Abstract
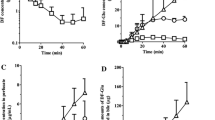
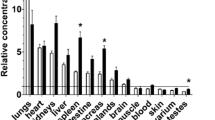
The effect of altered physiological conditions on the residence time distributions of sucrose, water, and taurocholate in the rat liver were studied using a bolus injection and quantifying fraction of total outflow per ml-time profiles. Retrograde perfusions increased the residence times of sucrose and water markedly and were associated with very low hepatic availabilities for taurocholate. Resistance by the inlet sinusoids sphincters, which become outlet sphincters during retrograde perfusions, is suggested as the explanation for the observation. Infusions of noradrenaline, propranolol, and lidocaine resulted in relatively small changes in the mean residence times for sucrose and water with no apparent relationship existing between the efficiency number of taurocholate and volumes of either water or sucrose. Taurochenodeoxycholate resulted in an increase in the availability and mean residence time for taurocholate relative to no infusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs: I. Theoretical considerations of a “well-stirred” model and a “parallel tube” model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding and hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:625–653 (1977).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs: II. Experimental evidence for acceptance of the “well-stirred” model over the “parallel tube” model using lidocaine in the perfused ratin situ preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:655–680 (1977).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs: III. Additional experimental evidence supporting the “well-stirred” model, using metabolite (MEGX) generated from lidocaine under varying hepatic blood flow rates and linear conditions in the perfused liver in situ preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:681–699 (1977).
A. B. Ahmad, P. N. Bennett, and M. Rowland. Models of hepatic drug clearance: Discrimination between the ‘well-stirred’ and ‘parallel tube’ models.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 35:219–224 (1983).
D. B. Jones, D. J. Morgan, G. W. Mihaly, L. K. Webster, and R. A. Smallwood. Discrimination between the venous equilibrium and sinusoidal models of hepatic drug elimination in the isolated perfused rat liver by perturbation of propranolol protein binding.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 229:522–526 (1984).
W. Colburn. Albumin does not mediate the removal of taurocholate by rat liver.J. Pharm. Sci. 71:373–374 (1982).
K. S. Pang and J. R. Gillette. Kinetics of metabolite formation and elimination in the perfused rat liver preparation: Differences between the elimination of preformed acetaminophen and acetaminophen formed from phenacetin.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 207:178–194 (1978).
S. Keiding and E. Chiarantini. Effect of sinusoidal perfusion on galactose elimination in perfused rat liver.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 205:465–470 (1978).
M. Rowland, K. Leitch, G. Fleming, and B. Smith. Protein binding and hepatic clearance: Discrimination between models of hepatic clearance with diazepam, a drug of high intrinsic clearance, in the isolated perfused rat liver preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 12:129–147 (1984).
S. Keiding and E. Steiness. Flow dependence of propranolol elimination in perfused rat liver.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 230:474–477 (1984).
L. Bass, P. J. Robinson, and A. J. Bracken. Hepatic elimination of flowing substances: The distributed model.J. Theoret. Biol. 72:161–184 (1978).
E. L. Forker and B. Luxon. Hepatic transport kinetics and plasma disappearance curves. Distributed modelling versus conventional approach.Am. J. Physiol. 235:E648-E660 (1978).
L. Bass. Saturation kinetics in hepatic drug removal: A statistical approach to functional heterogeneity.Am. J. Physiol. 244:G583-G589 (1983).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. Hepatic elimination-dispersion model.J. Pharm. Sci. 74:585–587 (1985).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. A dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 1. Formulation of the model and bolus considerations.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:227–260 (1986).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. A dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 2. Steady-state considerations. Influence of blood flow, protein binding and hepatocellular enzymatic activity.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:261–288 (1986).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. A dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 3. Application to metabolite formation and elimination kinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:289–308 (1986).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. Correlation between in vitro microsomal enzyme activity and whole organ hepatic elimination kinetics: analysis with a dispersion model.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 38:117–181 (1986).
