Abstract
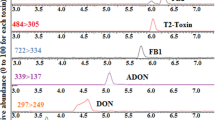
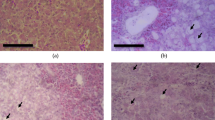
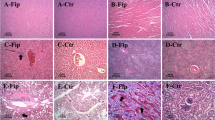
Feed samples of corn, pelleted feed, and oats associated with equine leucoencephalomalacia (ELEM) were obtained from North Carolina, Illinois, Indiana, and Oklahoma. These samples contained a high colony density ofFusarium moniliforme Sheldon which ranged from 64 to 87% of the total fungi. Fifty-nineF. moniliforme strains were isolated. Isolates ofF. moniliforme (27) in feed samples from Illinois, Indiana, and Oklahoma were cultured on corn. The fermented corn, mixed with regular feed and fed to one-day-old ducklings, effected a high mortality coefficient (average 55%). Methanol extracts of corn fermented with each of 14 representativeF. moniliforme isolates from North Carolina feed were toxic to mice and some caused rabbit skin necrosis. Vomitoxin (deoxynivalenol), T-2 toxin, zearalenone, and moniliformin were not detected in feed samples or fermented corn. However, 4 to 10 ng of aflatoxin B1 per gram of feed was present in the four North Carolina samples. Bikaverin (C20H14O8), a characteristic red pigment ofFusarium sp., was found in the North Carolina feed samples. This is the first report of bikaverin in feed samples associated with ELEM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buck WM, Haliburton JC, Thilsted JP, Lock TF, Vesonder RF (1979) Equine Leucoencephalomalacia: Comparative, Pathology of Naturally Occurring and Experimental Cases. Amer Assn Veterinary Laboratory Diagnostics. 22nd Annual Proceedings, pp 239–258
Eppley RM (1968) Screening method for zearalenone, aflatoxin and ochratoxin. J Assoc Offic Anal Chem 51:74–78
Gilman JC (1957) A Manual of the Soil Fungi. The Iowa State College Press, Ames, Iowa, 450 pp
Haliburton JC, Vesonder RF, Lock TF, Buck WB (1979) Equine leucoencephalomalacia (ELEM): A study ofFusarium moniliforme as an etiologic agent. Vet Human Toxicol 21:348–351
Joffe AZ (1986) Fusarium Species: Their Biology and Toxicology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 588 pp
Marasas WFO, Kellerman TS, Pienaar JG, Naude TW (1976) A mycotoxicoxis of equine caused byFusarium moniliforme Sheldon. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 43:113–122
Marasas WFO, Kriek NPJ, Fincham JE, vanRensburg SJ (1984) Primary liver cancer and oesophageal basal cell hyperplasia in rats caused byFusarium moniliforme. Int J Cancer 34:383–387
Nelson PE, Toussoun TA, Marasas WFO (1983) Fusarium Species—An Illustrated Manual for Identification. Pennsylvania State University Press, University Park, PA, 193 pp
Schwarte LH (1938) Moldy corn poisoning in horses. J Am Vet Med Assoc 92:152–158
Shannon GM, Shotwell OL, Kwolek WF (1983) Extraction and thin-layer chromatography of aflatoxin B1 in mixed feeds. J Assoc Offic Anal Chem 66:582–586
Vesonder RF, (1986) Moniliformin produced by cultures ofFusarium moniliforme Var.subglutinans isolated from swine feeds. Mycopathologia 95:149–153
Vesonder RF, Golinski P (1988) Metabolites of Fusarium. In: Chetkowski J (ed) Fusarium, Mycotoxins, Taxonomy, Pathogenicity. Elsevier (in press)
Wilson BJ, Maronpot RR, Hildebrandt PK (1973) Equine leucoencephalomalacia. J Amer Vet Med Assoc 163:1293–1295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vesonder, R., Haliburton, J. & Golinski, P. Toxicity of field samples andFusarium moniliforme from feed associated with equine-leueoencephalomalacia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 18, 439–442 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062371
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062371