B. Onuff and J. Collins, "Experimental researches on the localization of the sympathetic nerve in the spinal cord and brain and contribution to its physiology," J. Nerv. Ment. Dis.,25, 661 (1968).
C. Polosa, "The silent period of sympathetic preganglionic neurons," Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.,45, 1033 (1967).
K. Polosa, I. Vyshogradskii, and A. Mannard, "The nature of organized discharges of a sympathetic neuron lying at the basis of vasomotor waves," in: Interneuronal Transmission in the Autonomic Nervous System [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1972), pp. 58–67.
R. Porter, "Unit responses evoked in the medulla oblongata by vagus nerve stimulation," J. Physiol. (London),168, 717 (1963).
M. Rethelyi, "Cell and neuropil architecture of the intermediolateral (sympathetic) nucleus of cat spinal cord," Brain Res.,46, 203 (1972).
G. C. Salmoiraghi, "Cardiovascular neurons in the brain stem of cat," J. Neurophysiol.,25, 182 (1962).
A. Sato, N. Tsushima, and B. Fujimori, "Reflex potentials of lumbar and thoracic white rami," Jap. J. Physiol.,15, 532 (1965).
R. F. Schmidt and K. Schonfüss, "An analysis of the reflex activity in the cervical sympathetic trunk induced by myelinated somatic afferents," Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol.,314, 195 (1970).
A. M. Sillito, and A. W. Zbrozyna, "The localization of pupillo-constrictor function within the midbrain of the cat," J. Physiol. (London),211, 461 (1970).
R. Takahashi, "Slow and fast groups of pyramidal tract cells and their respective membrane properties," J. Neurophysiol.,28, 908 (1965).
A. Wyszograodski and C. Polosa, "The inhibition of sympathetic preganglionic neurons by somatic afferents," Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.,51, 29 (1973).
Additional information
I. P. Pavlov Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Leningrad. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol.6, No.3, pp.295–303, May–June, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedev, V.P., Skobelev, V.A. & Bushmarina, T.A. A study of single sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the lateral horns of the lumbar spinal cord. Neurophysiology 6, 233–240 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062422
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062422