M. S. Roberts, J. D. Donaldson, and M. Rowland. Models of hepatic elimination: Comparison of stochastic models to describe residence time distributions and to predict the influence of drug distribution, enzyme heterogeneity and systemic recycling or hepatic elimination.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 16:41–84 (1988).
M. S. Roberts, S. Fraser, A. Wagner, and L. J. McLeod. Residence time distributions of solutes in the perfused rat liver using the dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 1. Effect of changes in perfusate flow and albumin concentration on sucrose and taurocholate.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 18: 209–234 (1990).
E. L. Forker and B. A. Luxon. Albumin helps moderate removal of taurocholate by rat liver.J. Clin. Invest. 67:1517–1522 (1981).
L. Bass and S. Keiding. Physiologically based models and strategic experiments in hepatic pharmacology.Biochem. Pharmacol. 37:1425–1431 (1988).
R. A. Weisiger. Dissociation from albumin: A potentially rate-limiting step in the clearance of substances by the liver.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 82: 1563–1567 (1985).
K. S. Pang and J. A. Terrell. Retrograde perfusion to probe the heterogeneous distribution of hepatic drug metabolising enzymes in rats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 216:339–346 (1981).
K. S. Pang, H. Koster, I. C. M. Halsema, E. Scholters, G. J. Milder, and R. N. Stillwell. Normal and retrograde perfusion to probe the zonal distribution of sulfation and glucuronidation activities of harmol in the perfused rat liver preparation.J. Pharmacol Exp. Ther. 224:647–653 (1983).
K. S. Pang, J. A. Terrell, S. D. Nelson, K. F. Feuer, J.-J. Clements, and L. Endrenyi. An enzyme distributed system for lidocaine metabolism in the perfused rat liver preparation.J. Pharm. Biopharm. 14:107–130 (1986).
M. V. St-Pierre, A. J. Schwab, C. A. Goresky, W. Lee, and K. S. Pang. The multiple-indicator dilution technique for characterisation of normal and retrograde flow in once-through rat liver perfusions.Hepatology 9:285–296 (1989).
P. D. I. Richardson and P. G. Withrington. Liver blood flow. 1. Intrinsic and nervous control of liver blood flow.Gastroenterology 81:159–173 (1981).
P. D. I. Richardson and P. G. Withrington. Liver blood flow. 2. Effects of drugs and hormones on liver blood flow.Gastroenterology 81:356–375 (1981).
J. L. Campra and T. B. Reynolds. The hepatic circulation. In I. Arias, D. Popper, D. Schatchter, and D. A. Shafritz (eds.),The Liver Biology and Pathobiology, Raven, NY, chap. 37, pp. 627–645 (1982).
C. V. Greenway and G. Oshiro. Effects of histamine on hepatic volume (outflow block) in anaesthetised dogs.Br. J. Pharmacol. 47:282–290 (1973).
G. M. M. Groothuis, M. J. Hardonk, K. P. T. Keulemans, P. Nieuwenhuis, and D. K. M. Meijer. Autoradiographic and kinetic demonstration of acinar heterogeneity of taurocholate transport.Am. J. Physiol. 243:G455-G462 (1982).
L. R. Schwarz, R. Burr, M. Schwerk, E. Pfaff, and H. Greim. Uptake of taurocholic acid into isolated rat-liver cells.Eur. J. Biochem. 55: 617–623 (1975).
G. J. Gores, L. J. Kost, and N. F. LaRusso. The isolated perfused rat liver: Conceptual and practical considerations.Hepatology 6: 511–517 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Dean's MRC (NZ) Fund.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, M.S., Fraser, S., Wagner, A. et al. Residence time distributions of solutes in the perfused rat liver using a dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 2. Effect of pharmacological agents, retrograde perfusions, and enzyme inhibition on evans blue, sucrose, water, and taurocholate. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 18, 235–258 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062201
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062201